1. Github 地址
https://github.com/hanayashiki/Sudoku
2. PSP
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时 | 实际耗时 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 5min | 5min |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 5min | 5min |
| Development | 开发 | 22h | 42h |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 8h | 12h |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 2h | 2h |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 0h | 0h |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 0.5h | 0h |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 0.5h | 1h |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 3h | 6h |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 6h | 1h |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 2h | 30h |
| Reporting | 报告 | 3.5h | 3.5h |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 2h | 2h |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 0.5h | 5min |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 1h | 15min |
| 合计 | 25.5h |
3. 解题思路:
1. 解数独(旧思路)
首先查阅资料,得知:
数独问题可以转化为图着色问题:把每个空格当做一个个的结点P(i,j),则每个宫、每个行、每个列的结点都内部互相连接在一起,相邻的结点不可以是同样的颜色。然而,图着色问题是一个NPC问题,也就是说对于数独来讲,我们不一定能找到时间复杂度很低的算法。(输入的量是不变的,为81个0-9的数,然而由于图着色问题时间复杂度会很大,数独问题的复杂度也可能很大)。[1][2]
因此放弃了寻找动态规划等多项式时间复杂度算法的努力。
但是我们可以用比较暴力但是尽量减少无用尝试的算法尽快得出数独的一个解,下面给出伪代码:
class point: int number int candidates = [] int x, y point mat[9][9] = input(some_file) // or failure, stop. // Initialize a point map def get_candidates(point p): 清空p的candidates 若number是0,遍历p所在列的每一行、每一列和每一个宫 返回p的candidates数量 若number不是0,返回0。 def get_min_point(): 遍历mat分别运行 get_candidates ,找到返回值最小的一个point(减少分支) 返回这个point def solve(): point p stack changes // Records augments of trials stack rollback // Records used augments of trials, for recovery from failures p = get_min_point() do: 将所有p的candidates的 push 到 changes 中 change = changes.pop() rollback.push(change) 将 change 写入 mat 中 p = get_min_point() change.set_trials(len(p.candidates)) if p == 0: rollback.top.decre_trials() 根据rollback弹栈并回滚,对当前rollback栈顶进行decre_trials(),直到当前rollback.top.trials不是0 while not changes.is_empty()
难点在于维护尝试,我们需要进行一个尝试,即进行它的子尝试,然后当所有子尝试都走不通时,回滚。概念上,我们需要维护一棵树来记录决策,然而如果我们有顺序的进行尝试,即符合先序遍历的规则,那么可以用栈来实现,这样避免了建立树的动态分配等问题,提高了逼格和效率。
2.解数独(新思路)
花了一天的时间熟悉VS和c++后,我用朴素的思维写了一些轮子,把程序封装起来。比如说Matrix类用来记录点的填值和候选值,Change类用来记录工作树,等等。终于把算法实现好了的时候,发现旧思路处理一些数独题目奇慢无比,比如说:
4 7 0 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 0 1 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 0 1 0 0 2 5 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 4 0 0 0 0 0 5 1 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 0 0 0
由于分叉较多,程序漫无目的地扩展工作树,导致空间复杂度和时间复杂度都超过预期,解该题需要约0.5s,不能满足60s解1000道题的需求。
最后一天交作业,听ACM大佬和助教提到了DLX算法[3],就上网查找并且学习了DLX算法,然后亲自进行了实现,发现效果很好。DLX算法处理数独问题的思路如下:
1. 对于一个01矩阵,DLX可以在近似线性时间范围内求出一组行,使得这些行(a_i,j, a_i,j+1,...a_i,n)满足它们的和是(1,...,1),如果存在。
2. 对于数独,我们要求每一行、每一列、每一宫都有1...9这9个数字,对于数独的一次填写,我们可以这样表示它的性质:
feature = (fill, row, column, group),
fill是81维的01向量,表示填写的位置编号;row是9*9维向量,它每9位表示一行中已经填入的数;column和group也类似row。
通过合适的办法具体表示feature, 则数独正确填写完成等价于所有填写feature的向量和为(1,....,1)。
DLX算法:
是一种回溯的算法,但是可以排除掉较少不成功的尝试,因此比暴力回溯数独矩阵要快很多。
步骤:
对于矩阵A,有行r1, r2...r_n。假设所求向量集合叫S
1. 选择一个非零的行向量r,假定它属于S。
2. r有一些分量为1,删去其它包含同维非零分量的行向量。删去这些分量所在的列向量。得到新的矩阵A'。
3. 假如A`为空,那么算法结束,把所有选择过的r加入S。如果A'有零列向量,回溯并在上一步选择其它的尝试,同时这表明r不正确,它将不再被尝试。否则,把A'当做A,回到1。
利用双向链表,可以在较低的空间复杂度下实现DLX算法。
3. 生成终局:
虽然回溯算法很慢,但是我们可以让它在填满以后不结束自己,而是进行回溯,这样只要有足够的空间就可以生成1000,000甚至所有的数独终局。
4. 设计实现过程
1. 解数独:
类:DLX类,用于存一些执行DLX算法的函数和数据结构。struct Node用于存储结点,包括它的right, left, up, down四个双向链表指针。
函数:DLX的核心算法在于递归尝试算法search以及子过程recover和cover,cover用来实现算法的步骤2,recover用于回溯上一步。
2. 生成数独:
继承了旧思路,主要用到Matrix类来管理数独矩阵,用Change来记录工作树,用修改过的solve来实现填满回溯。
5. 改进思路:
主要难题在解数独不超时的问题上,实际上经历了五步:
1. 使用栈来存储工作步骤(由于没想清楚,失败了)
2. 改用树存储工作步骤(第一个能work的版本)
3. 改用位运算来节约计算时间(节约了2/3的时间,但仍然很慢)
4. 尝试剪枝的算法,但发现剪枝本身也很耗费时间,得不偿失。
5. 彻底重构,采用数独转换的DLX算法,快得飞起。
生成数独终局的时间分析:
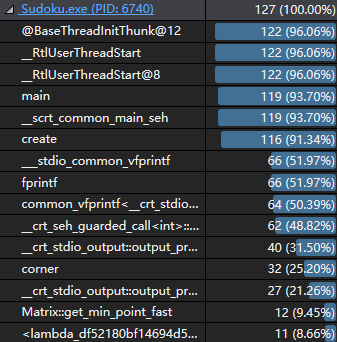
一半是IO,1/4用来回溯(create,修改自旧思路解数独的solve),1/4运行剪枝算法(corner)。
解数独的时间分析:
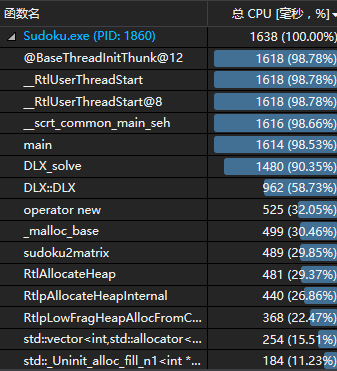
主要还是DLX算法比较耗费时间,其中一半时间用来把数独转化为矩阵这一中间过程。
6. 关键代码:
1. 生成数独:
void create(int gene_count) { matrix.fill_in_figure(1, 1, (7 + 7) % 9 + 1); int level = 0; int x, y, count; bool first = true; char candi_buf[10] = ""; // //cout << x << ", " << y << ", " << count << endl; //1. build up root //2. get a min point, if failed, rollback root's change, // try root.next (if null, rollback) or root.base (not null, otherwise quit) //3. build possible changes, linking them to the root, mark root as expanded //4. set now to be root's fchild //5. implement change //6. go to 2 // Change* now = root; while (true) { Point* p = matrix.get_min_point_fast(); Change* cut_trial = NULL; if ((p && (p->get_candi_count() > 1))) { cut_trial = corner(); } if (cut_trial) { //cout << "----------used cut-----------" << endl; cut_trial->set_base(now); cut_trial->set_next(NULL); now->set_fchild(cut_trial); //matrix.display(); //cout << "------" << endl; matrix.fill_in(cut_trial); now = cut_trial; //matrix.display(); // back to while head } else { //Point* p = matrix.get_min_point_fast(); if (p) { Change* new_change = NULL; Change* last_change = NULL; p->show_candidates(candi_buf); //cout << candi_buf << " => "; //shuffle(candi_buf); //cout << candi_buf << endl; if (DEBUG2) cout << "candi_buf:" << candi_buf; int x, y; p->get_pos(&x, &y); for (int i = 0; candi_buf[i] != 0; i++) { new_change = new Change(x, y, candi_buf[i] - '0'); new_change->set_next(last_change); new_change->set_base(now); last_change = new_change; } now->set_fchild(new_change); if (now == NULL) { matrix.display(); exit(1); } now = now->get_fchild(); matrix.fill_in(now); if (DEBUG2) now->display("fill in:"); if (DEBUG2) matrix.display(); if (matrix.get_zeroes() == 0) { matrix.dump(output); fprintf(output, " "); if (--gene_count == 0) { return; } } } else { //...todo: rollback} //now->display("roll back:"); matrix.roll_back(now); if (now->get_next() != NULL) { now = now->get_next(); } else { while (now->get_base()) { //now->get_base()->display("roll back:"); Change* base = now->get_base(); matrix.roll_back(now->get_base()); if (now->get_base()->get_next() != NULL) { now = now->get_base()->get_next(); // base->clean_desc(base); // delete base; break; } now = now->get_base(); } } matrix.fill_in(now); //now->display("fill in:"); } } } }
2. 解数独:
bool DLX::search(int k)
{
///cout << "search: " << k << endl;
if (head->right == head) {
return true;
}
int min_size = INT_MAX;
Node *c = head->right;
Node *c_root = c;
while (c != head) {
//find the row of smallest size
if (c->size < min_size) {
min_size = c->size;
c_root = c;
if (min_size == 1) {
break;
}
if (min_size == 0) {
return false;
}
}
c = c->right;
}
cover(c_root); //close the colomn and relevant rows
Node *current_row, *current;
for (current_row = c_root->down; current_row != c_root;
current_row = current_row->down) // try adding each row
{
result.push_back(current_row->row_root->num); // try regarding it as an answer
//cout << "result_push: " << current_row->row_root->num << "; " << endl;
for (current = current_row->right; current != current_row;
current = current->right)
{
//cout << "second cover" << endl;
cover(current->col_root);
}
if (search(k + 1)) {
return true;
}
for (current = current_row->left; current != current_row;
current = current->left)
{
//cout << "second recover" << endl;
recover(current->col_root);
}
result.pop_back();
}
recover(c_root);
return false;
}
参考资料:
[1] https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%9B%BE%E7%9D%80%E8%89%B2%E9%97%AE%E9%A2%98/8928655?fr=aladdin
[2] http://www.cnblogs.com/grenet/archive/2013/06/19/3138654.html
[3] http://www.jianshu.com/p/93b52c37cc65