装饰器:
定义:本质是函数,(装饰其它函数)就是为其它函数添加附加功能。
原则:
1. 不能修改被装饰的函数的源代码;
2. 不能修改被装饰的函数的调用方式;
实现装饰器知识储备:
1. 函数即“变量”;
2. 高阶函数;
3. 嵌套函数;
高阶函数+嵌套函数==>装饰器
装饰器,其实就是一种语法糖,语法糖(Syntactic sugar)也译为糖衣语法,是由英国计算机科学家彼得·约翰·兰达(Peter J. Landin)发明的一个术语,指计算机语言中添加的某种语法,这种语法对语言的功能并没有影响,但是更方便程序员使用。通常来说使用语法糖能够增加程序的可读性,从而减少程序代码出错的机会。
承祥君认为彼得·约翰·兰达(Peter J. Landin)在家中经常做饭且爱吃糖,因为糖并不影响饭菜的质变或量变,仅起到修饰口味的作用。
装饰器初阶:
这种方式可以实现装饰器的基本作用,即不修改原函数代码的情况下虽然实现了增加新功能,但此方法改变了函数的调用方式,严格意义上讲并不符合装饰器的使用;
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- # _Author_:George import time def decorator(test): start_time = time.time() test() end_time = time.time() print("Running time is :%s"%(end_time-start_time)) def test1(): time.sleep(0.5) print("I'm test1") def test2(): time.sleep(1) print("I'm test2") decorator(test1) decorator(test2)
输出结果:
-------The result-------- I'm test1 Running time is :0.5 I'm test2 Running time is :1.0
装饰器进阶:
不修改原函数代码的情况,同时不改变原函数的调用方式,用到高阶函数:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- # _Author_:George import time def timer(test): def decorator(): start_time = time.time() test() end_time = time.time() print("Running time is :%s"%(end_time-start_time)) return decorator def test1(): time.sleep(0.5) print("I'm test1") def test2(): time.sleep(1) print("I'm test2") print(timer(test1)," -------The result--------") test1=timer(test1) test2=timer(test2) test1() test2()
输出结果:
<function timer.<locals>.decorator at 0x0000000001EA2AE8> -------The result-------- I'm test1 Running time is :0.5 I'm test2 Running time is :1.0
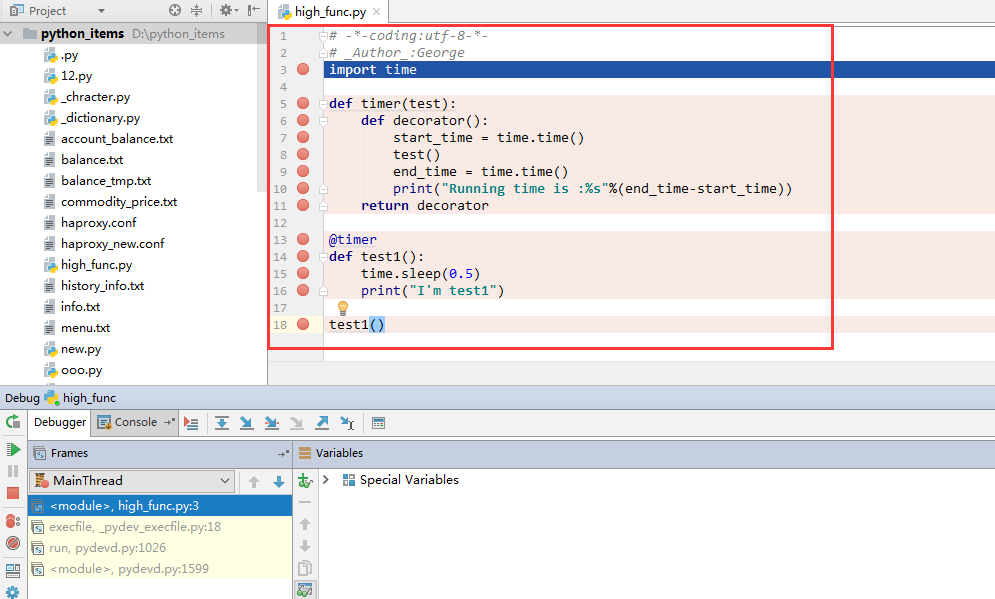
装饰器高阶:
上述进阶部分功能虽然全部实现,实现仍较为麻烦,且不符合标准装饰器语法,标准实现如下:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- # _Author_:George import time def timer(test): def decorator(): start_time = time.time() test() end_time = time.time() print("Running time is :%s"%(end_time-start_time)) return decorator @timer def test1(): time.sleep(0.5) print("I'm test1") @timer def test2(): time.sleep(1) print("I'm test2") print(" -------The result--------") test1() test2()
输出结果: -------The result-------- I'm test1 Running time is :0.5 I'm test2 Running time is :1.0
详细过程可以打断点Debug看一下,会让你更多一些理解: