1.动手实验:继承条件下的构造方法调用
源代码: class Grandparent {
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:"+string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent {
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits {
public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Child c=new Child(); }
}
运行结果截图:
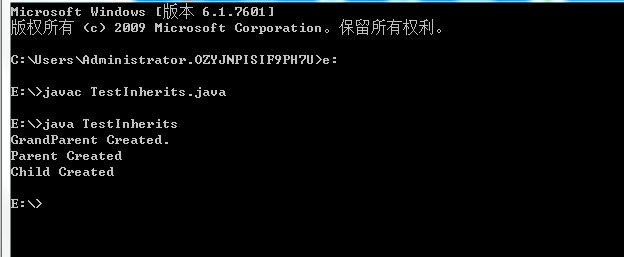
结论:
通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
思考:为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
构造函数(constructor)是一种特殊的方法 。主要用来在创建对象时初始化对象, 即为对象成员变量赋初始值,总与new运算符一起使用在创建对象的语句中 。特别的一个类可以有多个构造函数 ,可根据其参数个数的不同或参数类型的不同来区分它们 即构造函数的重载。构造函数的功能主要用于在类的对象创建时定义初始化的状态。 所以说构造函数的作用,简单来说就是初始化,初始化一个新建的对象。