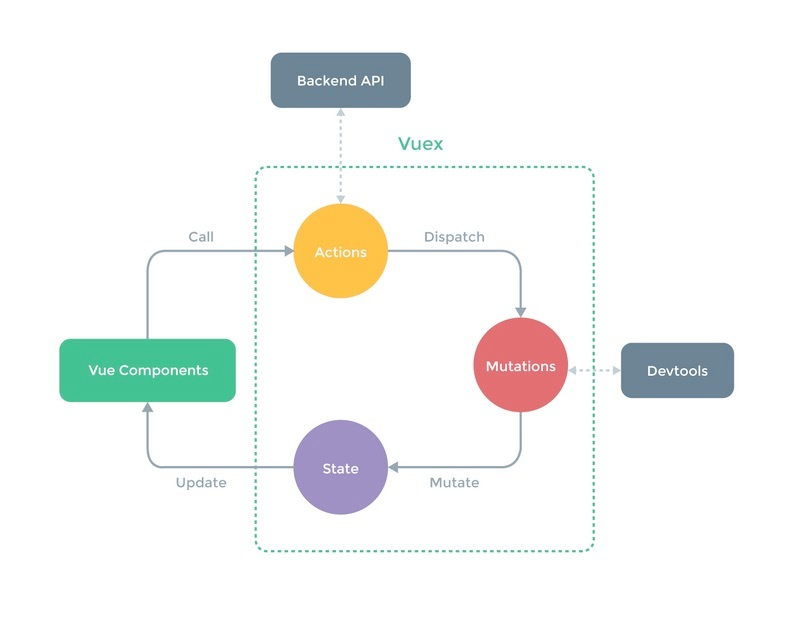
vuex图解
Vuex 理解
简单解释下:
Vuex 使用 单一状态树,通俗理解就是一个应用的数据集合,可以想象为一个“前端数据库”,让其在各个页面上实现数据的共享,并且可操作
Vuex 规定,属于应用层级的状态只能通过 Mutation 中的方法来修改,而派发 Mutation 中的事件只能通过 action。
从左到右,从组件出发,组件中调用 action,在 action 这一层级我们可以和后台数据交互,比如获取初始化的数据源,或者中间数据的过滤等。然后在 action 中去派发 Mutation。Mutation 去触发状态的改变,状态的改变,将触发视图的更新。
注意事项
-
数据流都是单向的
-
组件能够调用 action
-
action 用来派发 Mutation
-
只有 mutation 可以改变状态
-
store 是响应式的,无论 state 什么时候更新,组件都将同步更新
State
在 store 中的 state 对象,可以理解为 Vue 实例中的 data 对象,它用来保存最基本的数据。
声明
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import Vue from 'Vue';
import Vuex from 'Vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
stateA: 'a',
stateB: 'b',
stateC: 'c'
}
});
console.log(store.state.stateA); // a
|
在 Vue 中获取 store 中的状态
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
let app = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
template: '<h1>{}</h1>',
computed: {
myState() {
return store.state.stateA;
}
}
});
|
最简单的方式就是通过 Vue 中的计算属性(computed) 来将 store 中的状态映射为 Vue 的数据。但是当数据多时这种方法明显效率过低,所以 Vuex 中提供了 mapState 方法用于批量映射 store 中的状态。
mapState映射
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import { mapState } from 'Vuex';
let app = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
store,
data: {
local: 'L'
},
computed: mapState({
stateA: state => state.stateA,
stateB: 'stateB',
stateC(state) {
return state.stateC + this.local;
}
})
});
|
上例中,a. 可以通过 ES6 中的箭头函数进行数据的映射,b. 当计算属性的名称与 state 的属性名一致时可能直接通过字符串赋值,c. 当需要引用上下文中的 data 属性实,只能通过常规函数来使 this 生效。
如果所有计算属性的名称都与 state 一致,可以在 mapState 中以数组的方式进行映射。如果 Vue 中已经存在计算属性,可以通过 ES6 的展开操作符 (…) 进行组合。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
let app = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
store,
computed: {
local() {
return 'Local';
},
...mapState(['stateA', 'stateB', 'stateC'])
}
});
|
在 Vuex 模块化中,state 是唯一会根据组合时模块的别名来添加层级的,后面的 getters、mutations 以及 actions 都是直接合并在 store 下。
例如,访问模块 a 中的 state,要通过 store.state.a,访问根 store 上申明的 state,依然是通过 store.state.xxx 直接访问。
Mutations
在vuex中,更改state 的方式只有提交mutation.大家可以把他就想象成vue中methods 中的一个方法。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
addCount(state) {
state.count ++;
}
}
});
store.commit('addCount');
console.log(store.state.count); // 1
|
想要改变状态的时候都是用store.commit的方式
传参方式
每一个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型和一个回调函数,每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
第一种方式:提交载荷(Payload)
你可以向 store.commit 传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
...
mutations: {
addCount(state, n) {
state.count += n;
}
}
store.commit('addCount', 10);
|
官方推荐,载荷应该是一个对象,这样可以包含多个字段并且记录的 mutation 会更易读:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// ...
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
store.commit('increment', {
amount: 10
})
|
第二种方式:对象风格的传参方式
提交 mutation 的另一种方式是直接使用包含 type 属性的对象:
|
1
2
3
4
|
store.commit({
type: 'increment', // 事件名
amount: 10
})
|
Mutations 需遵守 Vue 的响应规则
在 mutation 中更改 state 应该以新对象替换老对象,不要在直接原对象上直接修改。
- 最好提前在你的 store 中初始化好所有所需属性。
- 当需要在对象上添加新属性时,你应该
- 使用 Vue.set(obj, ‘newProp’, 123),或者
- 以新对象替换老对象。例如,利用 stage-3 的对象展开运算符我们可以这样写:
1state.obj = { ...state.obj, newProp: 123 }
mutation 必须是同步函数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
mutations: {
someMutation (state) {
api.callAsyncMethod(() => {
state.count++
})
}
}
|
在上面的例子中 mutation 中的异步函数中的回调让这不可能完成:因为当 mutation 触发的时候,回调函数还没有被调用,devtools 不知道什么时候回调函数实际上被调用 —— 实质上任何在回调函数中进行的的状态的改变都是不可追踪的。
在组件中提交 Mutations
你可以在组件中使用 this.$store.commit(‘xxx’) 提交 mutation,或者使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用(需要在根节点注入 store)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment' // 映射 this.increment() 为 this.$store.commit('increment')
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 映射 this.add() 为 this.$store.commit('increment')
})
}
}
|
在 mutation 中混合异步调用会导致你的程序很难调试。例如,当你能调用了两个包含异步回调的 mutation 来改变状态,你怎么知道什么时候回调和哪个先回调呢?这就是为什么我们要区分这两个概念。在 Vuex 中,mutation 都是同步事务:
|
1
2
|
store.commit('increment')
// 任何由 "increment" 导致的状态变更都应该在此刻完成。
|
Actions
与 mutations 类似,不同模块的 actions 均可以通过 store.dispatch 直接触发。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
const moduleA = {
state: {
count: 1
},
mutations: {
sayCountA(state) {
console.log('Module A count: ', state.count);
}
},
actions: {
maAction(context) {
context.dispatch('mbAction');
}
}
};
const moduleB = {
state: {
count: 2
},
mutations: {
sayCountB(state, num) {
console.log('Module B count: ', state.count+num);
}
},
action: {
mbAction({ commit, rootState }) {
commit('sayCountA');
commit('sayCountB', rootState.a.count);
}
}
};
const store = {
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
};
store.dispatch('maAction'); // Module A count: 1、Module B count: 3
|
action 的回调函数接收一个 context 上下文参数,context 包含:1. state、2. rootState、3. getters、4. mutations、5. actions 五个属性,
有一点要注意的是,将 store 中的 state 绑定到 Vue 组件中的 computed 计算属性后,对 state 进行更改需要通过 mutation 或者 action,在 Vue 组件中直接进行赋值 (this.myState = ‘ABC’) 是不会生效的。