动态内存分配的意义:

malloc和free:
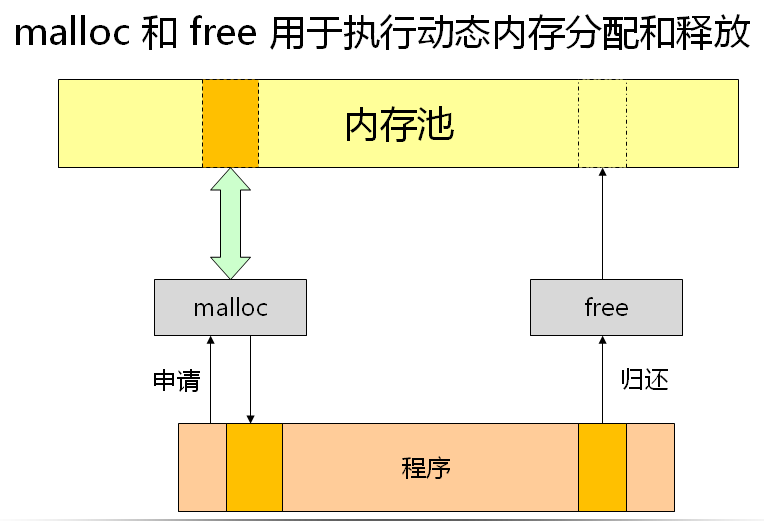

注意:

思考:
malloc(0)将返回什么?
运行结果如下:
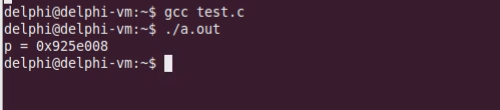
可以看到,返回了具体的地址。
我们所说的内存包括起始地址和长度。我们平时说内存的时候更多的是关注起始地址,而忽略了长度。
如果动态的综合这两部,我们使用malloc(0)返回了一个地址就不会奇怪了,因为这块内存的长度是0。这块内存我们可能无法正常使用,因为长度是0。
我们如果不停的malloc(0),会使系统的内存耗尽吗?
答案是会的,因为我们malloc的时候,得到的内存往往要比实际申请的大。
现在的内存申请一般都是四字节对齐的。
因此,malloc(0)也要使用free来释放这片内存。
避免内存泄漏的内存泄漏检测模块:
mleak.h如下:
1 #ifndef _MLEAK_H_ 2 #define _MLEAK_H_ 3 4 #include <malloc.h> 5 6 #define MALLOC(n) mallocEx(n, __FILE__, __LINE__) 7 #define FREE(p) freeEx(p) 8 9 void* mallocEx(size_t n, const char* file, const line); 10 void freeEx(void* p); 11 void PRINT_LEAK_INFO(); 12 13 #endif
mleak.c如下:
1 #include "mleak.h" 2 3 #define SIZE 256 4 5 /* 动态内存申请参数结构体 */ 6 typedef struct 7 { 8 void* pointer; 9 int size; 10 const char* file; 11 int line; 12 } MItem; 13 14 static MItem g_record[SIZE]; /* 记录动态内存申请的操作 */ 15 16 void* mallocEx(size_t n, const char* file, const line) 17 { 18 void* ret = malloc(n); /* 动态内存申请 */ 19 20 if( ret != NULL ) 21 { 22 int i = 0; 23 24 /* 遍历全局数组,记录此次操作 */ 25 for(i=0; i<SIZE; i++) 26 { 27 /* 查找位置 */ 28 if( g_record[i].pointer == NULL ) 29 { 30 g_record[i].pointer = ret; 31 g_record[i].size = n; 32 g_record[i].file = file; 33 g_record[i].line = line; 34 break; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 return ret; 40 } 41 42 void freeEx(void* p) 43 { 44 if( p != NULL ) 45 { 46 int i = 0; 47 48 /* 遍历全局数组,释放内存空间,并清除操作记录 */ 49 for(i=0; i<SIZE; i++) 50 { 51 if( g_record[i].pointer == p ) 52 { 53 g_record[i].pointer = NULL; 54 g_record[i].size = 0; 55 g_record[i].file = NULL; 56 g_record[i].line = 0; 57 58 free(p); 59 60 break; 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 66 void PRINT_LEAK_INFO() 67 { 68 int i = 0; 69 70 printf("Potential Memory Leak Info: "); 71 72 /* 遍历全局数组,打印未释放的空间记录 */ 73 for(i=0; i<SIZE; i++) 74 { 75 if( g_record[i].pointer != NULL ) 76 { 77 printf("Address: %p, size:%d, Location: %s:%d ", g_record[i].pointer, g_record[i].size, g_record[i].file, g_record[i].line); 78 } 79 } 80 }
主程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include "mleak.h" 3 4 void f() 5 { 6 MALLOC(100); 7 } 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 int* p = (int*)MALLOC(3 * sizeof(int)); 12 13 f(); 14 15 p[0] = 1; 16 p[1] = 2; 17 p[2] = 3; 18 19 FREE(p); 20 21 PRINT_LEAK_INFO(); 22 23 return 0; 24 }
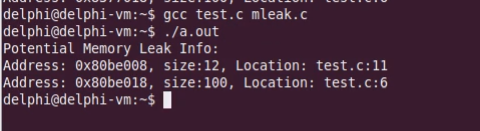
运行结果如下:
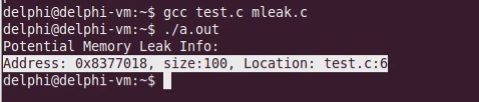
我们将第19行释放p的语句也注释掉,再次运次:
calloc和realloc:

示例程序:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <malloc.h> 3 4 #define SIZE 5 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int i = 0; 9 int* pI = (int*)malloc(SIZE * sizeof(int)); 10 short* pS = (short*)calloc(SIZE, sizeof(short)); 11 12 for(i=0; i<SIZE; i++) 13 { 14 printf("pI[%d] = %d, pS[%d] = %d ", i, pI[i], i, pS[i]); 15 } 16 17 printf("Before: pI = %p ", pI); 18 19 pI = (int*)realloc(pI, 2 * SIZE * sizeof(int)); 20 21 printf("After: pI = %p ", pI); 22 23 for(i=0; i<10; i++) 24 { 25 printf("pI[%d] = %d ", i, pI[i]); 26 } 27 28 free(pI); 29 free(pS); 30 31 return 0; 32 }
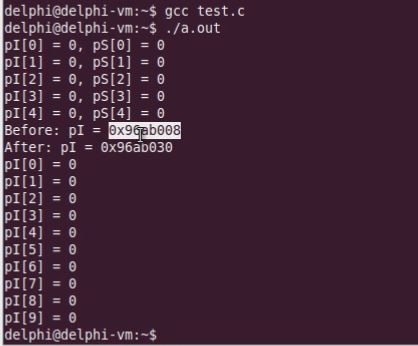
运行结果如下:
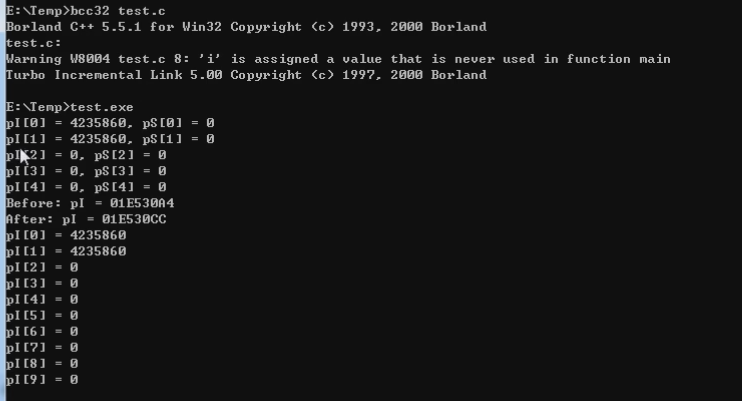
bcc32的运行结果如下:
vc编译器的结果如下;
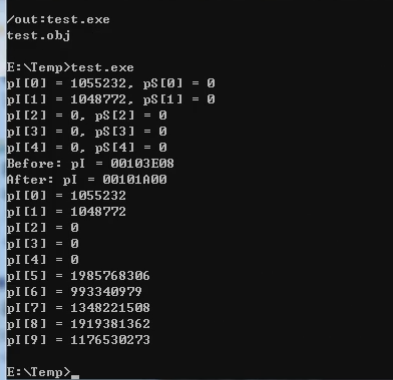
realloc重置之后地址值会发生变化。
可以得到结论:
calloc得到的内存是绝对会初始化的,malloc不会初始化。realloc会重置内存空间的大小,重置后扩大的内存部分可能是随机值。
小结:
