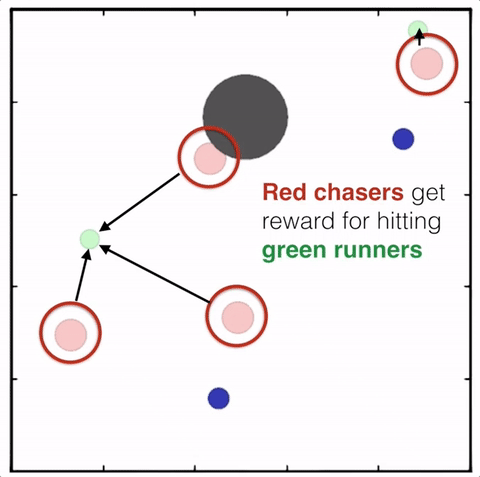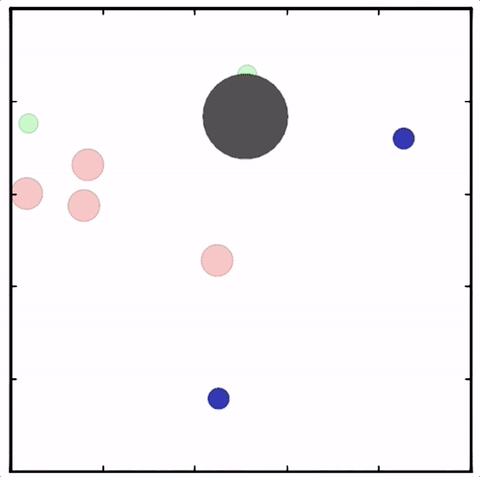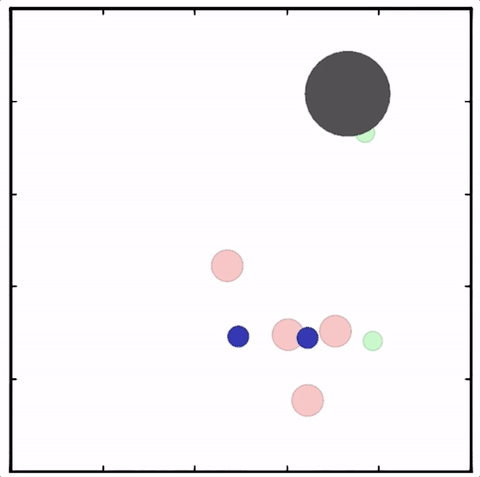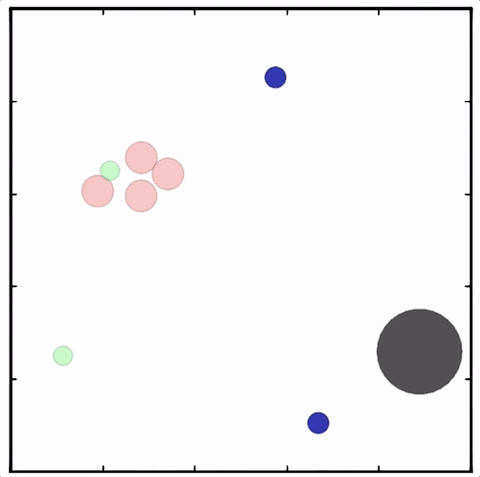
Multi-Agent Actor-Critic for Mixed Cooperative-Competitive Environments
2017-10-25 16:38:23
【Project Page】https://blog.openai.com/learning-to-cooperate-compete-and-communicate/
4. Method
4.1 Multi-Agent Actor Critic

该网络框架有如下假设条件:
(1) the learned policies can only use local information (i.e. their own observations) at execution time,
(2) we do not assume a differentiable model of the environment dynamics, unlike in [24],
(3) we do not assume any particular structure on the communication method between agents (that is, we don’t assume a differentiable communication channel).
================>>>
1. 学习到的策略在执行时,仅仅是利用局部的信息
2. 我们不假设环境动态的可微分模型
3. 我们不假设 agents 之间任何通信模型上的特定结构
本文的模型是以 centralized training with decentralized execution framework 为基础进行的,而这个框架的意思是:以全局的信息进行训练,而实际测试的时候是分散执行的。
更具体的来说,我们考虑有 N 个 agent 的游戏,所以,每个 agent i 的期望汇报可以记为:

此处的 Q 函数 是一个中心化的动作值函数(centralized action-value function),将所有 agent 的动作作为输入,除了某些状态信息 X,然后输出是 the Q-value for agent i。
在最简单的情况下,x 可以包含所有 agent 的观测,x = (o1, ... , oN),但是我们也可以包含额外的状态信息。由于每一个 Q 都是分别学习的,agent 可以拥有任意的奖励结构,包括在竞争设定下的冲突奖励。
我们可以将上述 idea 拓展到 deterministic policies。如果我们考虑到 N 个连续的策略,那么梯度可以写作:
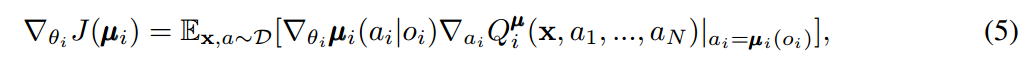
此处,经验回放池 D 包括 the tuples (x, x', a1, ... , aN, r1, ... , rN),记录所有 agents 的经验。中心化的动作值函数 Q可以通过如下的方程,进行更新:
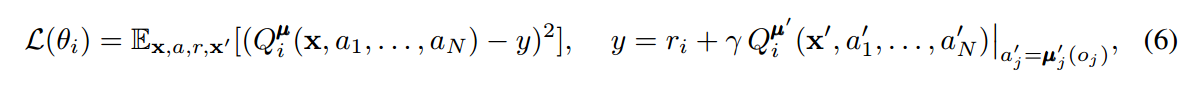

4.2 Inferring Policies of Other Agents
为了移除假设:knowing other agents' policies, 就像公式(6)中所要求的那样。每一个 agent i 可以估计 agent j 的真实策略。这个估计的策略可以通过最大化 agent 选择动作的 log 概率,且加上一个 entropy regularizer:
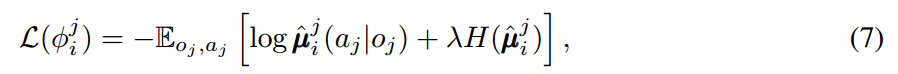
其中,H 是策略分布的熵。有了估计的策略,公式(6)中的 y 可以用估计的值 y^ 来进行计算:

其中,mu’ 代表用来估计策略的 target network。注意到,公式(7)可以完全在线的执行,before updating $Q_i^{mu}$, the centralized Q function, 我们采取每一个 agent j 的最新的样本,from the replay buffer to perform a single gradient step to update $phi^j_i$。另外,在上述公式中,我们直接将每个 agent 的动作 log 概率输入到 Q,而不是 sampling。
4.3 Agents with Policy Ensembles