本文转载自无始无终,原文连接 HashMap 在 JDK 1.8 后新增的红黑树结构
传统 HashMap 的缺点
JDK 1.8 以前 HashMap 的实现是 数组+链表,即使哈希函数取得再好,也很难达到元素百分百均匀分布。
当 HashMap哈希冲突严重时,有大量的元素都存放到同一个桶中时,这个桶下有一条长长的链表,这个时候 HashMap 就相当于一个单链表,假如单链表有 n 个元素,遍历的时间复杂度就是 O(n),完全失去了它的优势。
针对这种情况,JDK 1.8 中引入了 红黑树(查找时间复杂度为 O(logn))来优化这个问题。
HashMap 在 JDK 1.8 中新增的数据结构 – 红黑树
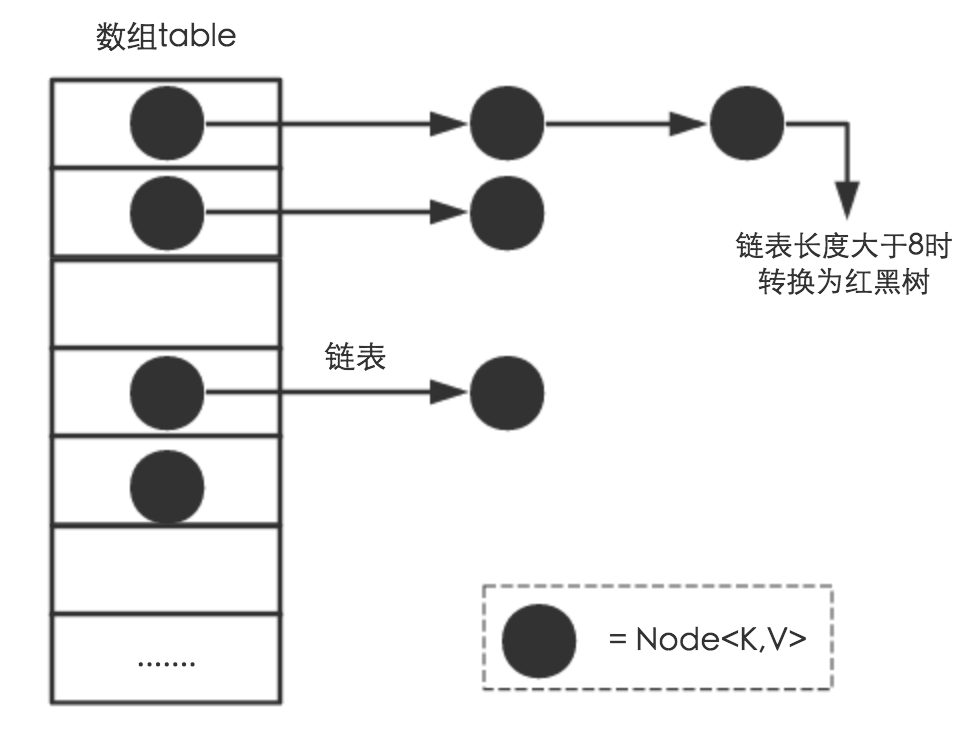
JDK 1.8 中 HashMap 中除了链表节点:
/** * Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for * TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.) */ static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { // 哈希值,就是位置 final int hash; // 键 final K key; // 值 V value; // 指向下一个节点的指针 Node<K,V> next; ...... }
还有另外一种节点:TreeNode,它是 1.8 新增的,属于数据结构中的 红黑树。
/** * Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn * extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or * linked node. */ static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red; TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, val, next); } }
可以看到就是个红黑树节点,有父亲、左右孩子、前一个元素的节点,还有个颜色值。
另外由于它继承自 LinkedHashMap.Entry ,而 LinkedHashMap.Entry 继承自 HashMap.Node ,因此还有额外的 6 个属性:
// 继承 LinkedHashMap.Entry 的 Entry<K,V> before, after; // 继承 HashMap.Node 的 final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next;
HashMap 中关于红黑树的三个关键参数
HashMap 中有三个关于红黑树的关键参数:
- TREEIFY_THRESHOLD
- UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD
- MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY
值及作用如下:
// 一个桶的树化阈值 // 当桶中元素个数超过这个值时,需要使用红黑树节点替换链表节点 // 这个值必须为 8,要不然频繁转换效率也不高 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // 一个树的链表还原阈值 // 当扩容时,桶中元素个数小于这个值,就会把树形的桶元素 还原(切分)为链表结构 // 这个值应该比上面那个小,至少为 6,避免频繁转换 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; // 哈希表的最小树形化容量 // 当哈希表中的容量大于这个值时,表中的桶才能进行树形化 // 否则桶内元素太多时会扩容,而不是树形化 // 为了避免进行扩容、树形化选择的冲突,这个值不能小于 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
HashMap 在 JDK 1.8 中新增的操作:桶的树形化 treeifyBin()
在Java 8 中,如果一个桶中的元素个数超过 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是 8 ),就使用红黑树来替换链表,从而提高速度。
这个替换的方法叫 treeifyBin() 即树形化。
/** * Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless * table is too small, in which case resizes instead. * 将桶内所有的 链表节点 替换成 红黑树节点 */ final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; // 如果当前哈希表为空,或者哈希表中元素的个数小于 进行树形化的阈值(默认为 64),就去新建/扩容 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); // 如果哈希表中的元素个数超过了 树形化阈值,进行树形化 // e 是哈希表中指定位置桶里的链表节点,从第一个开始 else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { // 红黑树的头、尾节点 TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; do { // 新建一个树形节点,内容和当前链表节点 e 一致 TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); if (tl == null) // 确定树头节点 hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); // 让桶的第一个元素指向新建的红黑树头结点,以后这个桶里的元素就是红黑树而不是链表了 if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) hd.treeify(tab); } }
上述操作做了这些事:
- 根据哈希表中元素个数确定是扩容还是树形化
- 如果是树形化
- 遍历桶中的元素,创建相同个数的树形节点,复制内容,建立起联系
- 然后让桶第一个元素指向新建的树头结点,替换桶的链表内容为树形内容
但是我们发现,之前的操作并没有设置红黑树的颜色值,现在得到的只能算是个二叉树。在 最后调用树形节点 hd.treeify(tab) 方法进行塑造红黑树:
/** * Forms tree of the nodes linked from this node. * @return root of tree */ final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) { TreeNode<K,V> root = null; for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) { next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next; x.left = x.right = null; if (root == null) { // 头回进入循环,确定头结点,为黑色 x.parent = null; x.red = false; root = x; } else { // 后面进入循环走的逻辑,x 指向树中的某个节点 K k = x.key; int h = x.hash; Class<?> kc = null; // 又一个循环,从根节点开始,遍历所有节点跟当前节点 x 比较,调整位置,有点像冒泡排序 for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) { int dir, ph; K pk = p.key; if ((ph = p.hash) > h) // 当比较节点的哈希值比 x 大时, dir 为 -1 dir = -1; else if (ph < h) // 哈希值比 x 小时 dir 为 1 dir = 1; else if ((kc == null && (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); // 把 当前节点变成 x 的父亲 // 如果当前比较节点的哈希值比 x 大,x 就是左孩子,否则 x 是右孩子 TreeNode<K,V> xp = p; if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { x.parent = xp; if (dir <= 0) xp.left = x; else xp.right = x; root = balanceInsertion(root, x); break; } } } } moveRootToFront(tab, root); }
可以看到,将二叉树变为红黑树时,需要保证有序。这里有个双重循环,拿树中的所有节点和当前节点的哈希值进行对比(如果哈希值相等,就对比键,这里不用完全有序),然后根据比较结果确定在树种的位置。
HashMap 在 JDK 1.8 中新增的操作: 红黑树中添加元素 putTreeVal()
上面介绍了如何把一个桶中的链表结构变成红黑树结构。
在添加时,如果一个桶中已经是红黑树结构,就要调用红黑树的添加元素方法 putTreeVal()。
/** * Tree version of putVal. */ final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int h, K k, V v) { Class<?> kc = null; boolean searched = false; TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this; // 每次添加元素时,从根节点遍历,对比哈希值 for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) { int dir, ph; K pk; if ((ph = p.hash) > h) dir = -1; else if (ph < h) dir = 1; else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) // 如果当前节点的哈希值、键和要添加的都一致,就返回当前节点 return p; else if ((kc == null && (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) { // 如果当前节点和要添加的节点哈希值相等,但是两个节点的键不是一个类,只好去挨个对比左右孩子 if (!searched) { TreeNode<K,V> q, ch; searched = true; if (((ch = p.left) != null && (q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) || ((ch = p.right) != null && (q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null)) // 如果从 ch 所在子树中可以找到要添加的节点,就直接返回 return q; } // 哈希值相等,但键无法比较,只好通过特殊的方法给个结果 dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); } // 经过前面的计算,得到了当前节点和要插入节点的一个大小关系 // 要插入的节点比当前节点小就插到左子树,大就插到右子树 TreeNode<K,V> xp = p; // 这里有个判断,如果当前节点还没有左孩子或者右孩子时才能插入,否则就进入下一轮循环 if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next; TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn); if (dir <= 0) xp.left = x; else xp.right = x; xp.next = x; x.parent = x.prev = xp; if (xpn != null) ((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x; // 红黑树中,插入元素后必要的平衡调整操作 moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x)); return null; } } }
/** * 这个方法用于 a 和 b 哈希值相同但是无法比较时,直接根据两个引用的地址进行比较 * 这里源码注释也说了,这个树里不要求完全有序,只要插入时使用相同的规则保持平衡即可 * * Tie-breaking utility for ordering insertions when equal * hashCodes and non-comparable. We don't require a total * order, just a consistent insertion rule to maintain * equivalence across rebalancings. Tie-breaking further than * necessary simplifies testing a bit. */ static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) { int d; if (a == null || b == null || (d = a.getClass().getName(). compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0) d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ? -1 : 1); return d; }
通过上面的代码可以知道,HashMap 中往红黑树中添加一个新节点 n 时,有以下操作:
- 从根节点开始遍历当前红黑树中的元素 p,对比 n 和 p 的哈希值;
- 如果哈希值相等并且键也相等,就判断为已经有这个元素;
- 如果哈希值相等但无法比较时,就通过其他信息,比如引用地址来给个大概比较结果,这里可以看到红黑树的比较并不是很准确,注释里也说了,只是保证个相对平衡即可;
- 最后得到哈希值比较结果后,如果当前节点 p 还没有左孩子或者右孩子时才能插入,否则就进入下一轮循环;
- 插入元素后还需要进行红黑树例行的平衡调整,还有确保根节点的领先地位。
HashMap 在 JDK 1.8 中新增的操作: 红黑树中查找元素 getTreeNode()
HashMap 的查找方法是 get():
public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V> e; return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; }
它通过计算指定 key 的哈希值后,调用内部方法 getNode():
/** * Implements Map.get and related methods * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @return the node, or null if none */ final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null; }
这个 getNode() 方法就是根据哈希表元素个数与哈希值求模(使用的公式是 (n - 1) &hash)得到 key 所在的桶的头结点,如果头节点恰好是红黑树节点,就调用红黑树节点的 getTreeNode() 方法,否则就遍历链表节点。
/** * Calls find for root node. */ final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) { return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null); }
getTreeNode 方法使通过调用树形节点的 find() 方法进行查找:
/** * 从根节点根据 哈希值和 key 进行查找 * Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key. * The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use * comparing keys. */ final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) { TreeNode<K,V> p = this; do { int ph, dir; K pk; TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q; if ((ph = p.hash) > h) p = pl; else if (ph < h) p = pr; else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) return p; else if (pl == null) p = pr; else if (pr == null) p = pl; else if ((kc != null || (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) && (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0) p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr; else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null) return q; else p = pl; } while (p != null); return null; }
由于之前添加时已经保证这个树是有序的,因此查找时基本就是折半查找,效率很高。
这里和插入时一样,如果对比节点的哈希值和要查找的哈希值相等,就会判断 key 是否相等,相等就直接返回;不相等就从子树中递归查找。
HashMap 在 JDK 1.8 中新增的操作: 树形结构修剪 split()
HashMap 中, resize() 方法的作用就是初始化或者扩容哈希表。当扩容时,如果当前桶中元素结构是红黑树,并且元素个数小于链表还原阈值 UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD (默认为 6),就会把桶中的树形结构缩小或者直接还原(切分)为链表结构,调用的就是 split():
/** * Splits nodes in a tree bin into lower and upper tree bins, * or untreeifies if now too small. Called only from resize; * see above discussion about split bits and indices. * * @param map the map * @param tab the table for recording bin heads 表示保存桶头结点的哈希表 * @param index the index of the table being split 示从哪个位置开始修剪 * @param bit the bit of hash to split on 要修剪的位数(哈希值) */ final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) { TreeNode<K,V> b = this; // Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; int lc = 0, hc = 0; for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) { next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next; e.next = null; // 如果当前节点哈希值的最后一位等于要修剪的 bit 值 if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) { // 就把当前节点放到 lXXX 树中 if ((e.prev = loTail) == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; // 然后 loTail 记录 e loTail = e; // 记录 lXXX 树的节点数量 ++lc; } else { // 如果当前节点哈希值最后一位不是要修剪的 // 就把当前节点放到 hXXX 树中 if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; // 记录 hXXX 树的节点数量 ++hc; } } if (loHead != null) { // 如果 lXXX 树的数量小于 6,就把 lXXX 树的枝枝叶叶都置为空,变成一个单节点 // 然后让这个桶中,要还原索引位置开始往后的结点都变成还原成链表的 lXXX 节点 // 这一段元素以后就是一个链表结构 if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map); else { // 否则让索引位置的结点指向 lXXX 树,这个树被修剪过,元素少了 tab[index] = loHead; if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified) loHead.treeify(tab); } } if (hiHead != null) { // 同理,让 指定位置 index + bit 之后的元素 // 指向 hXXX 还原成链表或者修剪过的树 if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map); else { tab[index + bit] = hiHead; if (loHead != null) hiHead.treeify(tab); } } }
从上述代码可以看到,HashMap 扩容时对红黑树节点的修剪主要分两部分,先分类、再根据元素个数决定是还原成链表还是精简一下元素仍保留红黑树结构。
- 分类
指定位置、指定范围,让指定位置中的元素 (hash & bit) == 0 的,放到 lXXX 树中,不相等的放到 hXXX 树中。
- 根据元素个数决定处理情况
符合要求的元素(即 lXXX 树),在元素个数小于 6 时还原成链表,最后让哈希表中修剪的痛 tab[index] 指向 lXXX 树;在元素个数大于 6 时,还是用红黑树,只不过是修剪了下枝叶;
不符合要求的元素(即 hXXX 树)也是一样的操作,只不过最后它是放在了修剪范围外 tab[index + bit]。
总结
JDK 1.8 以后哈希表的 添加、删除、查找、扩容方法都增加了一种 节点为 TreeNode 的情况:
- 添加时,当桶中链表个数超过 8 时会转换成红黑树;
- 删除、扩容时,如果桶中结构为红黑树,并且树中元素个数太少的话,会进行修剪或者直接还原成链表结构;
- 查找时即使哈希函数不优,大量元素集中在一个桶中,由于有红黑树结构,性能也不会差。
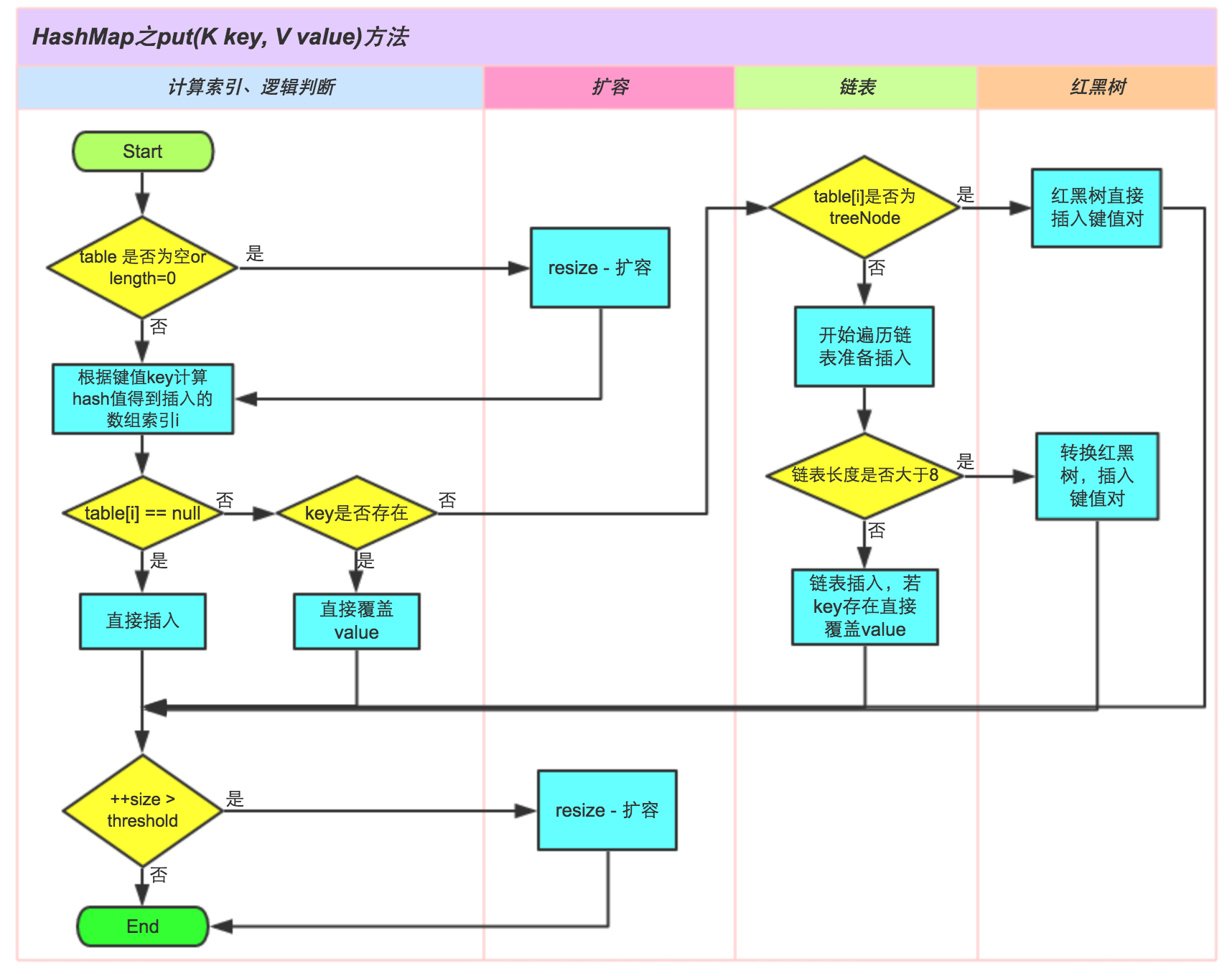
这篇文章根据源码分析了 HashMap 在 JDK 1.8 里新增的 TreeNode 的一些关键方法,可以看到,1.8 以后的 HashMap 结合了哈希表和红黑树的优点,不仅快速,而且在极端情况也能保证性能。