参考:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/transfer_learning_tutorial.html
以下是两种主要的迁移学习场景
- 微调convnet : 与随机初始化不同,我们使用一个预训练的网络初始化网络,就像在imagenet 1000 dataset上训练的网络一样。其余的训练看起来和往常一样。
- 将ConvNet作为固定的特征提取器 : 在这里,我们将冻结所有网络的权重,除了最后的全连接层。最后一个完全连接的层被替换为一个具有随机权重的新层,并且只训练这个层。
一开始先导入需要的包:
# License: BSD # Author: Sasank Chilamkurthy from __future__ import print_function, division import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim from torch.optim import lr_scheduler import numpy as np import torchvision from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import time import os import copy plt.ion() # 交互模式
1)下载数据
将会使用torchvision和torch.utils.data包去下载数据
今天我们 要解决的问题是建立一个模型去分类蚂蚁和蜜蜂。对于蚂蚁和蜜蜂,我们分别有大约120张训练图片。对于每个类有75张验证图像。通常,如果从零开始训练,这是一个非常小的数据集。由于使用了迁移学习,我们应该能够很好地概括。
这个数据集是imagenet的一个非常小的子集。
⚠️从 here下载数据集,并将其从当前目录中抽取出来
# 为训练对数据进行扩充和规范化,其实就是通过剪切,翻转等方法来扩充数据集的大小 # 验证只进行规范化 data_transforms = { 'train': transforms.Compose([ #将多个transform组合起来使用 transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), #将给定的图片随机切,然后再resize成给定的size=224大小 transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), #图片有一半概率进行翻转,另一半概率不翻转 transforms.ToTensor(), #将图片的像素值[0,255]转成取值范围为[0,1]的tensor transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) #两个参数分别代表均值mean和方差std,有三个值是对应三类像素image=[R,G,B],Normalized_image=(image-mean)/std ]), 'val': transforms.Compose([ transforms.Resize(256), #改变大小 transforms.CenterCrop(224), #进行中心切割,得到给定的size,切出来的图形形状是正方形的 transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) ]), } data_dir = './data/hymenoptera_data' image_datasets = {x: datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join(data_dir, x),data_transforms[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']} dataloaders = {x: torch.utils.data.DataLoader(image_datasets[x], batch_size=4,shuffle=True, num_workers=4) for x in ['train', 'val']} dataset_sizes = {x: len(image_datasets[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']} class_names = image_datasets['train'].classes #如果有CUDA则使用它,否则使用CPU device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
2)可视化一些图像
让我们可视化一些训练图像,以便理解数据扩充。
def imshow(inp, title=None): """Imshow for Tensor.""" inp = inp.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0)) mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]) std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) inp = std * inp + mean inp = np.clip(inp, 0, 1) plt.imshow(inp) if title is not None: plt.title(title) plt.pause(0.001) # 暂停一下,以便更新绘图 # 获得一批训练数据 inputs, classes = next(iter(dataloaders['train'])) # Make a grid from batch out = torchvision.utils.make_grid(inputs) imshow(out, title=[class_names[x] for x in classes])
运行到这里的时候就会显示如下图所示的图像:

3)训练模型
现在,让我们编写一个通用函数来训练模型。在这里,我们将举例说明:
- 调度学习比率
- 保存最佳模型
在下面,变量scheduler是一个来自torch.optim.lr_scheduler的LR调度对象,
def train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, num_epochs=25): since = time.time() best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict()) best_acc = 0.0 for epoch in range(num_epochs): print('Epoch {}/{}'.format(epoch, num_epochs - 1)) print('-' * 10) # 每个周期都有一个训练和验证阶段 for phase in ['train', 'val']: if phase == 'train': scheduler.step() model.train() # 设置模型为训练模式 else: model.eval() # 设置模型为评估模式 running_loss = 0.0 running_corrects = 0 #迭代数据 for inputs, labels in dataloaders[phase]: inputs = inputs.to(device) labels = labels.to(device) # zero the parameter gradients optimizer.zero_grad() # forward # 如果只是在训练要追踪历史 with torch.set_grad_enabled(phase == 'train'): outputs = model(inputs) _, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1) loss = criterion(outputs, labels) # backward + optimize ,仅在训练阶段 if phase == 'train': loss.backward() optimizer.step() # statistics running_loss += loss.item() * inputs.size(0) running_corrects += torch.sum(preds == labels.data) epoch_loss = running_loss / dataset_sizes[phase] epoch_acc = running_corrects.double() / dataset_sizes[phase] print('{} Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format( phase, epoch_loss, epoch_acc)) # 深度拷贝模型 if phase == 'val' and epoch_acc > best_acc: best_acc = epoch_acc best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict()) print() time_elapsed = time.time() - since print('Training complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format( time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60)) print('Best val Acc: {:4f}'.format(best_acc)) # 下载最好的模型权重 model.load_state_dict(best_model_wts) return model
4)可视化模型预测
泛型函数,显示对一些图像的预测
def visualize_model(model, num_images=6): was_training = model.training model.eval() images_so_far = 0 fig = plt.figure() with torch.no_grad(): for i, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(dataloaders['val']): inputs = inputs.to(device) labels = labels.to(device) outputs = model(inputs) _, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1) for j in range(inputs.size()[0]): images_so_far += 1 ax = plt.subplot(num_images//2, 2, images_so_far) ax.axis('off') ax.set_title('predicted: {}'.format(class_names[preds[j]])) imshow(inputs.cpu().data[j]) if images_so_far == num_images: model.train(mode=was_training) return model.train(mode=was_training)
5)
1》微调convent
下载预训练模型并重新设置最后的全连接层
model_ft = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) num_ftrs = model_ft.fc.in_features model_ft.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 2) model_ft = model_ft.to(device) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 观察到所有参数都被优化 optimizer_ft = optim.SGD(model_ft.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9) # 每7个周期,LR衰减0.1倍 exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer_ft, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
2》训练和评估
CPU可能会使用15-25分钟。如果使用的是GPU,将花费少于一分钟
model_ft = train_model(model_ft, criterion, optimizer_ft, exp_lr_scheduler, num_epochs=25)
⚠️使用的python2.7,如果使用的是python3则会报错:
(deeplearning) userdeMBP:neural transfer user$ python neural_style_tutorial.py
2019-03-13 19:30:06.194 python[4926:206321] -[NSApplication _setup:]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x7f8eb4895080
2019-03-13 19:30:06.199 python[4926:206321] *** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '-[NSApplication _setup:]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x7f8eb4895080'
终端运行:(我是在CPU上运行的)
(deeplearning2) userdeMBP:transfer learning user$ python transfer_learning_tutorial.py Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth" to /Users/user/.torch/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth 100.0% Epoch 0/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.5703 Acc: 0.7049 val Loss: 0.2565 Acc: 0.9020 Epoch 1/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.6009 Acc: 0.7951 val Loss: 0.3604 Acc: 0.8627 Epoch 2/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.5190 Acc: 0.7869 val Loss: 0.4421 Acc: 0.8105 Epoch 3/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.5072 Acc: 0.7910 val Loss: 0.4037 Acc: 0.8431 Epoch 4/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.6503 Acc: 0.7869 val Loss: 0.2961 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 5/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3840 Acc: 0.8730 val Loss: 0.2648 Acc: 0.8954 Epoch 6/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.6137 Acc: 0.7705 val Loss: 0.6852 Acc: 0.8170 Epoch 7/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.4130 Acc: 0.8279 val Loss: 0.3730 Acc: 0.8954 Epoch 8/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3953 Acc: 0.8648 val Loss: 0.3300 Acc: 0.9216 Epoch 9/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2753 Acc: 0.8934 val Loss: 0.2949 Acc: 0.9020 Epoch 10/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3192 Acc: 0.8648 val Loss: 0.2984 Acc: 0.9020 Epoch 11/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2942 Acc: 0.8852 val Loss: 0.2624 Acc: 0.9150 Epoch 12/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2738 Acc: 0.8811 val Loss: 0.2855 Acc: 0.9020 Epoch 13/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2697 Acc: 0.8648 val Loss: 0.2675 Acc: 0.9020 Epoch 14/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2534 Acc: 0.9016 val Loss: 0.2780 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 15/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2514 Acc: 0.8811 val Loss: 0.2873 Acc: 0.9020 Epoch 16/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2430 Acc: 0.9098 val Loss: 0.2901 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 17/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2970 Acc: 0.8402 val Loss: 0.2570 Acc: 0.9150 Epoch 18/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2779 Acc: 0.8934 val Loss: 0.2792 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 19/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2271 Acc: 0.9262 val Loss: 0.2655 Acc: 0.9150 Epoch 20/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2741 Acc: 0.8975 val Loss: 0.2726 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 21/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3221 Acc: 0.8320 val Loss: 0.2738 Acc: 0.9150 Epoch 22/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2228 Acc: 0.9139 val Loss: 0.2712 Acc: 0.9020 Epoch 23/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2881 Acc: 0.8975 val Loss: 0.2565 Acc: 0.9150 Epoch 24/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3219 Acc: 0.8648 val Loss: 0.2669 Acc: 0.9150 Training complete in 16m 22s Best val Acc: 0.921569
实现可视化:
visualize_model(model_ft)
第一次返回图像为:

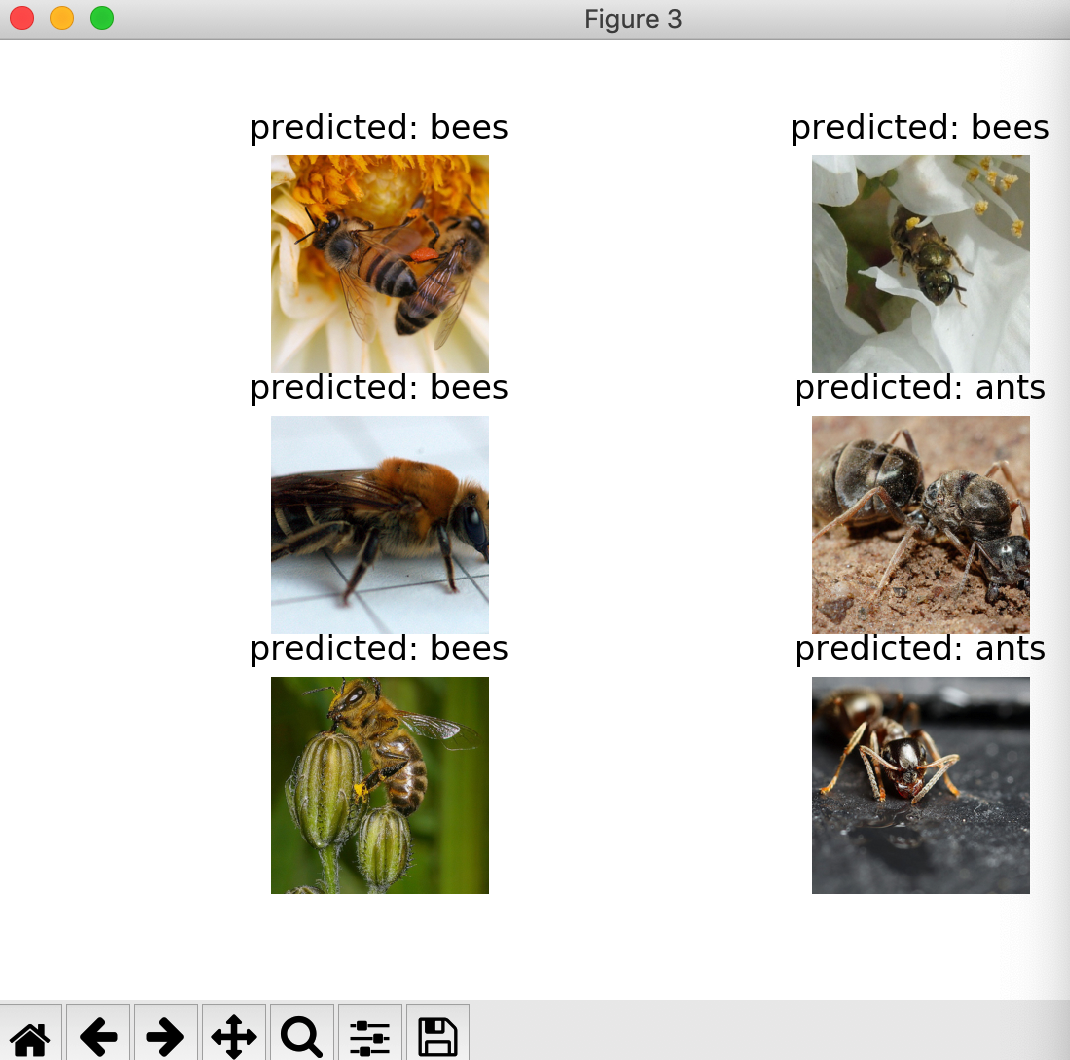
6)
1》将ConvNet作为固定的特征提取器
这里我们需要将除了最后一层的所有网络冻结。我们需要设置requires_grad == False去冻结参数以便梯度在backward()中不会被计算
我们可以从here读取更详细的内容
model_conv = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True) for param in model_conv.parameters(): param.requires_grad = False # 最新构造函数的参数默认设置requires_grad=True num_ftrs = model_conv.fc.in_features model_conv.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs, 2) model_conv = model_conv.to(device) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 观察到与之前相比,只有最后一层的参数被优化 optimizer_conv = optim.SGD(model_conv.fc.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9) # 每7个周期,LR衰减0.1倍 exp_lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer_conv, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
2》训练和评估
在CPU上,与之前的场景相比,这将只花费大约其一半的时间。因为这预期了对于大部分网络梯度不需要计算。当然forward还是需要计算的
model_conv = train_model(model_conv, criterion, optimizer_conv, exp_lr_scheduler, num_epochs=25)
接下来继续训练:(我是在CPU上运行的)
Epoch 0/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.6719 Acc: 0.6516 val Loss: 0.2252 Acc: 0.9281 Epoch 1/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.6582 Acc: 0.7254 val Loss: 0.4919 Acc: 0.7778 Epoch 2/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.5313 Acc: 0.8115 val Loss: 0.2488 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 3/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.5134 Acc: 0.7623 val Loss: 0.1881 Acc: 0.9412 Epoch 4/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3834 Acc: 0.8525 val Loss: 0.2220 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 5/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.5442 Acc: 0.7910 val Loss: 0.2865 Acc: 0.8954 Epoch 6/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.6136 Acc: 0.7213 val Loss: 0.2915 Acc: 0.9085 Epoch 7/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3393 Acc: 0.8730 val Loss: 0.1839 Acc: 0.9542 Epoch 8/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3616 Acc: 0.8156 val Loss: 0.1967 Acc: 0.9346 Epoch 9/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3798 Acc: 0.8402 val Loss: 0.1903 Acc: 0.9542 Epoch 10/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3918 Acc: 0.8320 val Loss: 0.1860 Acc: 0.9477 Epoch 11/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3950 Acc: 0.8115 val Loss: 0.1803 Acc: 0.9542 Epoch 12/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3094 Acc: 0.8566 val Loss: 0.1978 Acc: 0.9542 Epoch 13/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2791 Acc: 0.8811 val Loss: 0.1932 Acc: 0.9542 Epoch 14/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3797 Acc: 0.8484 val Loss: 0.2318 Acc: 0.9346 Epoch 15/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3456 Acc: 0.8689 val Loss: 0.1965 Acc: 0.9412 Epoch 16/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.4585 Acc: 0.7910 val Loss: 0.2264 Acc: 0.9346 Epoch 17/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3889 Acc: 0.8566 val Loss: 0.1847 Acc: 0.9477 Epoch 18/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3636 Acc: 0.8361 val Loss: 0.2680 Acc: 0.9346 Epoch 19/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.2616 Acc: 0.8730 val Loss: 0.1892 Acc: 0.9477 Epoch 20/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3114 Acc: 0.8648 val Loss: 0.2295 Acc: 0.9346 Epoch 21/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3597 Acc: 0.8443 val Loss: 0.1857 Acc: 0.9477 Epoch 22/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3794 Acc: 0.8402 val Loss: 0.1822 Acc: 0.9477 Epoch 23/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3553 Acc: 0.8279 val Loss: 0.1992 Acc: 0.9608 Epoch 24/24 ---------- train Loss: 0.3514 Acc: 0.8238 val Loss: 0.2144 Acc: 0.9346 Training complete in 13m 33s Best val Acc: 0.960784
实现可视化:
visualize_model(model_conv)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
返回图像为: