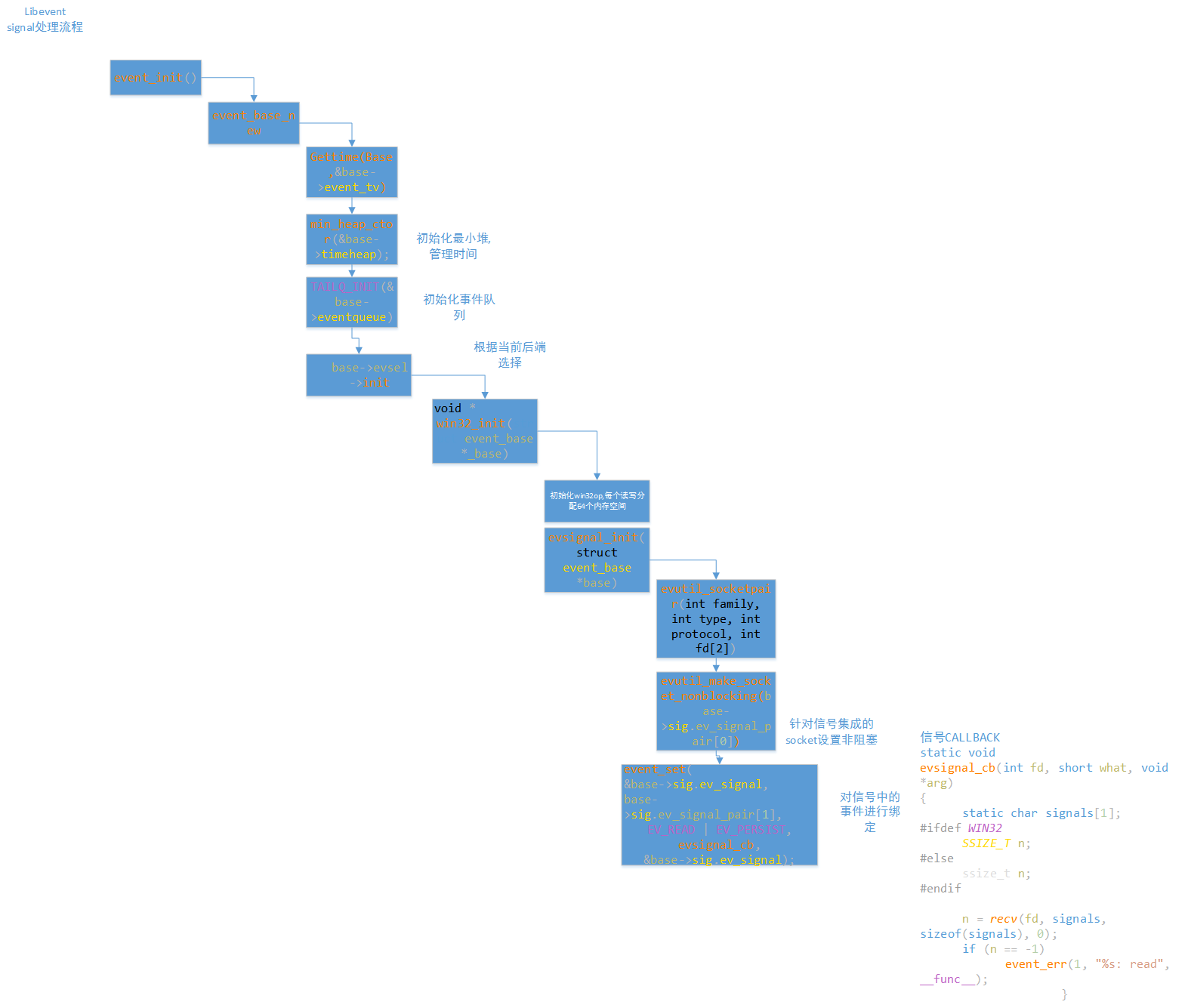
现在已经知道,libevent有三种事件类型,分别是时钟事件,信号事件,i/o事件。今天就分析一下信号事件,下面是一个简单的信号事件demo
#include <sys/types.h>
#ifdef HAVE_CONFIG_H
#include "config.h"
#endif
#include <sys/stat.h>
#ifndef WIN32
#include <sys/queue.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#else
#include <windows.h>
#endif
#include <signal.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <event.h>
int called = 0;
static void
signal_cb(int fd, short event, void *arg)
{
struct event *signal = arg;
printf("%s: got signal %d\n", __func__, EVENT_SIGNAL(signal));
if (called >= 2)
event_del(signal);
called++;
}
int
main (int argc, char **argv)
{
struct event signal_int;
/* Initalize the event library */
struct event_base* base = event_base_new();
/* Initalize one event */
event_set(&signal_int, SIGINT, EV_SIGNAL|EV_PERSIST, signal_cb,
&signal_int);
event_base_set(base, &signal_int);
event_add(&signal_int, NULL);
event_base_dispatch(base);
event_base_free(base);
return (0);
}
从代码看,这里event_set第二个参数是一个中断类型的信号(ctrl+c可触发),第三个参数代表这是一个信号事件并长存
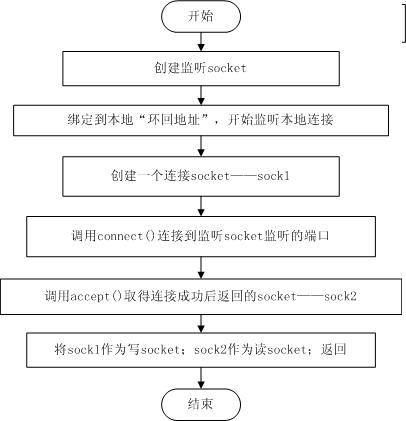
event_base_new中会调用base->evsel->init(这里先不放代码,末尾会放流程图),而这个函数会根据当前后端选择初始化函数,这里是win32_init,最终调用 evutil_socketpair(int family, int type, int protocol, int fd[2]),这个函数中用 tcp-socket将 两个socket句柄绑定到fd数组上
具体代码如下
int evutil_socketpair(int family, int type, int protocol, int fd[2]) { #ifndef WIN32 return socketpair(family, type, protocol, fd); #else /* This code is originally from Tor. Used with permission. */ /* This socketpair does not work when localhost is down. So * it's really not the same thing at all. But it's close enough * for now, and really, when localhost is down sometimes, we * have other problems too. */ int listener = -1; int connector = -1; int acceptor = -1; struct sockaddr_in listen_addr; struct sockaddr_in connect_addr; int size; int saved_errno = -1; if (protocol #ifdef AF_UNIX || family != AF_UNIX #endif ) { EVUTIL_SET_SOCKET_ERROR(WSAEAFNOSUPPORT); return -1; } if (!fd) { EVUTIL_SET_SOCKET_ERROR(WSAEINVAL); return -1; } listener = socket(AF_INET, type, 0); if (listener < 0) return -1; memset(&listen_addr, 0, sizeof(listen_addr)); listen_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; listen_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_LOOPBACK); listen_addr.sin_port = 0; /* kernel chooses port. */ if (bind(listener, (struct sockaddr *) &listen_addr, sizeof (listen_addr)) == -1) goto tidy_up_and_fail; if (listen(listener, 1) == -1) goto tidy_up_and_fail; connector = socket(AF_INET, type, 0); if (connector < 0) goto tidy_up_and_fail; /* We want to find out the port number to connect to. */ size = sizeof(connect_addr); if (getsockname(listener, (struct sockaddr *) &connect_addr, &size) == -1) goto tidy_up_and_fail; if (size != sizeof (connect_addr)) goto abort_tidy_up_and_fail; if (connect(connector, (struct sockaddr *) &connect_addr, sizeof(connect_addr)) == -1) goto tidy_up_and_fail; size = sizeof(listen_addr); acceptor = accept(listener, (struct sockaddr *) &listen_addr, &size); if (acceptor < 0) goto tidy_up_and_fail; if (size != sizeof(listen_addr)) goto abort_tidy_up_and_fail; EVUTIL_CLOSESOCKET(listener); /* Now check we are talking to ourself by matching port and host on the two sockets. */ if (getsockname(connector, (struct sockaddr *) &connect_addr, &size) == -1) goto tidy_up_and_fail; if (size != sizeof (connect_addr) || listen_addr.sin_family != connect_addr.sin_family || listen_addr.sin_addr.s_addr != connect_addr.sin_addr.s_addr || listen_addr.sin_port != connect_addr.sin_port) goto abort_tidy_up_and_fail; fd[0] = connector; fd[1] = acceptor; return 0; abort_tidy_up_and_fail: saved_errno = WSAECONNABORTED; tidy_up_and_fail: if (saved_errno < 0) saved_errno = WSAGetLastError(); if (listener != -1) EVUTIL_CLOSESOCKET(listener); if (connector != -1) EVUTIL_CLOSESOCKET(connector); if (acceptor != -1) EVUTIL_CLOSESOCKET(acceptor); EVUTIL_SET_SOCKET_ERROR(saved_errno); return -1; #endif }
//下面另一篇再写 event_add的代码如下
1 int 2 event_add(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv) 3 { 4 struct event_base *base = ev->ev_base; 5 const struct eventop *evsel = base->evsel; 6 void *evbase = base->evbase; 7 int res = 0; 8 9 event_debug(( 10 "event_add: event: %p, %s%s%scall %p", 11 ev, 12 ev->ev_events & EV_READ ? "EV_READ " : " ", 13 ev->ev_events & EV_WRITE ? "EV_WRITE " : " ", 14 tv ? "EV_TIMEOUT " : " ", 15 ev->ev_callback)); 16 17 assert(!(ev->ev_flags & ~EVLIST_ALL)); 18 19 /* 20 * prepare for timeout insertion further below, if we get a 21 * failure on any step, we should not change any state. 22 */ 23 if (tv != NULL && !(ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_TIMEOUT)) 24 { 25 if (min_heap_reserve(&base->timeheap, 26 1 + min_heap_size(&base->timeheap)) == -1) 27 return (-1); /* ENOMEM == errno */ 28 } 29 30 if ((ev->ev_events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE|EV_SIGNAL)) && 31 !(ev->ev_flags & (EVLIST_INSERTED|EVLIST_ACTIVE))) { 32 res = evsel->add(evbase, ev); 33 if (res != -1) 34 event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_INSERTED); 35 } 36 37 /* 38 * we should change the timout state only if the previous event 39 * addition succeeded. 40 */ 41 if (res != -1 && tv != NULL) { 42 struct timeval now; 43 44 /* 45 * we already reserved memory above for the case where we 46 * are not replacing an exisiting timeout. 47 */ 48 if (ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_TIMEOUT) 49 event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT); 50 51 /* Check if it is active due to a timeout. Rescheduling 52 * this timeout before the callback can be executed 53 * removes it from the active list. */ 54 if ((ev->ev_flags & EVLIST_ACTIVE) && 55 (ev->ev_res & EV_TIMEOUT)) { 56 /* See if we are just active executing this 57 * event in a loop 58 */ 59 if (ev->ev_ncalls && ev->ev_pncalls) { 60 /* Abort loop */ 61 *ev->ev_pncalls = 0; 62 } 63 64 event_queue_remove(base, ev, EVLIST_ACTIVE); 65 } 66 67 gettime(base, &now); 68 evutil_timeradd(&now, tv, &ev->ev_timeout); 69 70 event_debug(( 71 "event_add: timeout in %ld seconds, call %p", 72 tv->tv_sec, ev->ev_callback)); 73 74 event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT); 75 } 76 77 return (res); 78 }
第五行,代表的是当前系统所支持的后端模式,base->evsel和base->evbase先不要纠结,都是用在一个地方
第23行关于最小堆的逻辑先跳过
第30行,当事件ev不在已注册或者激活链表中,则调用evbase注册事件,这里的ev_events,ev_flags分别代表event关注的事件类型与当前的状态
ev_events有四种类型
I/O事件: EV_WRITE和EV_READ
定时事件:EV_TIMEOUT
信号: EV_SIGNAL
辅助选项:EV_PERSIST,表明是一个永久事件
ev_flags有以下几种状态
#define EVLIST_TIMEOUT 0x01 // event在time堆中 #define EVLIST_INSERTED 0x02 // event在已注册事件链表中 #define EVLIST_SIGNAL 0x04 // 未见使用 #define EVLIST_ACTIVE 0x08 // event在激活链表中 #define EVLIST_INTERNAL 0x10 // 内部使用标记 #define EVLIST_INIT 0x80 // event已被初始化
重点分析一下res = evsel->add(evbase, ev);我所在为win32平台,实际调用的是int win32_insert(void *op, struct event *ev)
1 int 2 win32_insert(void *op, struct event *ev) 3 { 4 struct win32op *win32op = op; 5 struct event_entry *ent; 6 7 if (ev->ev_events & EV_SIGNAL) { 8 if (win32op->signals_are_broken) 9 return (-1); 10 return (evsignal_add(ev)); 11 } 12 if (!(ev->ev_events & (EV_READ|EV_WRITE))) 13 return (0); 14 ent = get_event_entry(win32op, ev->ev_fd, 1); 15 if (!ent) 16 return (-1); /* out of memory */ 17 18 event_debug(("%s: adding event for %d", __func__, (int)ev->ev_fd)); 19 if (ev->ev_events & EV_READ) { 20 if (do_fd_set(win32op, ent, 1)<0) 21 return (-1); 22 ent->read_event = ev; 23 } 24 if (ev->ev_events & EV_WRITE) { 25 if (do_fd_set(win32op, ent, 0)<0) 26 return (-1); 27 ent->write_event = ev; 28 } 29 return (0); 30 }