一 闭包函数
内函数使用了外函数的局部变量,并且外函数把内函数返回出来的过程叫做闭包,这个内函数叫做闭包函数
1.1 闭包函数语法
def outer():
a = 5
def inner():
print(a)
return inner
对比正常的局部变量
局部变量的生命周期最短,在调用结束之后,立即释放.
def func():
a = 5
print(a)
func()
print(a)
执行
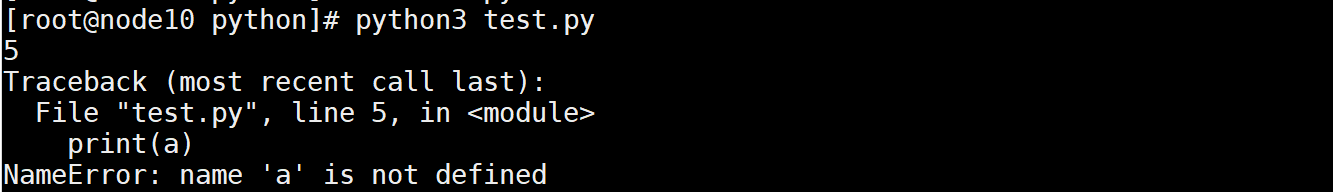
1.2 闭包函数的定义
def bibao():
people = "孙仲谋"
def caocao_say():
print("生子当如%s" % (people))
return caocao_say
func = bibao()
# func = caocao_say
func()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 生子当如孙仲谋
1.3 闭包函数的特点(升级)
- 内函数使用了外函数的局部变量,外函数的局部变量与内函数发生绑定,延长该变量的生命周期(实际内存给它存储了这个值,暂时不释放)
示例
def grade(str1):
def func_in(str2):
print(str1+str2)
return func_in
a=grade('小李:')
a('语文:118')
b=grade('小红:')
b('语文:109')
b('数学:98')
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 小李:语文:118 小红:语文:109 小红:数学:98
示例2
def family():
jiejie = "小红"
meimei = "小明"
money = 100
def jiejie_hobby():
nonlocal money
money -=40
print("姐姐%s喜欢买零食,买了辣条钱还剩下%s" % (jiejie,money))
return money
def meimei_hobby():
nonlocal money
money -= 30
print("妹妹%s喜欢买衣服,还剩下%s" % (meimei,money))
return money
def big_manager():
return (jiejie_hobby,meimei_hobby)
return big_manager
func = family()
# func = big_manager
print(func,type(func))
# func() = big_manager()
tup = func()
print(tup,type(tup))
# 调用姐姐
# jiejie = tup[0]
# jiejie()
res1 = tup[0]()
print(res1)
# 调用妹妹
# meimei = tup[1]
# meimei()
res2 = tup[1]()
print(res2)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py <function family.<locals>.big_manager at 0x7fee9c4f21e0> <class 'function'> (<function family.<locals>.jiejie_hobby at 0x7fee9c4f20d0>, <function family.<locals>.meimei_hobby at 0x7fee9c4f2158>) <class 'tuple'> 姐姐小红喜欢买零食,买了辣条钱还剩下60 60 妹妹小明喜欢买衣服,还剩下30 30
示例3
def outer(val):
def inner(num):
return val + num
return inner
func = outer(10)
# func = inner
res = func(5)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 15
过程
func = outer(10)
val 形参接收到实参值10
因为内函数使用了外函数的局部变量val,val与内函数发生绑定,延长val的生命周期
res = func(5)
num 形参接收到实参值5
return 10 + 5 => return 15 返回到函数的调用处
func(5) 是调用处 所以
res = 15
1.4 获取闭包函数使用的变量
闭包函数.__closure__ 返回单元cell , cell 里面存的是对应的绑定变量 res = func.__closure__ # 获取到一个元组 res = res[0].cell_contents # res[0] 获取元组当中的第一个值 是一个cell单元 通过单元.cell_contents来获取其中的值,就会知道绑定的变量是谁了. cell_contents是一个属性 print(res,type(res)) # print(res.cell_content) # (<cell at 0x000001D6DAE17708: int object at 0x000000005EC26D30>,)
示例
def outer(val):
def inner(num):
return val + num
return inner
func = outer(10)
# func = inner
res = func(5)
print(res)
print(func.__closure__)
print(func.__closure__,type(func.__closure__))
res = func.__closure__[0]
print(res,type(res))
res = func.__closure__[0].cell_contents
print(res,type(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 15 (<cell at 0x7fe07763b7f8: int object at 0x7fe07750c7e0>,) (<cell at 0x7fe07763b7f8: int object at 0x7fe07750c7e0>,) <class 'tuple'> <cell at 0x7fe07763b7f8: int object at 0x7fe07750c7e0> <class 'cell'> 10 <class 'int'>
1.5 闭包的意义
- 闭包可以优先使用外函数中的变量,并对闭包中的值起到了封装保护的作用.外部无法访问.
模拟鼠标点击次数
num = 0
def click():
global num
num += 1
return num
res = click()
res = click()
res = click()
# num = 100 恶意串改,我们获取的值就会出现错误
res = click()
res = click()
print(res)
使用闭包函数重写鼠标点击次数
def click():
x = 0
def func():
nonlocal x
x+=1
return x
return func
click = click()
res = click()
res = click()
res = click()
x = 100 #恶意修改,但是不影响结果
res = click()
res = click()
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 5
二 locals 和 globals
2.1 locals()
返回字典,获取当前作用域的所有内容
- 如果在函数里:获取locals()调用之前,该作用域出现的内容
- 如果在函数外:获取locals()打印返回值之前,该作用域出现的内容
a = 1 b = 2 print(locals())
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'__name__': '__main__',
'__doc__': None, 如果在函数里:获取locals()调用之前,该作用域出现的内容
如果在函数外:获取locals()打印返回值之前,该作用域出现的内容
',
'__package__': None,
'__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x7ffa9ddb7208>,
'__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {},
'__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>,
'__file__': 'test.py',
'__cached__': None,
'a': 1,
'b': 2,
'func': <function func at 0x7ffa9de8ae18>, #全局中又这个函数,但是函数内部的局部变量不能获取
'res': {...},
'c': 3}
所在作用域是局部命名空间,获取locals() 调用之前所出现的所有局部命名空间内容
c=3
d = 4
def func():
a = 1
b = 2
res = locals()
c = 3
print(res)
f = 5
func()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'b': 2, 'a': 1}
2.2 globals()
返回字典,获取全局作用域的所有内容
- 如果在函数里: 获取globals()调用之前,全局作用域出现的内容
- 如果在函数外: 获取globals()打印返回值之前,全局作用域出现的内容
globals在全局作用域中,只获取globals 打印返回值之前的所有全局空间的内容
a = 1 b = 2 res = globals() print(res) c = 3
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'__name__': '__main__',
'__doc__': None,
'__package__': None,
'__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x7fcd746f5208>,
'__spec__': None,
'__annotations__': {},
'__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>,
'__file__': 'test.py',
'__cached__': None,
'a': 1,
'b': 2,
'res': {...}}
globals在局部作用域中,也仍然获取全局空间的所有内容,但是是在globals,打印返回值之前的所有.
c = 13
d = 14
def func():
a = 11
b = 12
res = globals()
print(res)
f = 19
func()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'__name__': '__main__',
'__doc__': None,
'__package__': None,
'__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x7f16a5144208>,
'__spec__': None,
'__annotations__': {},
'__builtins__': <module
'builtins' (built-in)>,
'__file__': 'test.py',
'__cached__': None,
'c': 13,
'd': 14,
'func': <function func at 0x7f16a5217e18>,
'f': 19}
只获取全局,没有ab的值
动态创建全局变量 利用globals
- globals 返回的是一个系统的全局字典,键是变量名,值是该标量所指向的值
dic = globals()
dic['hero'] = "风流倜傥,高大威猛,威武帅气,万人迷"
print(hero)
# 动态创建5个全局变量p1~p5
def func():
for i in range(1,6):
dic["p%d" % (i)] = i
func()
print(p1)
print(p2)
print(p3)
print(p4)
print(p5)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 风流倜傥,高大威猛,威武帅气,万人迷 1 2 3 4 5
