sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程)
http://zetcode.com/gui/pyqt4/layoutmanagement/
zetcode官网
PyQt4 tutorial
This is PyQt4 tutorial. The tutorial is suited for beginners and intermediate programmers. After reading this tutorial, you will be able to program non trivial PyQt4 applications. PyQt5 tutorial is the successor of this tutorial.
目录内容
Table of contents
- Introduction
- First programs
- Menus and toolbars
- Layout management
- Events and signals
- Dialogs
- Widgets
- Widgets II
- Drag & drop
- Drawing
- Custom widgets
- The Tetris game
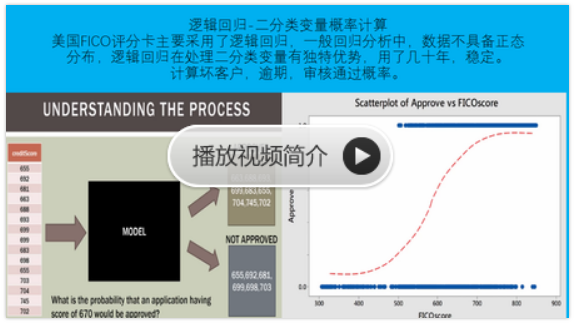
计算器
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In this example, we create a skeleton
of a calculator using a QtGui.QGridLayout.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: July 2014
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
grid = QtGui.QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(grid)
names = ['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close',
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+']
positions = [(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)]
for position, name in zip(positions, names):
if name == '':
continue
button = QtGui.QPushButton(name)
grid.addWidget(button, *position)
self.move(300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Calculator')
self.show()
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
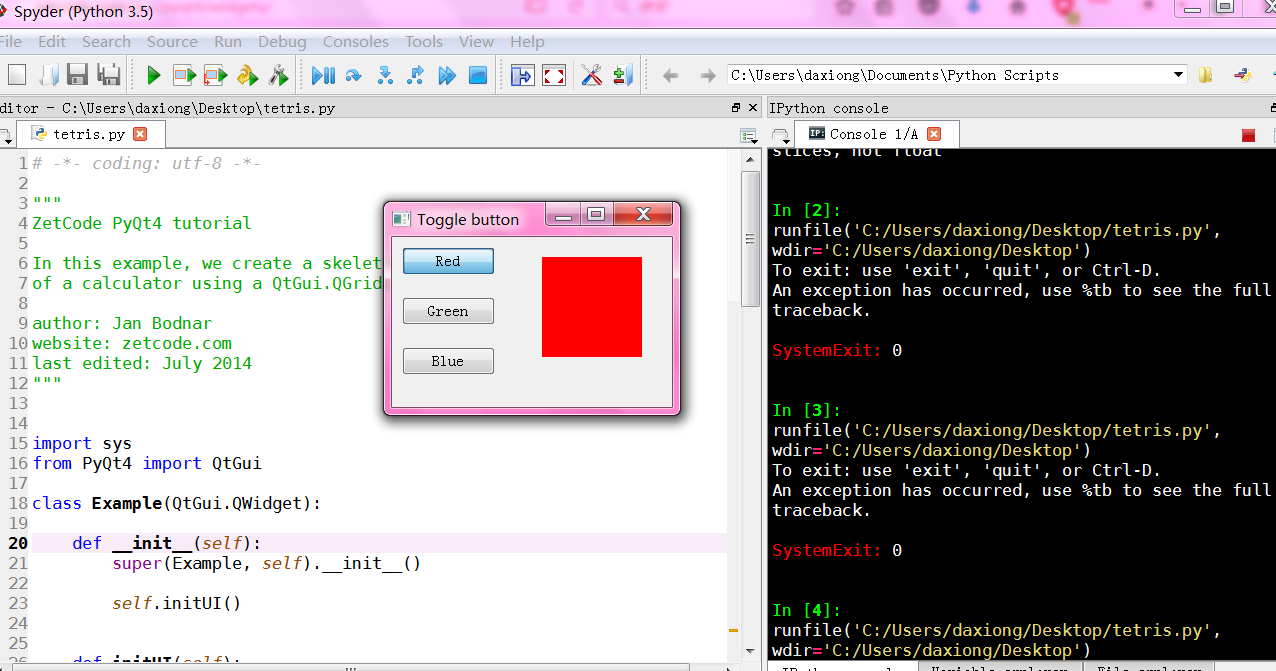
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
In this example, we create three toggle buttons.
They will control the background color of a
QtGui.QFrame.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: September 2011
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.col = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0)
redb = QtGui.QPushButton('Red', self)
redb.setCheckable(True)
redb.move(10, 10)
redb.clicked[bool].connect(self.setColor)
greenb = QtGui.QPushButton('Green', self)
greenb.setCheckable(True)
greenb.move(10, 60)
greenb.clicked[bool].connect(self.setColor)
blueb = QtGui.QPushButton('Blue', self)
blueb.setCheckable(True)
blueb.move(10, 110)
blueb.clicked[bool].connect(self.setColor)
self.square = QtGui.QFrame(self)
self.square.setGeometry(150, 20, 100, 100)
self.square.setStyleSheet("QWidget { background-color: %s }" %
self.col.name())
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170)
self.setWindowTitle('Toggle button')
self.show()
def setColor(self, pressed):
source = self.sender()
if pressed:
val = 255
else: val = 0
if source.text() == "Red":
self.col.setRed(val)
elif source.text() == "Green":
self.col.setGreen(val)
else:
self.col.setBlue(val)
self.square.setStyleSheet("QFrame { background-color: %s }" %
self.col.name())
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
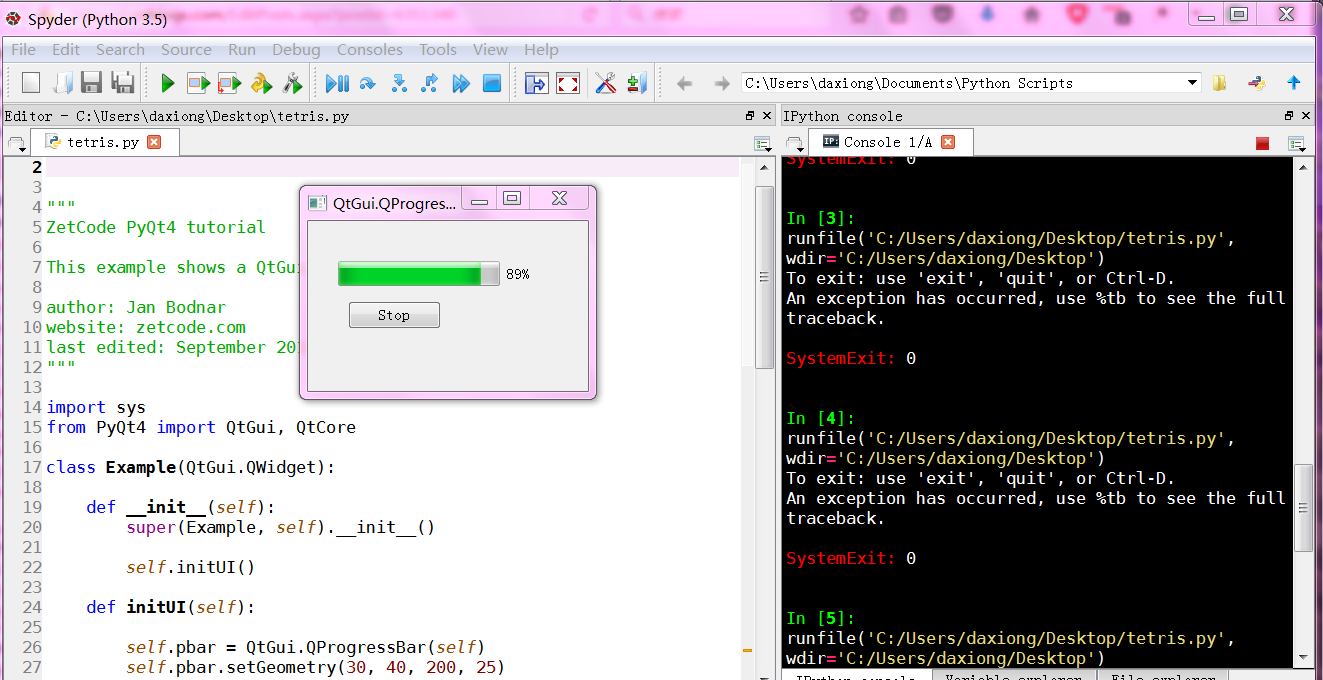
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
This example shows a QtGui.QProgressBar widget.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: September 2011
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.pbar = QtGui.QProgressBar(self)
self.pbar.setGeometry(30, 40, 200, 25)
self.btn = QtGui.QPushButton('Start', self)
self.btn.move(40, 80)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.doAction)
self.timer = QtCore.QBasicTimer()
self.step = 0
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 280, 170)
self.setWindowTitle('QtGui.QProgressBar')
self.show()
def timerEvent(self, e):
if self.step >= 100:
self.timer.stop()
self.btn.setText('Finished')
return
self.step = self.step + 1
self.pbar.setValue(self.step)
def doAction(self):
if self.timer.isActive():
self.timer.stop()
self.btn.setText('Start')
else:
self.timer.start(100, self)
self.btn.setText('Stop')
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
下拉菜单

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.lbl = QtGui.QLabel("Ubuntu", self)
combo = QtGui.QComboBox(self)
combo.addItem("Ubuntu")
combo.addItem("Mandriva")
combo.addItem("Fedora")
combo.addItem("Red Hat")
combo.addItem("Gentoo")
combo.move(50, 50)
self.lbl.move(50, 150)
combo.activated[str].connect(self.onActivated)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 200)
self.setWindowTitle('QtGui.QComboBox')
self.show()
def onActivated(self, text):
self.lbl.setText(text)
self.lbl.adjustSize()
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
拖动技术
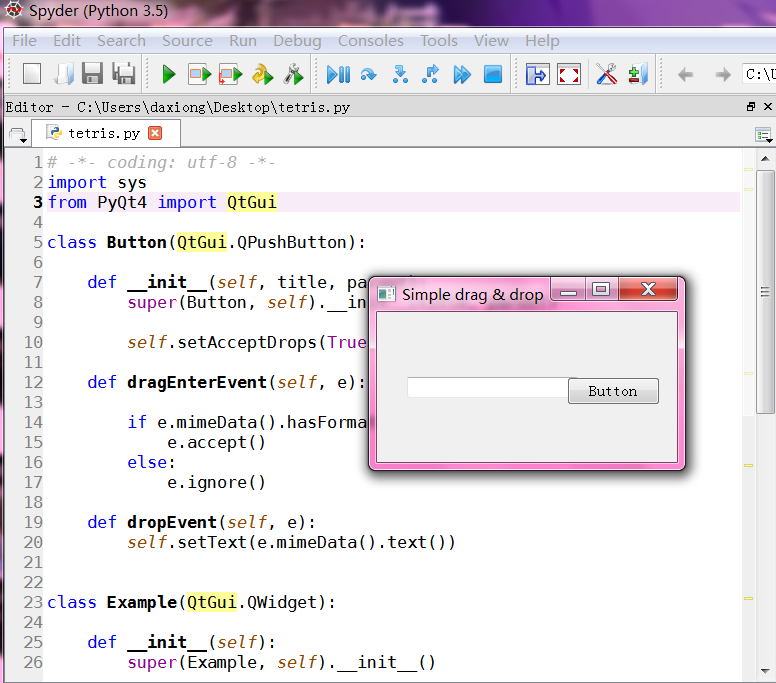
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui
class Button(QtGui.QPushButton):
def __init__(self, title, parent):
super(Button, self).__init__(title, parent)
self.setAcceptDrops(True)
def dragEnterEvent(self, e):
if e.mimeData().hasFormat('text/plain'):
e.accept()
else:
e.ignore()
def dropEvent(self, e):
self.setText(e.mimeData().text())
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
edit = QtGui.QLineEdit('', self)
edit.setDragEnabled(True)
edit.move(30, 65)
button = Button("Button", self)
button.move(190, 65)
self.setWindowTitle('Simple drag & drop')
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 150)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
ex.show()
app.exec_()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
绘图
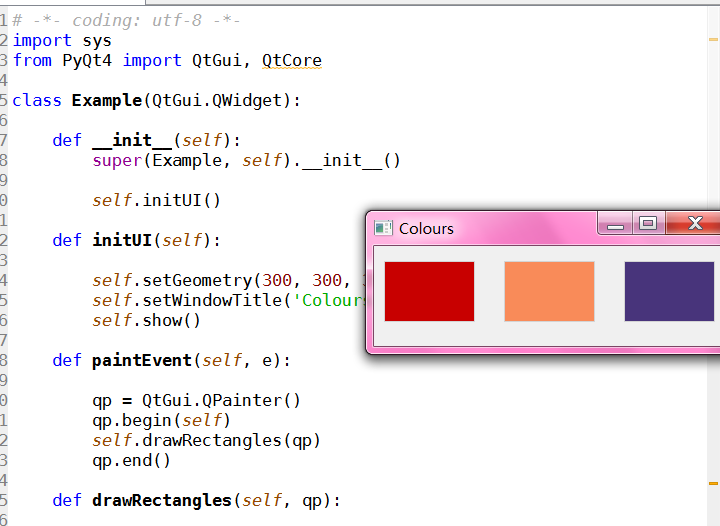
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode PyQt4 tutorial
This example draws three rectangles in three
different colours.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: September 2011
"""
import sys
from PyQt4 import QtGui, QtCore
class Example(QtGui.QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 100)
self.setWindowTitle('Colours')
self.show()
def paintEvent(self, e):
qp = QtGui.QPainter()
qp.begin(self)
self.drawRectangles(qp)
qp.end()
def drawRectangles(self, qp):
color = QtGui.QColor(0, 0, 0)
color.setNamedColor('#d4d4d4')
qp.setPen(color)
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(200, 0, 0))
qp.drawRect(10, 15, 90, 60)
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(255, 80, 0, 160))
qp.drawRect(130, 15, 90, 60)
qp.setBrush(QtGui.QColor(25, 0, 90, 200))
qp.drawRect(250, 15, 90, 60)
def main():
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
其它例子
Screenshots
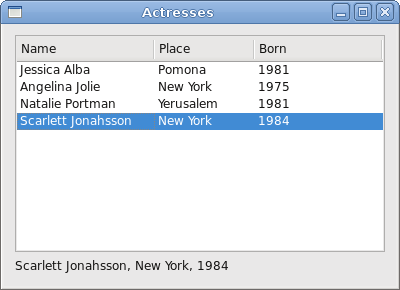
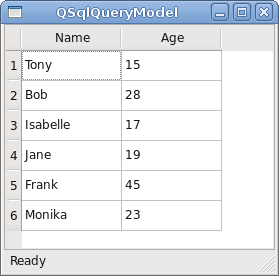
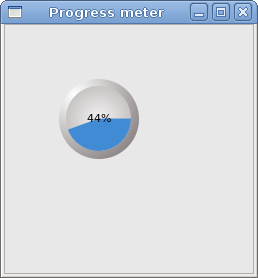
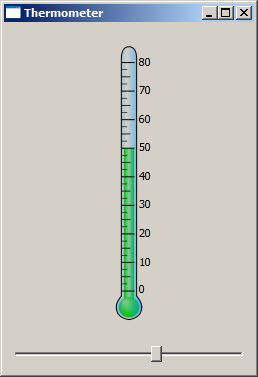
Here you can see some of the screenshots from the e-book.

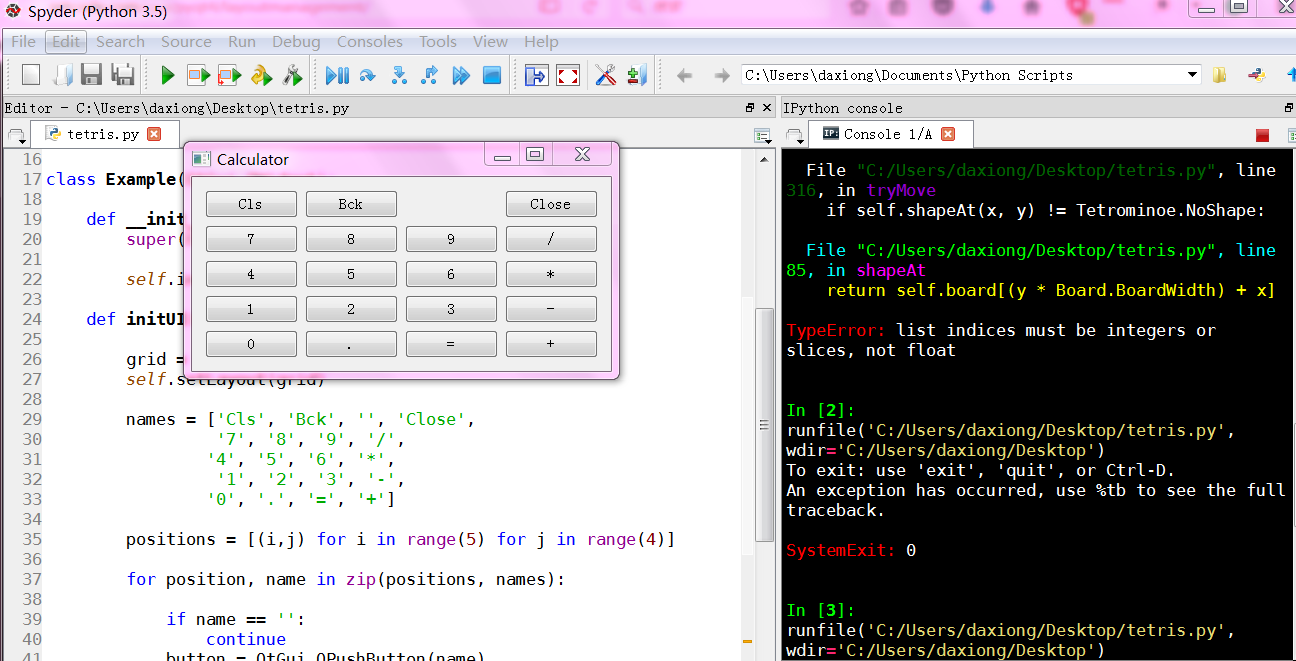
俄罗斯方块