------------------------------------移动构造------------------------------------------
传统的深拷贝深赋值
对于类中,含有指针的情况,要自实现其拷贝构造和拷贝赋值。也就是所谓的深拷贝和深赋值。我想这己经成为一种共识了。
比如如下类:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class HasPtrMem
{
public:
HasPtrMem():_d(new int(0)){
cout<<"HasPtrMem()"<<this<<endl;
}
HasPtrMem(const HasPtrMem& another)
:_d(new int(*another._d))
{
cout<<"HasPtrMem(const HasPtrMem&
another)"<<this<<"->"<<&another<<endl;
}
~HasPtrMem(){
delete _d;
cout<<"~HasPtrMem()"<<this<<endl;
}
int * _d;
};
HasPtrMem getTemp()
{
return HasPtrMem();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// HasPtrMem a;
// HasPtrMem b(a);
// cout<<*a._d<<endl;
// cout<<*b._d<<endl;
HasPtrMem&& ret = getTemp();
return 0;
}
上面的过程,我们己经知晓,ret 作为右值引用,引用了临时对象,由于临时对象是待返回对象的复本,所以表面上看起来是,待返回对象的作用域扩展了,生命周期也延长了。
从右值引到移动构造
前面我们建立起来了一个概念,就是右值引用。用右值引用的思想,再来实现一下拷贝。这样,顺便把临时对象的问题也解决了。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class HasPtrMem
{
public:
HasPtrMem():_d(new int(0)){
cout<<"HasPtrMem()"<<this<<endl;
}
HasPtrMem(const HasPtrMem& another)
:_d(new int(*another._d)){
cout<<"HasPtrMem(const HasPtrMem& another)" <<this<<"->"<< &another<<endl;
}
HasPtrMem(HasPtrMem &&another)
{
cout<<this<<" Move resourse from "<<&another<<"->"<< another._d <<endl;
_d = another._d;
another._d = nullptr;
}
~HasPtrMem(){
delete _d;
cout<<"~HasPtrMem()"<<this<<endl;
}
int * _d;
};
HasPtrMem getTemp()
{
return HasPtrMem();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
HasPtrMem a = getTemp();
return 0;
}
移动构造
如下是,移动构造函数。我们借用临时变量,将待返回对象的内容“偷”了过来。
移动构造充分体现了右值引用的设计思想,通过移动构造我们也在对象层面看清了右值引用的本质。从而对于普通类型右值引用内部是怎样操作的的也就不难理解了。
//移动构造
HasPtrMem(HasPtrMem &&another)
{
cout<<this<<" Move resourse from "<<&another<<"->"<< another._d<<endl;
_d = another._d;
another._d = nullptr;
}
再来看一下拷贝构造函数,我们对比一下区别:
HasPtrMem(const HasPtrMem& another)
:_d(new int(*another._d)){
cout<<"HasPtrMem(const HasPtrMem& another)" <<this<<"->"<< &another<<endl;
}
移动构造相比于拷贝构造的区别,移动构造通过指针的赋值,在临时对象析构之前,及时的接管了临时对象在堆上的空间地址。
关于默认的移动构造函数
对于不含有资源的对象来说,自实现拷贝与移动语义并没有意义,对于这样的类型 而言移动就是拷贝,拷贝就是移动。
拷贝构造/赋值和移动构造/赋值,必须同时提供或是同时不提供。才能保证同时俱有拷贝和移动语义。只声明一种的话,类只能实现一种语义。
只有拷贝语义的类,也就是 C++98 中的类。而只有移动语义的类,表明该类的变量所拥有的资源只能被移动,而不能被拷贝。那么这样的资源必须是唯一的。只有移动语义构造的类型往往是“资源型”的类型。比如智能指针,文件流等。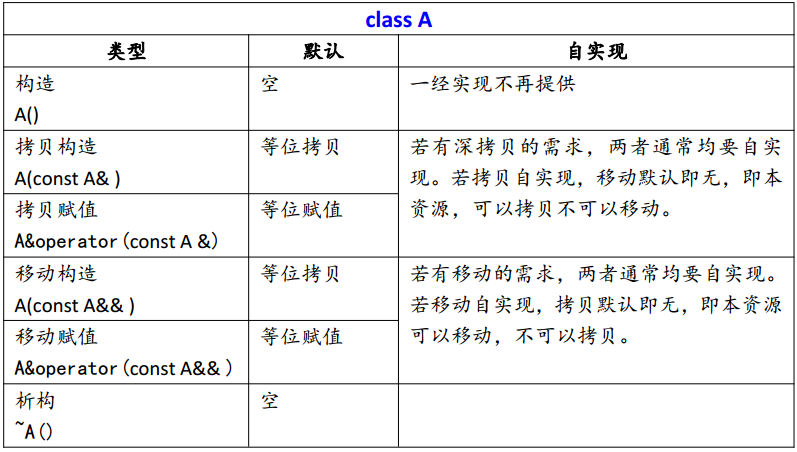
效率问题
#include <iostream>
using namesapce std;
class Copyable
{
public:
Copyable(int i)
:_i(new int(i))
{
cout<<"Copyable(int i):"<<this<<endl;
}
Copyable(const Copyable & another)
:_i(new int(*another._i))
{
cout<<"Copyable(const Copyable & another):"<<this<<endl;
}
Copyable(Copyable && another)
{
cout<<"Copyable(Copyable && another):"<<this<<endl;
_i = another._i;
}
Copyable & operator=(const Copyable &another)
{
cout<<"Copyable & operator=(const Copyable &another):"<<this<<endl;
if(this == & another)
return *this;
*_i=*another._i;
return *this;
}
Copyable & operator=(Copyable && another)
{
cout<<"Moveable & operator=(Moveable && another):"<<this<<endl;
if(this != &another)
{
*_i = *another._i;
another._i = NULL;
}
return * this;
}
~Copyable()
{
cout<<"~Copyable():"<<this<<endl;
if(_i)
delete _i;
}
void dis()
{
cout<<"class Copyable is called"<<endl;
}
void dis() const
{
cout<<"const class Copyable is called"<<endl;
}
private:
int * _i;
};
void putRRValue(Copyable && a)
{
cout<<"putRRValue(Copyable && a)"<<endl;
a.dis();
}
void putCLValue(const Copyable & a)
{
cout<<"putCRValue(Copyable & a)"<<endl;
a.dis();//error!
}
//const T&和T&&重载同时存在先调用谁?
void whichCall(const Copyable & a)
{
a.dis();
}
void whichCall(Copyable && a)
{
a.dis();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// Copyable rrc = getCopyable();
cout<<"调用移动构造"<<endl;
Copyable a =Copyable(2);//匿名对象/临时对象优先调用右值引用 构造-右值构造
cout<<"调拷贝构造"<<endl;
Copyable ca(a);
cout<<"直接构造右值"<<endl;
Copyable && rra =Copyable(2);
cout<<"=================================="<<endl;
//右值引用与const引用。 效率是否一样?
cout<<"右值引用传参"<<endl;
putRRValue(Copyable(2));
cout<<"Const 引用传参"<<endl;
putCLValue(Copyable(2));
cout<<"----------------------"<<endl;
//优先调用哪种重载? T&& 还是 const T&?
whichCall(Copyable(2));
//这个没什么好纠结的!T&&的出现就是了解决 const T &接受匿名/临时对象后,不能调用非cosnt函数的问题。
return 0;
}
在接收一个右值的情况下,T&& 与 const T& 在效率别无二致,关键的是,T&&满足了我们non-const对象的使用情况。
--------------------------------------------------移动构造-----------------------------------------------
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Copyable
{
public:
Copyable(int i)
:_i(new int(i))
{
cout<<"Copyable(int i):"<<this<<endl;
}
Copyable(const Copyable & another)
:_i(new int(*another._i))
{
cout<<"Copyable(const Copyable & another):"<<this<<endl;
}
Copyable(Copyable && another)
{
cout<<"Copyable(Copyable && another):"<<this<<endl;
_i = another._i;
}
Copyable & operator=(const Copyable &another)
{
cout<<"Copyable & operator=(const Copyable &another):"<<this<<endl;
if(this == & another)
return *this;
*_i=*another._i;
return *this;
}
Copyable & operator=(Copyable && another)
{
cout<<"Moveable & operator=(Moveable && another):"<<this<<endl;
if(this != &another)
{
delete _i;
_i = another._i;
}
return * this;
}
~Copyable()
{
cout<<"~Copyable():"<<this<<endl;
if(_i)
delete _i;
}
void dis()
{
cout<<"class Copyable is called"<<endl;
}
void dis() const
{
cout<<"const class Copyable is called"<<endl;
}
int * _i;
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Copyable a(1);
Copyable b(2);
cout<<"-----copyassin start------"<<endl;
a = b; //拷贝赋值
cout<<"-----moveassin start------"<<endl;
a = Copyable(3); //移动赋值
getchar();
return 0;
}
移动赋值,拷贝赋值的区分,前者是在两个对象都存在的情况下,一个给另一个赋值。后者是拿一个即将构造的对象给一个已存在的对象赋值。
效率问题:移动赋值也是将一个将亡值的资源直接接管了过来,无需再去申请新的内存。尤其是对象中所含堆上资源比较大的情况下,在效率上的体现是非常高的。
移动构造,移动赋值,是有极高效率的。右值引用的价值也体现在这里。主题的思想是把把将亡值的资源接管过来。而不用自己去申请空空间。
------------------------------------模板函数std::move----------------------------
虽然不能将一个右值引用直接绑定到左值上,但是我们可以显式的将一个左值转换为对应的右值引用类型。我们还可以通过调用一个名为move的新标准库函数来获得绑定到左值上的右值引用,此函数定义在untility中。move函数使用了**机制来返回给定对象的右值引用。
int &&rra = rr1; //error: //! error!右值引用不能直接绑定到左值
int &&rr = std::move(rr1); // ok!
move调用告诉编译器:我们有一个左值,但是我们希望像处理一个右值一样去处理他。
调用move就意味着承诺:除了对rr1赋值或者销毁它之外,我们将不能再使用它。在调用move之后,我们不能对移动后的源对象值做任何的假设。