本文分析基于Linux Kernel 3.2.1
原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7979838
更多请查看专栏http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/linux-kernel-net.html
作者:闫明
Linux内核中协议族有INET协议族,UNIX协议族等,我们还是以INET协议族为例。
下面是内核中的协议族声明:
- /* Supported address families. */
- #define AF_UNSPEC 0
- #define AF_UNIX 1 /* Unix domain sockets */
- #define AF_LOCAL 1 /* POSIX name for AF_UNIX */
- #define AF_INET 2 /* Internet IP Protocol */
- #define AF_AX25 3 /* Amateur Radio AX.25 */
- #define AF_IPX 4 /* Novell IPX */
- #define AF_APPLETALK 5 /* AppleTalk DDP */
- #define AF_NETROM 6 /* Amateur Radio NET/ROM */
- #define AF_BRIDGE 7 /* Multiprotocol bridge */
- #define AF_ATMPVC 8 /* ATM PVCs */
- #define AF_X25 9 /* Reserved for X.25 project */
- #define AF_INET6 10 /* IP version 6 */
- #define AF_ROSE 11 /* Amateur Radio X.25 PLP */
- #define AF_DECnet 12 /* Reserved for DECnet project */
- #define AF_NETBEUI 13 /* Reserved for 802.2LLC project*/
- #define AF_SECURITY 14 /* Security callback pseudo AF */
- #define AF_KEY 15 /* PF_KEY key management API */
- #define AF_NETLINK 16
- #define AF_ROUTE AF_NETLINK /* Alias to emulate 4.4BSD */
- #define AF_PACKET 17 /* Packet family */
- #define AF_ASH 18 /* Ash */
- #define AF_ECONET 19 /* Acorn Econet */
- #define AF_ATMSVC 20 /* ATM SVCs */
- #define AF_RDS 21 /* RDS sockets */
- #define AF_SNA 22 /* Linux SNA Project (nutters!) */
- #define AF_IRDA 23 /* IRDA sockets */
- #define AF_PPPOX 24 /* PPPoX sockets */
- #define AF_WANPIPE 25 /* Wanpipe API Sockets */
- #define AF_LLC 26 /* Linux LLC */
- #define AF_CAN 29 /* Controller Area Network */
- #define AF_TIPC 30 /* TIPC sockets */
- #define AF_BLUETOOTH 31 /* Bluetooth sockets */
- #define AF_IUCV 32 /* IUCV sockets */
- #define AF_RXRPC 33 /* RxRPC sockets */
- #define AF_ISDN 34 /* mISDN sockets */
- #define AF_PHONET 35 /* Phonet sockets */
- #define AF_IEEE802154 36 /* IEEE802154 sockets */
- #define AF_CAIF 37 /* CAIF sockets */
- #define AF_ALG 38 /* Algorithm sockets */
- #define AF_NFC 39 /* NFC sockets */
- #define AF_MAX 40 /* For now.. */
内核中的PF_***和AF_***其实可以混用,它的宏定义如下:
- /* Protocol families, same as address families. */
- #define PF_UNSPEC AF_UNSPEC
- #define PF_UNIX AF_UNIX
- #define PF_LOCAL AF_LOCAL
- #define PF_INET AF_INET
- #define PF_AX25 AF_AX25
- #define PF_IPX AF_IPX
- #define PF_APPLETALK AF_APPLETALK
- #define PF_NETROM AF_NETROM
- #define PF_BRIDGE AF_BRIDGE
- #define PF_ATMPVC AF_ATMPVC
- #define PF_X25 AF_X25
- #define PF_INET6 AF_INET6
- #define PF_ROSE AF_ROSE
- #define PF_DECnet AF_DECnet
- #define PF_NETBEUI AF_NETBEUI
- #define PF_SECURITY AF_SECURITY
- #define PF_KEY AF_KEY
- #define PF_NETLINK AF_NETLINK
- #define PF_ROUTE AF_ROUTE
- #define PF_PACKET AF_PACKET
- #define PF_ASH AF_ASH
- #define PF_ECONET AF_ECONET
- #define PF_ATMSVC AF_ATMSVC
- #define PF_RDS AF_RDS
- #define PF_SNA AF_SNA
- #define PF_IRDA AF_IRDA
- #define PF_PPPOX AF_PPPOX
- #define PF_WANPIPE AF_WANPIPE
- #define PF_LLC AF_LLC
- #define PF_CAN AF_CAN
- #define PF_TIPC AF_TIPC
- #define PF_BLUETOOTH AF_BLUETOOTH
- #define PF_IUCV AF_IUCV
- #define PF_RXRPC AF_RXRPC
- #define PF_ISDN AF_ISDN
- #define PF_PHONET AF_PHONET
- #define PF_IEEE802154 AF_IEEE802154
- #define PF_CAIF AF_CAIF
- #define PF_ALG AF_ALG
- #define PF_NFC AF_NFC
- #define PF_MAX AF_MAX
以后的分析就是以INET协议族为例来分析的。
下面的结构体就是在系统初始化时用来管理协议族初始化的结构体:
- struct net_proto_family {
- int family;
- int (*create)(struct net *net, struct socket *sock,
- int protocol, int kern);
- struct module *owner;
- };
第二个属性就是协议族对应的初始化函数指针;
INET协议族对应该结构的定义如下:
- static const struct net_proto_family inet_family_ops = {
- .family = PF_INET,
- .create = inet_create,
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- };
下面结构体是协议族操作集结构体定义:
- struct proto_ops {
- int family;
- struct module *owner;
- int (*release) (struct socket *sock);
- int (*bind) (struct socket *sock,
- struct sockaddr *myaddr,
- int sockaddr_len);
- int (*connect) (struct socket *sock,
- struct sockaddr *vaddr,
- int sockaddr_len, int flags);
- int (*socketpair)(struct socket *sock1,
- struct socket *sock2);
- int (*accept) (struct socket *sock,
- struct socket *newsock, int flags);
- int (*getname) (struct socket *sock,
- struct sockaddr *addr,
- int *sockaddr_len, int peer);
- unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *file, struct socket *sock,
- struct poll_table_struct *wait);
- int (*ioctl) (struct socket *sock, unsigned int cmd,
- unsigned long arg);
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- int (*compat_ioctl) (struct socket *sock, unsigned int cmd,
- unsigned long arg);
- #endif
- int (*listen) (struct socket *sock, int len);
- int (*shutdown) (struct socket *sock, int flags);
- int (*setsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval, unsigned int optlen);
- int (*getsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval, int __user *optlen);
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- int (*compat_setsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval, unsigned int optlen);
- int (*compat_getsockopt)(struct socket *sock, int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval, int __user *optlen);
- #endif
- int (*sendmsg) (struct kiocb *iocb, struct socket *sock,
- struct msghdr *m, size_t total_len);
- int (*recvmsg) (struct kiocb *iocb, struct socket *sock,
- struct msghdr *m, size_t total_len,
- int flags);
- int (*mmap) (struct file *file, struct socket *sock,
- struct vm_area_struct * vma);
- ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct socket *sock, struct page *page,
- int offset, size_t size, int flags);
- ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct socket *sock, loff_t *ppos,
- struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, size_t len, unsigned int flags);
- };
INET协议族中TCP和UDP协议对应的上述操作集的定义不同:
TCP协议z在INET层操作集inet_stream_ops
- const struct proto_ops inet_stream_ops = {
- .family = PF_INET,
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .release = inet_release,
- .bind = inet_bind,
- .connect = inet_stream_connect,
- .socketpair = sock_no_socketpair,
- .accept = inet_accept,
- .getname = inet_getname,
- .poll = tcp_poll,
- .ioctl = inet_ioctl,
- .listen = inet_listen,
- .shutdown = inet_shutdown,
- .setsockopt = sock_common_setsockopt,
- .getsockopt = sock_common_getsockopt,
- .sendmsg = inet_sendmsg,
- .recvmsg = inet_recvmsg,
- .mmap = sock_no_mmap,
- .sendpage = inet_sendpage,
- .splice_read = tcp_splice_read,
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- .compat_setsockopt = compat_sock_common_setsockopt,
- .compat_getsockopt = compat_sock_common_getsockopt,
- .compat_ioctl = inet_compat_ioctl,
- #endif
- };
- const struct proto_ops inet_dgram_ops = {
- .family = PF_INET,
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .release = inet_release,
- .bind = inet_bind,
- .connect = inet_dgram_connect,
- .socketpair = sock_no_socketpair,
- .accept = sock_no_accept,
- .getname = inet_getname,
- .poll = udp_poll,
- .ioctl = inet_ioctl,
- .listen = sock_no_listen,
- .shutdown = inet_shutdown,
- .setsockopt = sock_common_setsockopt,
- .getsockopt = sock_common_getsockopt,
- .sendmsg = inet_sendmsg,
- .recvmsg = inet_recvmsg,
- .mmap = sock_no_mmap,
- .sendpage = inet_sendpage,
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- .compat_setsockopt = compat_sock_common_setsockopt,
- .compat_getsockopt = compat_sock_common_getsockopt,
- .compat_ioctl = inet_compat_ioctl,
- #endif
- };
上面两个操作集是属于INET协议族层次,可以由协议族层套接字socket来管理,下面是协议族层析的套接字结构体(BSD Socket)定义:
- /**
- * struct socket - general BSD socket
- * @state: socket state (%SS_CONNECTED, etc)
- * @type: socket type (%SOCK_STREAM, etc)
- * @flags: socket flags (%SOCK_ASYNC_NOSPACE, etc)
- * @ops: protocol specific socket operations
- * @file: File back pointer for gc
- * @sk: internal networking protocol agnostic socket representation
- * @wq: wait queue for several uses
- */
- struct socket {
- socket_state state;
- kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(type);
- short type;
- kmemcheck_bitfield_end(type);
- unsigned long flags;
- struct socket_wq __rcu *wq;
- struct file *file;
- struct sock *sk;
- const struct proto_ops *ops;
- };
最后一个属性就指向了上面所述的操作集。若使用TCP协议,ops就是inet_stream_ops,若是UDP协议,ops就是inet_dgram_ops。
short type属性的取值可以是如下值:
- enum sock_type {
- SOCK_DGRAM = 1,
- SOCK_STREAM = 2,
- SOCK_RAW = 3,
- SOCK_RDM = 4,
- SOCK_SEQPACKET = 5,
- SOCK_DCCP = 6,
- SOCK_PACKET = 10,
- };
传输层的协议操作集结构体定义:
- struct proto {
- void (*close)(struct sock *sk,
- long timeout);
- int (*connect)(struct sock *sk,
- struct sockaddr *uaddr,
- int addr_len);
- int (*disconnect)(struct sock *sk, int flags);
- struct sock * (*accept) (struct sock *sk, int flags, int *err);
- int (*ioctl)(struct sock *sk, int cmd,
- unsigned long arg);
- int (*init)(struct sock *sk);
- void (*destroy)(struct sock *sk);
- void (*shutdown)(struct sock *sk, int how);
- int (*setsockopt)(struct sock *sk, int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval,
- unsigned int optlen);
- int (*getsockopt)(struct sock *sk, int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval,
- int __user *option);
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- int (*compat_setsockopt)(struct sock *sk,
- int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval,
- unsigned int optlen);
- int (*compat_getsockopt)(struct sock *sk,
- int level,
- int optname, char __user *optval,
- int __user *option);
- int (*compat_ioctl)(struct sock *sk,
- unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
- #endif
- int (*sendmsg)(struct kiocb *iocb, struct sock *sk,
- struct msghdr *msg, size_t len);
- int (*recvmsg)(struct kiocb *iocb, struct sock *sk,
- struct msghdr *msg,
- size_t len, int noblock, int flags,
- int *addr_len);
- int (*sendpage)(struct sock *sk, struct page *page,
- int offset, size_t size, int flags);
- int (*bind)(struct sock *sk,
- struct sockaddr *uaddr, int addr_len);
- int (*backlog_rcv) (struct sock *sk,
- struct sk_buff *skb);
- /* Keeping track of sk's, looking them up, and port selection methods. */
- void (*hash)(struct sock *sk);
- void (*unhash)(struct sock *sk);
- void (*rehash)(struct sock *sk);
- int (*get_port)(struct sock *sk, unsigned short snum);
- void (*clear_sk)(struct sock *sk, int size);
- /* Keeping track of sockets in use */
- #ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
- unsigned int inuse_idx;
- #endif
- /* Memory pressure */
- void (*enter_memory_pressure)(struct sock *sk);
- atomic_long_t *memory_allocated; /* Current allocated memory. */
- struct percpu_counter *sockets_allocated; /* Current number of sockets. */
- /*
- * Pressure flag: try to collapse.
- * Technical note: it is used by multiple contexts non atomically.
- * All the __sk_mem_schedule() is of this nature: accounting
- * is strict, actions are advisory and have some latency.
- */
- int *memory_pressure;
- long *sysctl_mem;
- int *sysctl_wmem;
- int *sysctl_rmem;
- int max_header;
- bool no_autobind;
- struct kmem_cache *slab;
- unsigned int obj_size;
- int slab_flags;
- struct percpu_counter *orphan_count;
- struct request_sock_ops *rsk_prot;
- struct timewait_sock_ops *twsk_prot;
- union {
- struct inet_hashinfo *hashinfo;
- struct udp_table *udp_table;
- struct raw_hashinfo *raw_hash;
- } h;
- struct module *owner;
- char name[32];
- struct list_head node;
- #ifdef SOCK_REFCNT_DEBUG
- atomic_t socks;
- #endif
- };
TCP协议的操作集定义如下:
- struct proto tcp_prot = {
- .name = "TCP",
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .close = tcp_close,
- .connect = tcp_v4_connect,
- .disconnect = tcp_disconnect,
- .accept = inet_csk_accept,
- .ioctl = tcp_ioctl,
- .init = tcp_v4_init_sock,
- .destroy = tcp_v4_destroy_sock,
- .shutdown = tcp_shutdown,
- .setsockopt = tcp_setsockopt,
- .getsockopt = tcp_getsockopt,
- .recvmsg = tcp_recvmsg,
- .sendmsg = tcp_sendmsg,
- .sendpage = tcp_sendpage,
- .backlog_rcv = tcp_v4_do_rcv,
- .hash = inet_hash,
- .unhash = inet_unhash,
- .get_port = inet_csk_get_port,
- .enter_memory_pressure = tcp_enter_memory_pressure,
- .sockets_allocated = &tcp_sockets_allocated,
- .orphan_count = &tcp_orphan_count,
- .memory_allocated = &tcp_memory_allocated,
- .memory_pressure = &tcp_memory_pressure,
- .sysctl_mem = sysctl_tcp_mem,
- .sysctl_wmem = sysctl_tcp_wmem,
- .sysctl_rmem = sysctl_tcp_rmem,
- .max_header = MAX_TCP_HEADER,
- .obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock),
- .slab_flags = SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU,
- .twsk_prot = &tcp_timewait_sock_ops,
- .rsk_prot = &tcp_request_sock_ops,
- .h.hashinfo = &tcp_hashinfo,
- .no_autobind = true,
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- .compat_setsockopt = compat_tcp_setsockopt,
- .compat_getsockopt = compat_tcp_getsockopt,
- #endif
- };
- struct proto udp_prot = {
- .name = "UDP",
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .close = udp_lib_close,
- .connect = ip4_datagram_connect,
- .disconnect = udp_disconnect,
- .ioctl = udp_ioctl,
- .destroy = udp_destroy_sock,
- .setsockopt = udp_setsockopt,
- .getsockopt = udp_getsockopt,
- .sendmsg = udp_sendmsg,
- .recvmsg = udp_recvmsg,
- .sendpage = udp_sendpage,
- .backlog_rcv = __udp_queue_rcv_skb,
- .hash = udp_lib_hash,
- .unhash = udp_lib_unhash,
- .rehash = udp_v4_rehash,
- .get_port = udp_v4_get_port,
- .memory_allocated = &udp_memory_allocated,
- .sysctl_mem = sysctl_udp_mem,
- .sysctl_wmem = &sysctl_udp_wmem_min,
- .sysctl_rmem = &sysctl_udp_rmem_min,
- .obj_size = sizeof(struct udp_sock),
- .slab_flags = SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU,
- .h.udp_table = &udp_table,
- #ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
- .compat_setsockopt = compat_udp_setsockopt,
- .compat_getsockopt = compat_udp_getsockopt,
- #endif
- .clear_sk = sk_prot_clear_portaddr_nulls,
- };
现在介绍struct socket结构体中一个属性struct sock类型的结构体指针,这个结构体就是传输层的套接字,所有套接字通过该结构来使用网络协议的所有服务。定义如下:
- struct sock {
- /*
- * Now struct inet_timewait_sock also uses sock_common, so please just
- * don't add nothing before this first member (__sk_common) --acme
- */
- struct sock_common __sk_common;
- #define sk_node __sk_common.skc_node
- #define sk_nulls_node __sk_common.skc_nulls_node
- #define sk_refcnt __sk_common.skc_refcnt
- #define sk_tx_queue_mapping __sk_common.skc_tx_queue_mapping
- #define sk_dontcopy_begin __sk_common.skc_dontcopy_begin
- #define sk_dontcopy_end __sk_common.skc_dontcopy_end
- #define sk_hash __sk_common.skc_hash
- #define sk_family __sk_common.skc_family
- #define sk_state __sk_common.skc_state
- #define sk_reuse __sk_common.skc_reuse
- #define sk_bound_dev_if __sk_common.skc_bound_dev_if
- #define sk_bind_node __sk_common.skc_bind_node
- #define sk_prot __sk_common.skc_prot
- #define sk_net __sk_common.skc_net
- socket_lock_t sk_lock;
- struct sk_buff_head sk_receive_queue;
- /*
- * The backlog queue is special, it is always used with
- * the per-socket spinlock held and requires low latency
- * access. Therefore we special case it's implementation.
- * Note : rmem_alloc is in this structure to fill a hole
- * on 64bit arches, not because its logically part of
- * backlog.
- */
- struct {
- atomic_t rmem_alloc;
- int len;
- struct sk_buff *head;
- struct sk_buff *tail;
- } sk_backlog;
- #define sk_rmem_alloc sk_backlog.rmem_alloc
- int sk_forward_alloc;
- #ifdef CONFIG_RPS
- __u32 sk_rxhash;
- #endif
- atomic_t sk_drops;
- int sk_rcvbuf;
- struct sk_filter __rcu *sk_filter;
- struct socket_wq __rcu *sk_wq;
- #ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA
- struct sk_buff_head sk_async_wait_queue;
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
- struct xfrm_policy *sk_policy[2];
- #endif
- unsigned long sk_flags;
- struct dst_entry *sk_dst_cache;
- spinlock_t sk_dst_lock;
- atomic_t sk_wmem_alloc;
- atomic_t sk_omem_alloc;
- int sk_sndbuf;
- struct sk_buff_head sk_write_queue;
- kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags);
- unsigned int sk_shutdown : 2,
- sk_no_check : 2,
- sk_userlocks : 4,
- sk_protocol : 8,
- sk_type : 16;
- kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags);
- int sk_wmem_queued;
- gfp_t sk_allocation;
- int sk_route_caps;
- int sk_route_nocaps;
- int sk_gso_type;
- unsigned int sk_gso_max_size;
- int sk_rcvlowat;
- unsigned long sk_lingertime;
- struct sk_buff_head sk_error_queue;
- struct proto *sk_prot_creator;
- rwlock_t sk_callback_lock;
- int sk_err,
- sk_err_soft;
- unsigned short sk_ack_backlog;
- unsigned short sk_max_ack_backlog;
- __u32 sk_priority;
- struct pid *sk_peer_pid;
- const struct cred *sk_peer_cred;
- long sk_rcvtimeo;
- long sk_sndtimeo;
- void *sk_protinfo;
- struct timer_list sk_timer;
- ktime_t sk_stamp;
- struct socket *sk_socket;
- void *sk_user_data;
- struct page *sk_sndmsg_page;
- struct sk_buff *sk_send_head;
- __u32 sk_sndmsg_off;
- int sk_write_pending;
- #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
- void *sk_security;
- #endif
- __u32 sk_mark;
- u32 sk_classid;
- void (*sk_state_change)(struct sock *sk);
- void (*sk_data_ready)(struct sock *sk, int bytes);
- void (*sk_write_space)(struct sock *sk);
- void (*sk_error_report)(struct sock *sk);
- int (*sk_backlog_rcv)(struct sock *sk,
- struct sk_buff *skb);
- void (*sk_destruct)(struct sock *sk);
- };
若要将协议族操作集和具体协议操作集整合起来为IP协议提供接口,就需要下面的结构体定义:
- struct inet_protosw {
- struct list_head list;
- /* These two fields form the lookup key. */
- unsigned short type; /* This is the 2nd argument to socket(2). */
- unsigned short protocol; /* This is the L4 protocol number. */
- struct proto *prot;
- const struct proto_ops *ops;
- char no_check; /* checksum on rcv/xmit/none? */
- unsigned char flags; /* See INET_PROTOSW_* below. */
- };
INET三种套接字定义的inetsw_array数组如下:
- static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] =
- {
- {
- .type = SOCK_STREAM,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
- .prot = &tcp_prot,
- .ops = &inet_stream_ops,
- .no_check = 0,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |
- INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
- },
- {
- .type = SOCK_DGRAM,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_UDP,
- .prot = &udp_prot,
- .ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
- .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT,
- },
- {
- .type = SOCK_DGRAM,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP,
- .prot = &ping_prot,
- .ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
- .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
- },
- {
- .type = SOCK_RAW,
- .protocol = IPPROTO_IP, /* wild card */
- .prot = &raw_prot,
- .ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
- .no_check = UDP_CSUM_DEFAULT,
- .flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
- }
- };
- static struct list_head inetsw[SOCK_MAX];
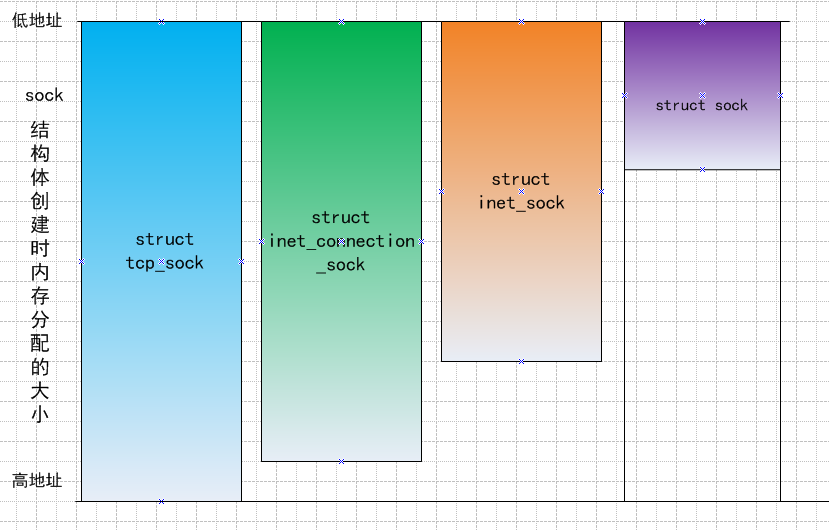
那内核中套接字struct socket、struct sock、struct inet_sock、struct tcp_sock、struct raw_sock、struct udp_sock、struct inet_connection_sock、struct inet_timewait_sock和struct tcp_timewait_sock的关系是怎样的呢?
*struct socket这个是BSD层的socket,应用程序会用过系统调用首先创建该类型套接字,它和具体协议无关。
*struct inet_sock是INET协议族使用的socket结构,可以看成位于INET层,是struct sock的一个扩展。它的第一个属性就是struct sock结构。
*struct sock是与具体传输层协议相关的套接字,所有内核的操作都基于这个套接字。
*struct tcp_sock是TCP协议的套接字表示,它是对struct inet_connection_sock的扩展,其第一个属性就是struct inet_connection_sock inet_conn。
*struct raw_sock是原始类型的套接字表示,ICMP协议就使用这种套接字,其是对struct sock的扩展。
*struct udp_sock是UDP协议套接字表示,其是对struct inet_sock套接字的扩展。
*struct inet_connetction_sock是所有面向连接协议的套接字,是对struct inet_sock套接字扩展。
后面两个是用于控制超时的套接字。
就拿struct inet_sock和struct sock为例来说明,为什么内核中可以直接将sock结构体首地址强制转换成inet_sock的首地址?并且inet_sock的大小要大于sock,直接进行如下强制转换
- inet = inet_sk(sk);
- static inline struct inet_sock *inet_sk(const struct sock *sk)
- {
- return (struct inet_sock *)sk;
- }
不会发生内存非法访问吗?!那就是在分配的时候并不只是分配的struct sock结构体大小的存储空间!
可以细看sock结构体分配的代码:
- struct sock *sk_alloc(struct net *net, int family, gfp_t priority,
- struct proto *prot)
- {
- struct sock *sk;
- sk = sk_prot_alloc(prot, priority | __GFP_ZERO, family);
- if (sk) {
- sk->sk_family = family;
- sk->sk_prot = sk->sk_prot_creator = prot;
- sock_lock_init(sk);
- sock_net_set(sk, get_net(net));
- atomic_set(&sk->sk_wmem_alloc, 1);
- sock_update_classid(sk);
- }
- return sk;
- }
- static struct sock *sk_prot_alloc(struct proto *prot, gfp_t priority,
- int family)
- {
- struct sock *sk;
- struct kmem_cache *slab;
- slab = prot->slab;
- if (slab != NULL) {
- sk = kmem_cache_alloc(slab, priority & ~__GFP_ZERO);
- ..............................
- } else
- sk = kmalloc(prot->obj_size, priority);
- .....................
- return sk;
- ......................
- }
如果是TCP协议中的tcp_prot中指明该属性的大小为.obj_size = sizeof(struct tcp_sock)。
所以,程序中给struct sock指针分配的不是该结构体的实际大小,而是大于其实际大小,以便其扩展套接字的属性占用。
以图例说明tcp_sock是如何从sock强制转换来的:
下篇将分析套接字的绑定、连接等一系列操作的实现。
下篇将分析套接字的操作函数。