1.题目
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于位于数组的后半部分。
2.思路
本题有两种解法,一种是不保证数组稳定性的解法,一种是保证数组稳定性的解法。数组的稳定性是指数组的奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。
- 不要求稳定性的解法:
两个指针,p指向第一个元素,q指向最后一个元素。两个指针遍历数组,向后移动p使得p指向偶数,向前移动q使得q指向奇数,交换p和q的内容。指针p位于指针q后面时,结束遍历。举例:12345->15342。
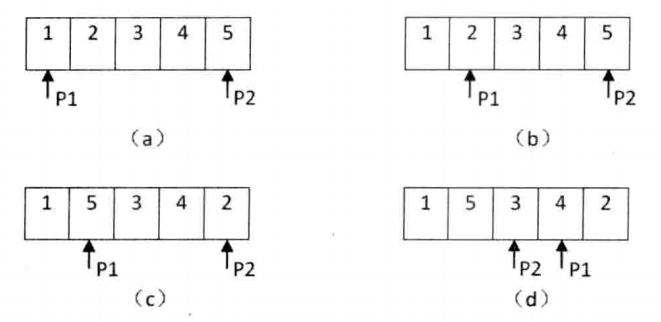
- 要求稳定性的解法:
借鉴冒泡排序思想,每次确定一个位置。
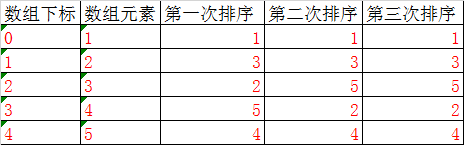
3.code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 稳定的解法
class Solution_stable{
public:
void ReArray(vector<int > &array)
{
// 特殊输入
if(array.size() == 0 || array.size() == 1)
return;
// 冒泡排序
for(int i = 0;i < array.size();++i)
for(int j = array.size()-1;j>i;--j)
if(array[j]%2 == 1 && array[j-1]%2 ==0)
swap(array[j],array[j-1]);
}
};
// 不稳定的解法
class Solution_no_stable{
public:
void ReArray(int *array2,int length)
{
// 特殊输入
if(array2 == nullptr || length == 0)
return;
// 指针遍历数组
int *pLeft = array2;
int *pRight = array2 + length-1;
while(pLeft<pRight)
{
// 向后移动pLeft,直到指向偶数
while(pLeft<pRight && *pLeft %2 == 1)
pLeft++;
// 向前移动pRight,直到指向奇数
while(pLeft<pRight && *pRight %2 == 0)
pRight--;
// 奇偶数交换
if(pLeft < pRight)
swap(*pLeft,*pRight);
}
}
};
int main()
{
// 稳定的解法
cout<<"稳定的解法"<<endl;
Solution_stable solution1;
vector<int> array = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
solution1.ReArray(array);
for(int i = 0;i<array.size();++i)
cout<<array[i]<<endl;
// 不稳定的解法
cout<<"不稳定的解法"<<endl;
Solution_no_stable solution2;
int length = 10;
int array2[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
solution2.ReArray(array2,length);
for(int i = 0;i<length;i++)
cout<<array2[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}
4.复杂度
时间复杂度为O(n2)
5.测试用例
- 特殊输入:空数组、含一个元素的数组
- 功能测试:奇偶交替、全部偶数在全部奇数之前、全部奇数在全部偶数之前