普通使用:
在没有用测试框架之前,我们要用一个main方法来跑代码,而有了像junit这样的测试框架后,就可以不用次次写个main方法了。
直接上代码,注释里有说明:
package com.stuPayment; import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.AfterClass; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.BeforeClass; import org.junit.Ignore; import org.junit.Test; /** * 简单地演示了junit的基本用法 * @author 85060 * */ public class MyTest { private static NumberTest numberTest = null; public void get3(NumberTest num) { num.a = num.a*num.a*num.a; } public void get2(NumberTest num) { num.a = num.a*num.a; } @Ignore //这个注释下的方法是会被忽略暂时不会运行的 public void ignoreMethod() { System.out.println("i am ingnored"); } @Before //这个注释是在每个测试方法之前都会跑的,也就是每个@Test的方法跑之前 public void sayBefore() { System.out.println("hello i am the before"); } @After //这个注释是在每个测试方法之后都会跑的,也就是每个@Test的方法跑之后 public void sayAfter() { System.out.println("hello i am the after"); } @BeforeClass //这个注释是在整个测试开始前会跑的 public static void befC() { System.out.println("hello i am the before class"); numberTest = new NumberTest(3); } @AfterClass //这个注释是在整个测试结束后会跑的 public static void aftC() { System.out.println("hello i am the after class and the a is "+numberTest.a+" now"); } @Test public void test1() { System.out.println("i am the test1"); get2(numberTest); assertEquals(9, numberTest.a); } @Test public void test2() { System.out.println("i am the test2"); /*if(numberTest.a == 3) { } else if(numberTest.a == 9)*/ get3(numberTest); assertEquals(729, numberTest.a); } } class NumberTest { int a; public NumberTest(int a) { this.a = a; } }
运行的方法就直接run as Junit Test,运行结果:

在Springboot中使用junit:
这里只是提供一个简单的测试例子,可以用来单独测试service或者是你的dao接口。
关于@Runwiht:
@RunWith
在JUnit中有很多个Runner,他们负责调用你的测试代码,每一个Runner都有各自的特殊功能,你要根据需要选择不同的Runner来运行你的测试代码。
如果我们只是简单的做普通Java测试,不涉及Spring Web项目,你可以省略@RunWith注解,这样系统会自动使用默认Runner来运行你的代码。
也是直接上代码,注释里面有说明:
package com.stuPayment; import static org.junit.Assert.assertArrayEquals; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import com.stuPayment.dao.LoginMapper; import com.stuPayment.entiy.User; /** * 演示了springboot环境下的junit测试 * @author 85060 * */ @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) // SpringJUnit支持,由此引入Spring-Test框架支持! @SpringBootTest //提供spring环境 public class MyTest2 { @Autowired private LoginMapper loginMapper; @Test public void testVoid() { Map<String, Object> user = new HashMap<>(); user.put("userAccount", "123"); user.put("userPassword", "123"); List<User> userList = loginMapper.getThisUser(user); assertArrayEquals( new Object[]{ userList.isEmpty() }, new Object[]{ false } ); } }
junit的参数化测试:
其实就是,当有一个方法,要用多组参数来验证其正确性,这个时候你就可以考虑用这个@RunWith(Parameterized.class)注解
上代码,代码里面有注解解释:
package com.stuPayment; import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.junit.runners.Parameterized; import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters; /** * 演示一下参数测试 * @author 85060 * */ @RunWith(Parameterized.class) //一定要用这个注解 public class MyTest3 { private String name; private boolean result; /** * 在参数测试中只能有一个构造方法,因为参数测试是需要一个构造方法参与的 * 这个构造方法的参数和等一下@Parameters注解的方法中的Object数组中值的顺序对应 * @param name * @param result */ public MyTest3(String name, boolean result) { this.name = name; this.result = result; } /** * 必须提供@Parameters方法,方法签名必须是public static Collection,不能有参数, * 并且collection元素必须是相同长度的数组。 * 同事数组的长度必须与唯一的公共构造函数的参数数量相匹配。 */ @Parameters public static Collection<?> data() { return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{ {"jflksadjflkasdlkfj",false}, {"mikjsdkalfjlksdjfmifjaslkdjf",true}, {"mimimimisdfsadfsd",true} });//意思其实就是拿这些数据去用MyTest3(String name, boolean result)一直new } @Test //真正测试也就是跑的那个方法,用@parameters方法返回的那些参数每组都用MyTest3(String name, bolean result) //然后再跑下面这个方法。 public void test() { assertTrue(name.contains("mi") == result);//看看每个用上面那些数据new的实例是否符合要求 } }
测试结果的效果:
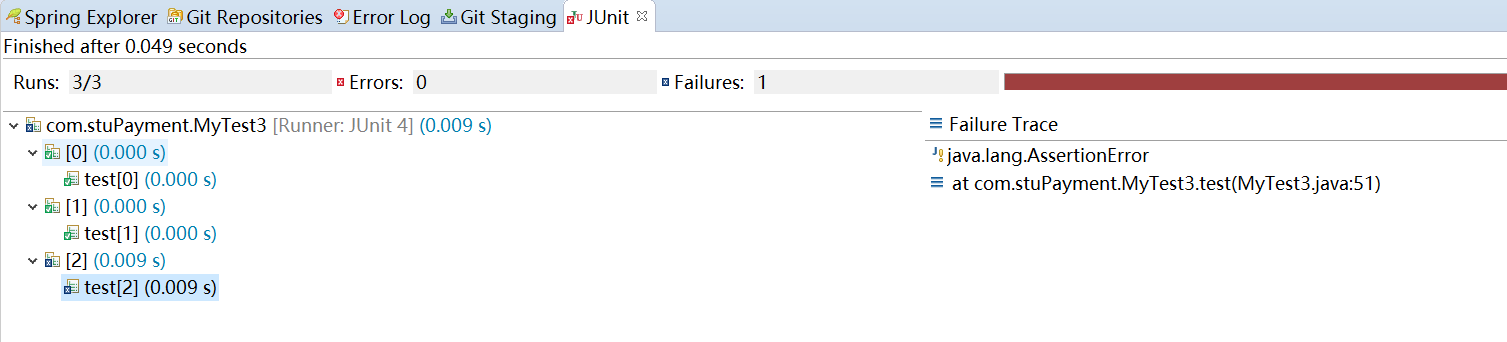
可以看到,如果有错的话会有蓝色的叉叉,然后点击这个错误,在failure trace那可以看到简单的错误说明。