对象模型的原理
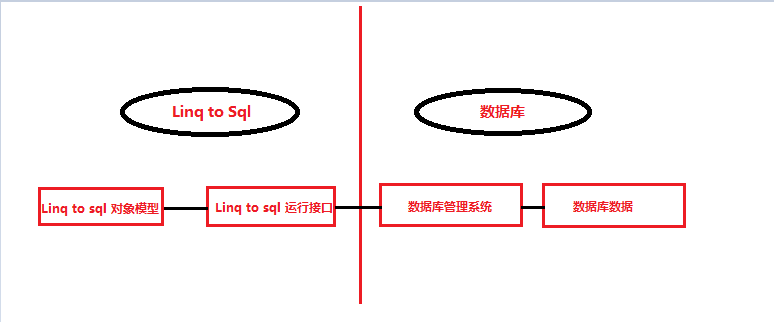
Linq to sql 包括两个主要组件,对象模型提供对象的访问模式和开发接口。运行接口主要为对象模型和数据库管理系统之间提供映射功能
创建对象模型的三种方法
1.对象关系设计器(O/R设计器)
2.SQLMetal代码生成工具
3.代码编辑器
O/R设计器的构成
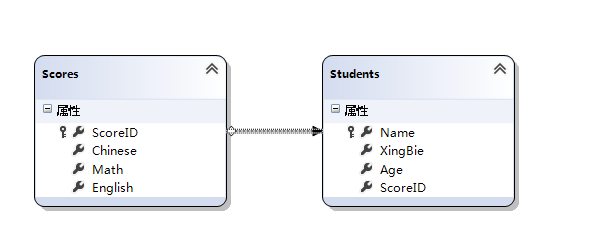
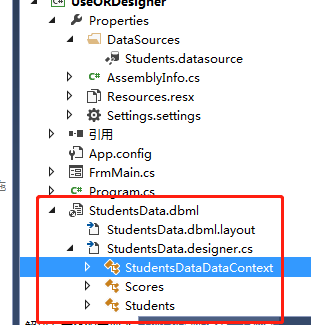
一个LinQ to SQL 类包含有四个文件。
1.DBML文件。该文件本身是一个XML文件,用来描述关系模型中数据库的表、字段、链接字符串、对象模型中的类等。
2.Layout文件,该文件本职也是XML文件,记录当前LINQ to SQL在O/R设计器中的布局等信息
3.设计代码文件(.designer.cs)。该文件是C#代码文件,包含O/R设计器自动生成的对象模型中的类实现。除了每个数据表对应的类,还包括一个DaTaContext类,对来实现对象模型和关系模型之间的数据的传输。
4.用户实现代码。
深入学习Linq to SQL
Linq to SQL 通过DataContext类实现数据对象与数据库之间的数据交换。
DataContext主要从System.Data.Linq.DataContext派生而来,主要负责数据库的数据交换,包括几个主要的只读属性

namespace UseORDesigner { using System.Data.Linq; using System.Data.Linq.Mapping; using System.Data; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Reflection; using System.Linq; using System.Linq.Expressions; using System.ComponentModel; using System; [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.DatabaseAttribute(Name="exercise")] public partial class StudentsDataDataContext : System.Data.Linq.DataContext { private static System.Data.Linq.Mapping.MappingSource mappingSource = new AttributeMappingSource(); #region 可扩展性方法定义 partial void OnCreated(); partial void InsertScores(Scores instance); partial void UpdateScores(Scores instance); partial void DeleteScores(Scores instance); partial void InsertStudents(Students instance); partial void UpdateStudents(Students instance); partial void DeleteStudents(Students instance); #endregion public StudentsDataDataContext() : base(global::UseORDesigner.Properties.Settings.Default.exerciseConnectionString, mappingSource) { OnCreated(); } public StudentsDataDataContext(string connection) : base(connection, mappingSource) { OnCreated(); } public StudentsDataDataContext(System.Data.IDbConnection connection) : base(connection, mappingSource) { OnCreated(); } public StudentsDataDataContext(string connection, System.Data.Linq.Mapping.MappingSource mappingSource) : base(connection, mappingSource) { OnCreated(); } public StudentsDataDataContext(System.Data.IDbConnection connection, System.Data.Linq.Mapping.MappingSource mappingSource) : base(connection, mappingSource) { OnCreated(); } public System.Data.Linq.Table<Scores> Scores { get { return this.GetTable<Scores>(); } } public System.Data.Linq.Table<Students> Students { get { return this.GetTable<Students>(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.TableAttribute(Name="dbo.Scores")] public partial class Scores : INotifyPropertyChanging, INotifyPropertyChanged { private static PropertyChangingEventArgs emptyChangingEventArgs = new PropertyChangingEventArgs(String.Empty); private int _ScoreID; private System.Nullable<int> _Chinese; private System.Nullable<int> _Math; private System.Nullable<int> _English; private EntitySet<Students> _Students; #region 可扩展性方法定义 partial void OnLoaded(); partial void OnValidate(System.Data.Linq.ChangeAction action); partial void OnCreated(); partial void OnScoreIDChanging(int value); partial void OnScoreIDChanged(); partial void OnChineseChanging(System.Nullable<int> value); partial void OnChineseChanged(); partial void OnMathChanging(System.Nullable<int> value); partial void OnMathChanged(); partial void OnEnglishChanging(System.Nullable<int> value); partial void OnEnglishChanged(); #endregion public Scores() { this._Students = new EntitySet<Students>(new Action<Students>(this.attach_Students), new Action<Students>(this.detach_Students)); OnCreated(); } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_ScoreID", DbType="Int NOT NULL", IsPrimaryKey=true)] public int ScoreID { get { return this._ScoreID; } set { if ((this._ScoreID != value)) { this.OnScoreIDChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._ScoreID = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("ScoreID"); this.OnScoreIDChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_Chinese", DbType="Int")] public System.Nullable<int> Chinese { get { return this._Chinese; } set { if ((this._Chinese != value)) { this.OnChineseChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._Chinese = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("Chinese"); this.OnChineseChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_Math", DbType="Int")] public System.Nullable<int> Math { get { return this._Math; } set { if ((this._Math != value)) { this.OnMathChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._Math = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("Math"); this.OnMathChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_English", DbType="Int")] public System.Nullable<int> English { get { return this._English; } set { if ((this._English != value)) { this.OnEnglishChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._English = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("English"); this.OnEnglishChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.AssociationAttribute(Name="Scores_Students", Storage="_Students", ThisKey="ScoreID", OtherKey="ScoreID")] public EntitySet<Students> Students { get { return this._Students; } set { this._Students.Assign(value); } } public event PropertyChangingEventHandler PropertyChanging; public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; protected virtual void SendPropertyChanging() { if ((this.PropertyChanging != null)) { this.PropertyChanging(this, emptyChangingEventArgs); } } protected virtual void SendPropertyChanged(String propertyName) { if ((this.PropertyChanged != null)) { this.PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } } private void attach_Students(Students entity) { this.SendPropertyChanging(); entity.Scores = this; } private void detach_Students(Students entity) { this.SendPropertyChanging(); entity.Scores = null; } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.TableAttribute(Name="dbo.Students")] public partial class Students : INotifyPropertyChanging, INotifyPropertyChanged { private static PropertyChangingEventArgs emptyChangingEventArgs = new PropertyChangingEventArgs(String.Empty); private string _Name; private string _XingBie; private System.Nullable<int> _Age; private System.Nullable<int> _ScoreID; private EntityRef<Scores> _Scores; #region 可扩展性方法定义 partial void OnLoaded(); partial void OnValidate(System.Data.Linq.ChangeAction action); partial void OnCreated(); partial void OnNameChanging(string value); partial void OnNameChanged(); partial void OnXingBieChanging(string value); partial void OnXingBieChanged(); partial void OnAgeChanging(System.Nullable<int> value); partial void OnAgeChanged(); partial void OnScoreIDChanging(System.Nullable<int> value); partial void OnScoreIDChanged(); #endregion public Students() { this._Scores = default(EntityRef<Scores>); OnCreated(); } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_Name", DbType="NVarChar(50) NOT NULL", CanBeNull=false, IsPrimaryKey=true)] public string Name { get { return this._Name; } set { if ((this._Name != value)) { this.OnNameChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._Name = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("Name"); this.OnNameChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_XingBie", DbType="NVarChar(50)")] public string XingBie { get { return this._XingBie; } set { if ((this._XingBie != value)) { this.OnXingBieChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._XingBie = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("XingBie"); this.OnXingBieChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_Age", DbType="Int")] public System.Nullable<int> Age { get { return this._Age; } set { if ((this._Age != value)) { this.OnAgeChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._Age = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("Age"); this.OnAgeChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.ColumnAttribute(Storage="_ScoreID", DbType="Int")] public System.Nullable<int> ScoreID { get { return this._ScoreID; } set { if ((this._ScoreID != value)) { if (this._Scores.HasLoadedOrAssignedValue) { throw new System.Data.Linq.ForeignKeyReferenceAlreadyHasValueException(); } this.OnScoreIDChanging(value); this.SendPropertyChanging(); this._ScoreID = value; this.SendPropertyChanged("ScoreID"); this.OnScoreIDChanged(); } } } [global::System.Data.Linq.Mapping.AssociationAttribute(Name="Scores_Students", Storage="_Scores", ThisKey="ScoreID", OtherKey="ScoreID", IsForeignKey=true)] public Scores Scores { get { return this._Scores.Entity; } set { Scores previousValue = this._Scores.Entity; if (((previousValue != value) || (this._Scores.HasLoadedOrAssignedValue == false))) { this.SendPropertyChanging(); if ((previousValue != null)) { this._Scores.Entity = null; previousValue.Students.Remove(this); } this._Scores.Entity = value; if ((value != null)) { value.Students.Add(this); this._ScoreID = value.ScoreID; } else { this._ScoreID = default(Nullable<int>); } this.SendPropertyChanged("Scores"); } } } public event PropertyChangingEventHandler PropertyChanging; public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; protected virtual void SendPropertyChanging() { if ((this.PropertyChanging != null)) { this.PropertyChanging(this, emptyChangingEventArgs); } } protected virtual void SendPropertyChanged(String propertyName) { if ((this.PropertyChanged != null)) { this.PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } } } }
主要了解各段代码的作用
通过绑定浏览数据库记录
在创建Linq to Sql 后,就可以轻松的通过类浏览数据。
1.新建一个窗体应用程序,直接从数据源将需要查询的表拖到form上,会自动生成一个DataGridView表格
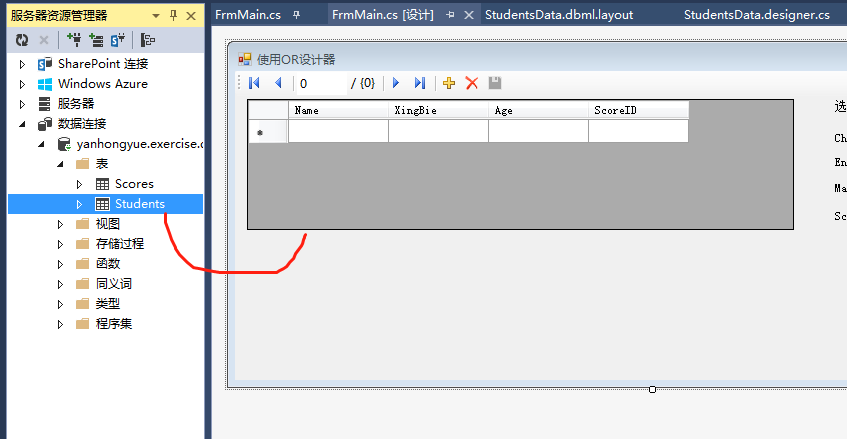
2.如果要将数据加载到界面,则需要通过DataContext对象才行,在frmMain添加一个类成员,在把数据源绑定到界面
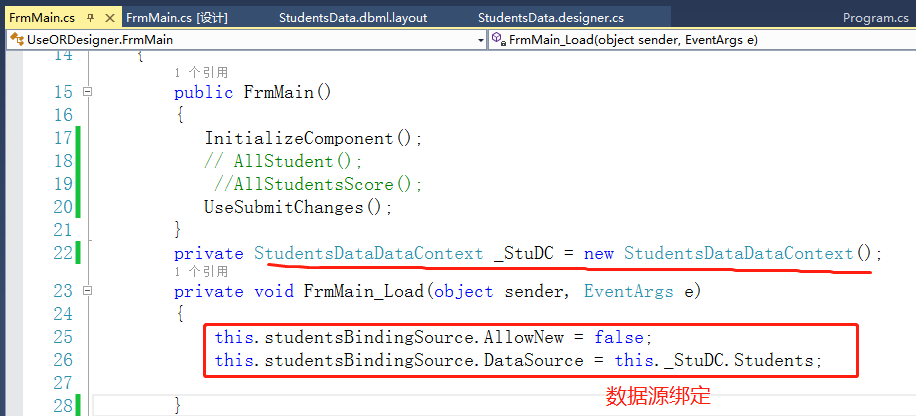
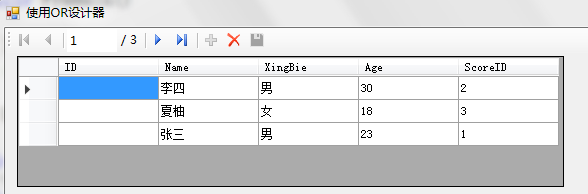 这样我们就可以浏览数据库表记录了
这样我们就可以浏览数据库表记录了
用Linq 查询 Linq to Sql类
LInQ to Sql 类同样可以与LInq绑定查询,通常包含以下几个步骤
1.在已有数据库的情况下为项目添加LINQ to SQL对象模型
2.根据对象模型获取对应的DataContext类。该类是应用程序与数据之间的桥梁,他提供数据库的查询,修改等操作。
3.通过DataContext获取对应的数据源
4.编写LINQ查询对数据源进行查询
//用Linq查询Linq to Sql类,即DataContext static void AllStudent() { StudentsDataDataContext dc = new StudentsDataDataContext(); IEnumerable<Students> query = from stu in dc.Students orderby stu.Age select stu; var query1 = from stu in dc.Students orderby stu.Age select stu; foreach (var item in query1) { Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1}:{2}", item.Name, item.XingBie, item.Age); } }
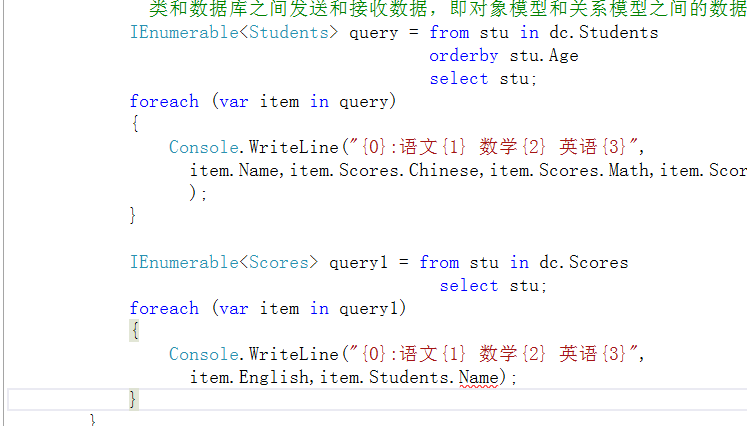
//有表关系的Linq 查询操作 static void AllStudentsScore() { StudentsDataDataContext dc = new StudentsDataDataContext();//用于在实体类和数据库之间发送和接收数据,即对象模型和关系模型之间的数据的传输。 IEnumerable<Students> query = from stu in dc.Students orderby stu.Age select stu; foreach (var item in query) { Console.WriteLine("{0}:语文{1} 数学{2} 英语{3}", item.Name,item.Scores.Chinese,item.Scores.Math,item.Scores.English); } }
在这里补充一个新的知识,Student表里包含Score表的主键,Student表就是从表,在添加关联的时候如果主从关系弄错了,Item.Scores后面就点不住来Scores里的属性。
父类点子类结果是集合,子类点父类,才会产生对象
 v
v 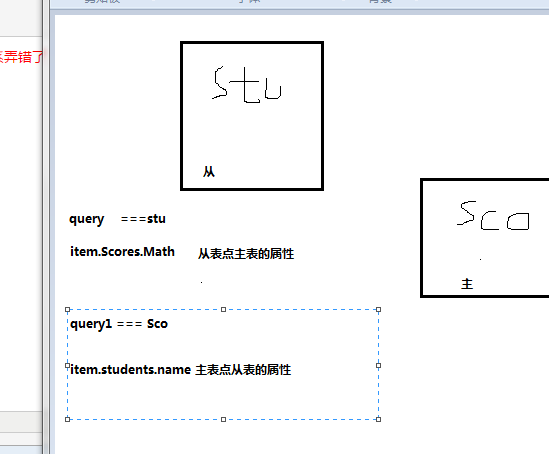
主表点不出从表的属性,只有从表能点出主表的属性
修改数据库记录
Datacontext还提供了数据库的修改接口,,修改数据库记录包含下面三个步骤
1.创建对象关系模型 2.通过DataContext提供的数据表对象获取数据记录 3.通过DataContext类的SubmitChanges()方法,将修改后的数据提交到数据库
//Linq to DataSql 修改数据库记录 static void UseSubmitChanges() { StudentsDataDataContext dc = new StudentsDataDataContext(); IEnumerable<Students> query = from stu in dc.Students.AsEnumerable() orderby stu.Age select stu; foreach (var item in query) { item.Scores.Math = item.Scores.Math + 17; Console.WriteLine("姓名{0}:语文{1} 数学{2} 英语{3}", item.Name, item.Scores.Chinese, item.Scores.Math, item.Scores.English); dc.SubmitChanges(); } }
dc.SubmitChanges();将修改后的数据提交到数据库
