本次和大家分享的是在springboot集成使用redis,这里使用的是redis的jedis客户端(这里我docker运行的redis,可以参考 docker快速搭建几个常用的第三方服务),如下添加依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> </dependency>
然后需要redis的相关配置(这里我的redis密码是空),在application.yml设置如:
spring: redis: single: 192.168.146.28:6378 jedis: pool: max-idle: 8 max-active: 8 max-wait: 3000 timeout: 3000 password:
这是redis的一般配置,具体调优可以设置这些参数,下面在JedisConfig类中读取这些设置:
1 @Value("${spring.redis.single}") 2 private String strSingleNode; 3 4 @Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle}") 5 private Integer maxIdle; 6 7 @Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active}") 8 private Integer maxActive; 9 10 @Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait}") 11 private Integer maxAWait; 12 13 @Value("${spring.redis.timeout}") 14 private Integer timeout; 15 16 @Value("${spring.redis.password}") 17 private String password;
有上面的配置,就需要有代码里面设置下,这里创建一个返回JedisPoolConfig的方法
1 /** 2 * jedis配置 3 * 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public JedisPoolConfig getJedisPoolConfig() { 7 JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig(); 8 config.setMaxIdle(maxIdle); #最大空闲数 9 config.setMaxWaitMillis(maxAWait); #最大等待时间 10 config.setMaxTotal(maxActive); #最大连接数 11 return config; 12 }
有了配置,接下来就创建JedisPool,这里把JedisPool托管到spring中
1 /** 2 * 获取jedispool 3 * 4 * @return 5 */ 6 @Bean 7 public JedisPool getJedisPool() { 8 JedisPoolConfig config = getJedisPoolConfig(); 9 System.out.println("strSingleNode:" + this.strSingleNode); 10 String[] nodeArr = this.strSingleNode.split(":"); 11 12 JedisPool jedisPool = null; 13 if (this.password.isEmpty()) { 14 jedisPool = new JedisPool( 15 config, 16 nodeArr[0], 17 Integer.valueOf(nodeArr[1]), 18 this.timeout); 19 } else { 20 jedisPool = new JedisPool( 21 config, 22 nodeArr[0], 23 Integer.valueOf(nodeArr[1]), 24 this.timeout, 25 this.password); 26 } 27 return jedisPool; 28 }
上面简单区分了无密码的情况,到此jedis的配置和连接池就基本搭建完了,下面就是封装使用的方法,这里以set和get为例;首先创建个JedisComponent组件,代码如下:
/** * Created by Administrator on 2018/8/18. */ @Component public class JedisComponent { @Autowired JedisPool jedisPool; public boolean set(String key, String val) { Jedis jedis = null; try { jedis = jedisPool.getResource(); return jedis.set(key, val).equalsIgnoreCase("OK"); } finally { if (jedis != null) { jedis.close(); } } } public <T> boolean set(String key, T t) { String strJson = JacksonConvert.serilize(t); if (strJson.isEmpty()) { return false; } return this.set(key, strJson); } public String get(String key) { Jedis jedis = null; try { jedis = jedisPool.getResource(); return jedis.get(key); } finally { if (jedis != null) { jedis.close(); } } } public <T> T get(String key, Class<T> tClass) { String strJson = this.get(key); return JacksonConvert.deserilize(strJson, tClass); } }
有了对jedis的调用封装,我们在Controller层的测试用例如下:
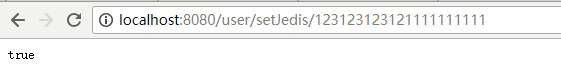
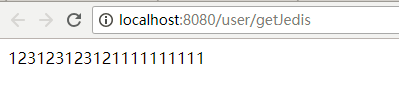
1 @Autowired 2 JedisComponent jedis; 3 4 @GetMapping("/setJedis/{val}") 5 public boolean setJedis(@PathVariable String val) { 6 return jedis.set("token", val); 7 } 8 9 @GetMapping("/getJedis") 10 public String getJedis() { 11 return jedis.get("token"); 12 }
运行set和get的接口效果如: