原文:Reading Related Data with the Entity Framework in an ASP.NET MVC Application
1.延迟(Lazy)加载、预先(Eager)加载、显式(Explicit)加载:
EF加载相关数据到实体导航属性有以下几种方式:
- 延迟加载:当实体第一次读取时,相关数据没有加载。当第一次试图访问导航属性时,所需的导航数据自动加载。这导致多条查询语句被发送到数据库:一条查询实体本身,一条查询实体相关数据。DbContext类默认启用延迟加载。

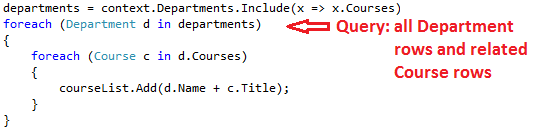
- 预先加载:当读取实体时,相关数据同时读取。这通常会导致一个连接查询,查询所有所需的数据。使用
Include方法指定预先加载。
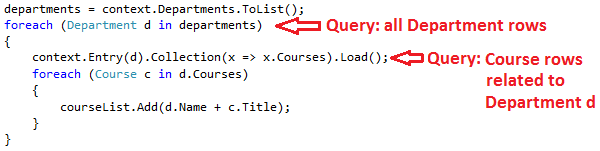
- 显示加载:这种加载方式类似于延迟加载,不同的是我们要在代码中明确地查询相关数据;当我们访问导航属性时,它不会自动查询。我们需要手动获取实体的对象状态管理器入口,并且需要调用Collection.Load方法获取集合或者调用Reference.Load方法获取单个实体来加载相关数据(在下面的例子中如果我们想要获取Administrator导航属性,使用
Reference(x => x.Administrator)代替Collection(x => x.Courses))。通常情况下,我们不需要使用显示加载,除非禁用了延迟加载。
 因为不立即获取属性值,延迟加载和显式加载同时又被称为延后(deferred)加载。
因为不立即获取属性值,延迟加载和显式加载同时又被称为延后(deferred)加载。
1.1.考虑性能:
如果我们知道,我们需要每个实体的相关数据,预先加载大多数情况下会有最好的性能,因为一条查询数据通常比单独查询每个实体更有效率。例如,在上面的例子中,假设每个department有10相关的course。预先加载加载数据只产生一条(连接)查询语句和1次往返。延迟加载和显式加载加载数据均会产生11条查询语句和11次往返。额外的往返尤其不利于性能的提高。
另一方面,在一些情况下,延迟加载会更有效率。预先加载可能会产生一个SQL Server不能有效处理的非常复杂的连接。或者,我们只是需要访问导航属性的子集,延迟加载会比预先加载性能高,因为预先加载返回的数据比我们实际需要的要多。如果性能是至关重要的,最好同时测试这两种方式的性能以作出做好的选择。
延迟加载会遮掩代码这样会造成性能问题。例如,代码没有指定预先加载或者显式加载,但是需要处理大量的实体,并且在每个迭代中使用多个导航属性,这是效率将会非常低(因为多次往返数据库)。
一个程序可能在开发时使用SQL Server性能表现良好,但是当部署在Azure SQL数据库上时,由于增加了延迟和延迟加载,可能会遇到性能问题。使用实际负载测试分析数据库查询会帮助我们确定延迟加载是否适当。更多信息请查看:Demystifying Entity Framework Strategies: Loading Related Data和Using the Entity Framework to Reduce Network Latency to SQL Azure。
1.2.在序列化之前禁用延迟加载:
如果在序列化过程中延迟加载是启用的,我们获取到的数据会比我们想要的要多。序列化通常会访问一个类型每个实例的每个属性。对属性的访问会触发延迟加载,延迟加载的实体被实例化。序列化过程访问延迟加载实体的每个属性,可能会会触发更多的延迟加载和序列化。为了防止这种连锁反应失控,我们要在序列化实体前禁用延迟加载。
EF使用的代理类也会使序列化变得复杂,请查看:Advanced Scenarios tutorial。
一种避免序列化问题的方法是不序列化实体对象而是序列化数据传输对象(DTO),请查看:Using Web API with Entity Framework。
如果不使用DTO,我们可以禁用延迟加载和避免代理,请查看:disabling proxy creation。
禁用延迟加载的其他方法:
- 禁用特定的导航属性的延迟加载,在定义时不使用virtual关键字。
- 对所有的导航属性禁用延迟加载,在上下文类的构造函数中添加如下代码:
this.Configuration.LazyLoadingEnabled = false;
2.创建Course页面,显示Department的Name:
创建CourseController(选择MVC 5 Controller with views, using Entity Framework):

修改ViewsCourseIndex.cshtml:
@model IEnumerable<ContosoUniversity.Models.Course> @{ ViewBag.Title = "Courses"; } <h2>Courses</h2> <p> @Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create") </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.CourseID) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Title) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Credits) </th> <th> Department </th> <th></th> </tr> @foreach (var item in Model) { <tr> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.CourseID) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Credits) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Department.Name) </td> <td> @Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id=item.CourseID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id=item.CourseID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id=item.CourseID }) </td> </tr> } </table>
运行:
3.创建Instructors页面显示Courses和Enrollments:
本节最终页面:

3.1.为Instructor的Index视图创建视图模型:
在ViewModels文件夹新建InstructorIndexData.cs:
public class InstructorIndexData { public IEnumerable<Instructor> Instructors { get; set; } public IEnumerable<Course> Courses { get; set; } public IEnumerable<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } }
3.2.创建Instructor控制器和视图:
使用EF read/write创建InstructorController:

修改Index方法:
public ActionResult Index(int? id, int? courseID) { var viewModel = new InstructorIndexData(); viewModel.Instructors = db.Instructors .Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment) .Include(i => i.Courses.Select(c => c.Department)) .OrderBy(i => i.LastName); if (id != null) { ViewBag.InstructorID = id.Value; viewModel.Courses = viewModel.Instructors.Where( i => i.ID == id.Value).Single().Courses; } if (courseID != null) { ViewBag.CourseID = courseID.Value; viewModel.Enrollments = viewModel.Courses.Where( x => x.CourseID == courseID).Single().Enrollments; } return View(viewModel); }
当我们知道集合中只有一个项目时我们使用Single方法。如果传递给集合的为空值或者多于一个项目Single方法会抛出异常。SingleOrDefault方法会在集合为空值时返回一个默认值(在本例中会返回空值)。但是在本例中还是会抛出异常(在一个空引用视图搜索Courses属性时),并且异常消息将不会标明问题的原因。如果我们使用Single方法时,我们同时可以给它传递Where条件,这样可以不用再调用Where方法:
.Single(i => i.ID == id.Value)
可以取代:
.Where(i => i.ID == id.Value).Single()
3.3.修改Index视图:
@model ContosoUniversity.ViewModels.InstructorIndexData @{ ViewBag.Title = "Instructors"; } <h2>Instructors</h2> <p> @Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create") </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>Last Name</th> <th>First Name</th> <th>Hire Date</th> <th>Office</th> <th></th> </tr> @foreach (var item in Model.Instructors) { string selectedRow = ""; if (item.ID == ViewBag.InstructorID) { selectedRow = "success"; } <tr class="@selectedRow"> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LastName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstMidName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.HireDate) </td> <td> @if (item.OfficeAssignment != null) { @item.OfficeAssignment.Location } </td> <td> @Html.ActionLink("Select", "Index", new { id = item.ID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id = item.ID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id = item.ID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id = item.ID }) </td> </tr> } </table>
在Index视图最后添加:
@if (Model.Courses != null) { <h3>Courses Taught by Selected Instructor</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <th></th> <th>Number</th> <th>Title</th> <th>Department</th> </tr> @foreach (var item in Model.Courses) { string selectedRow = ""; if (item.CourseID == ViewBag.CourseID) { selectedRow = "success"; } <tr class="@selectedRow"> <td> @Html.ActionLink("Select", "Index", new { courseID = item.CourseID }) </td> <td> @item.CourseID </td> <td> @item.Title </td> <td> @item.Department.Name </td> </tr> } </table> }
再次在Index视图最后添加:
@if (Model.Enrollments != null) { <h3> Students Enrolled in Selected Course </h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Grade</th> </tr> @foreach (var item in Model.Enrollments) { <tr> <td> @item.Student.FullName </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Grade) </td> </tr> } </table> }
3.4.添加显示加载:
修改Index方法:
public ActionResult Index(int? id, int? courseID) { var viewModel = new InstructorIndexData(); viewModel.Instructors = db.Instructors .Include(i => i.OfficeAssignment) .Include(i => i.Courses.Select(c => c.Department)) .OrderBy(i => i.LastName); if (id != null) { ViewBag.InstructorID = id.Value; viewModel.Courses = viewModel.Instructors.Where( i => i.ID == id.Value).Single().Courses; } if (courseID != null) { ViewBag.CourseID = courseID.Value; // Lazy loading //viewModel.Enrollments = viewModel.Courses.Where( // x => x.CourseID == courseID).Single().Enrollments; // Explicit loading var selectedCourse = viewModel.Courses.Where(x => x.CourseID == courseID).Single(); db.Entry(selectedCourse).Collection(x => x.Enrollments).Load(); foreach (Enrollment enrollment in selectedCourse.Enrollments) { db.Entry(enrollment).Reference(x => x.Student).Load(); } viewModel.Enrollments = selectedCourse.Enrollments; } return View(viewModel); }