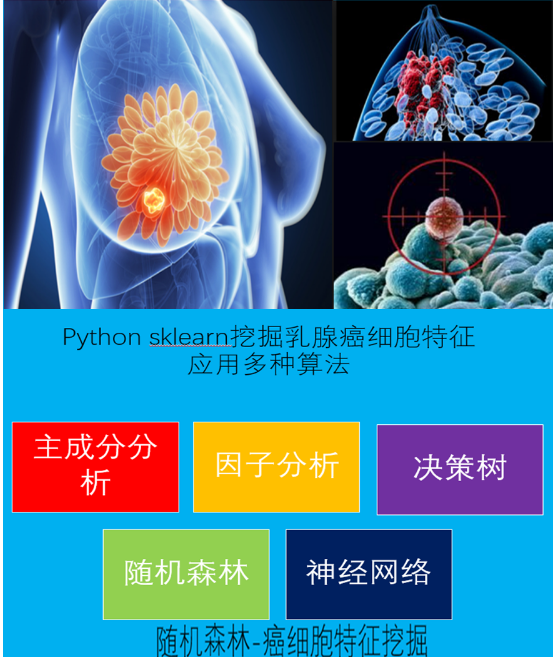
python机器学习-乳腺癌细胞挖掘(博主亲自录制视频)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
机器学习,统计项目联系:QQ231469242
#mental
group1=[2,2,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,4]
#physical
group2=[4,4,3,5,4,1,1,2,3,3]
#medical
group3=[1,2,2,2,3,2,3,1,3,1]
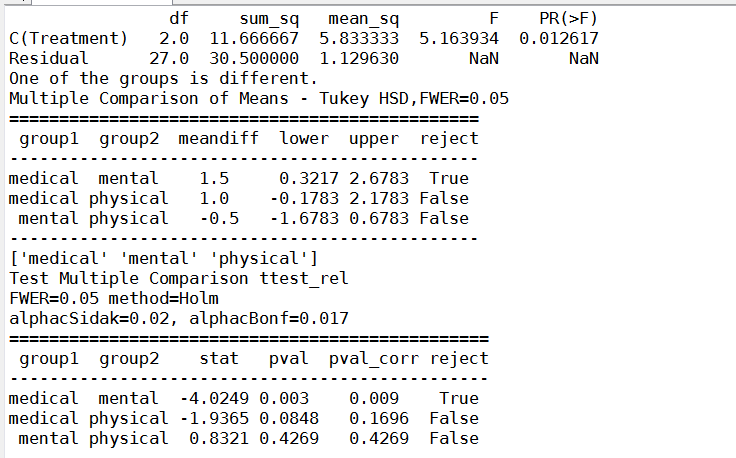
多重检验结果和贾俊平的LSD结果不一样,经过T配对试验,多重检验和T配对试验一致,LSD对小样本可能不准确
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Import standard packages
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
import pandas as pd
import os
# additional packages
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.join('..', '..', 'Utilities'))
try:
# Import formatting commands if directory "Utilities" is available
from ISP_mystyle import showData
except ImportError:
# Ensure correct performance otherwise
def showData(*options):
plt.show()
return
# Other required packages
from statsmodels.stats.multicomp import (pairwise_tukeyhsd,
MultiComparison)
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
from statsmodels.stats.anova import anova_lm
from statsmodels.stats.libqsturng import psturng
def setData():
''' Set up the data, as a structured array. '''
# The first and last field are 32-bit intergers; the second field is an
# 8-byte string. Note that here we can also give names to the individual
# fields!
data = np.rec.array([
( 1, 'mental', 2 ),
( 2, 'mental', 2 ),
( 3, 'mental', 3 ),
( 4, 'mental', 4 ),
( 5, 'mental', 4 ),
( 6, 'mental', 5 ),
( 7, 'mental', 3 ),
( 8, 'mental', 4 ),
( 9, 'mental', 4 ),
( 10, 'mental', 4 ),
( 11, 'physical', 4 ),
( 12, 'physical', 4 ),
( 13, 'physical', 3 ),
( 14, 'physical', 5 ),
( 15, 'physical', 4 ),
( 16, 'physical', 1 ),
( 17, 'physical', 1 ),
( 18, 'physical', 2 ),
( 19, 'physical', 3 ),
( 20, 'physical', 3 ),
( 21, 'medical', 1 ),
( 22, 'medical', 2 ),
( 23, 'medical', 2 ),
( 24, 'medical', 2 ),
( 25, 'medical', 3 ),
( 26, 'medical', 2 ),
( 27, 'medical', 3 ),
( 28, 'medical', 1 ),
( 29, 'medical', 3 ),
( 30, 'medical', 1 )], dtype=[('idx', '<i4'),
('Treatment', '|S8'),
('StressReduction', '<i4')])
return data
def doAnova(data):
'''one-way ANOVA'''
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
model = ols('StressReduction ~ C(Treatment)',df).fit()
anovaResults = anova_lm(model)
print(anovaResults)
if anovaResults['PR(>F)'][0] < 0.05:
print('One of the groups is different.')
def doTukey(data, multiComp):
'''Do a pairwise comparison, and show the confidence intervals'''
print((multiComp.tukeyhsd().summary()))
# Calculate the p-values:
res2 = pairwise_tukeyhsd(data['StressReduction'], data['Treatment'])
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
numData = len(df)
numTreatments = len(df.Treatment.unique())
dof = numData - numTreatments
# Show the group names
print((multiComp.groupsunique))
# Generate a print -------------------
# Get the data
xvals = np.arange(3)
res2 = pairwise_tukeyhsd(data['StressReduction'], data['Treatment'])
errors = np.ravel(np.diff(res2.confint)/2)
# Plot them
plt.plot(xvals, res2.meandiffs, 'o')
plt.errorbar(xvals, res2.meandiffs, yerr=errors, fmt='o')
# Put on labels
pair_labels = multiComp.groupsunique[np.column_stack(res2._multicomp.pairindices)]
plt.xticks(xvals, pair_labels)
# Format the plot
xlim = -0.5, 2.5
plt.hlines(0, *xlim)
plt.xlim(*xlim)
plt.title('Multiple Comparison of Means - Tukey HSD, FWER=0.05' +
'
Pairwise Mean Differences')
# Save to outfile, and show the data
outFile = 'multComp.png'
showData(outFile)
def Holm_Bonferroni(multiComp):
''' Instead of the Tukey's test, we can do pairwise t-test '''
# First, with the "Holm" correction
rtp = multiComp.allpairtest(stats.ttest_rel, method='Holm')
print((rtp[0]))
# and then with the Bonferroni correction
print((multiComp.allpairtest(stats.ttest_rel, method='b')[0]))
# Any value, for testing the program for correct execution
checkVal = rtp[1][0][0,0]
return checkVal
def main():
# Get the data
data = setData()
# Do a one-way ANOVA
doAnova(data)
#Then, do the multiple testing
multiComp = MultiComparison(data['StressReduction'], data['Treatment'])
doTukey(data, multiComp) # Tukey's HSD test
checkVal = Holm_Bonferroni(multiComp) # Alternatives to Tukey's HSD test
return checkVal # this is only for regression testing of the program
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
多重检验结果和贾俊平的LSD结果不一样,经过T配对试验,多重检验和T配对试验一致,LSD对小样本可能不准确

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scipy,math
from scipy.stats import f
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.stats as stats
# additional packages
from statsmodels.stats.diagnostic import lillifors
#多重比较
from statsmodels.sandbox.stats.multicomp import multipletests
#用于排列组合
import itertools
#独立T检验
from scipy.stats import ttest_ind
#配对T检验
from scipy.stats import ttest_rel
#mental
group1=[2,2,3,4,4,5,3,4,4,4]
#physical
group2=[4,4,3,5,4,1,1,2,3,3]
#medical
group3=[1,2,2,2,3,2,3,1,3,1]
list_groups=[group1,group2,group3]
list_total=group1+group2+group3
a=0.05
#one within group error,also know as random error
def SE(group):
se=0
mean1=np.mean(group)
for i in group:
error=i-mean1
se+=error**2
return se
'''
>>> SE(group1)
22.0
>>> SE(group2)
18.0
>>> SE(group3)
14.0
'''
#sum of squares within group error,also know as random error
def SSE(list_groups):
sse=0
for group in list_groups:
se=SE(group)
sse+=se
return sse
#误差总平方和
def SST(list_total):
sst=0
mean1=np.mean(list_total)
for i in list_total:
error=i-mean1
sst+=error**2
return sst
#SSA,between-group sum of squares 组间平方和,公式1:ssa=sst-sse
def SSA(list_groups,list_total):
sse=SSE(list_groups)
sst=SST(list_total)
ssa=sst-sse
return ssa
#SSA,between-group sum of squares 组间平方和
def SSA1(list_groups,list_total):
mean_total=np.mean(list_total)
ssa=0
for group in list_groups:
group_mean=np.mean(group)
distance=(mean_total-group_mean)**2
ssa+=distance
ssa=ssa*5
return ssa
#处理效应均方
def MSA(list_groups,list_total):
ssa=SSA(list_groups,list_total)
msa=ssa/(len(list_groups)-1)*1.0
return msa
# 误差均方
def MSE(list_groups,list_total):
sse=SSE(list_groups)
mse=sse/(len(list_total)-1*len(list_groups))*1.0
return mse
#F score
def F(list_groups,list_total):
msa=MSA(list_groups,list_total)
mse=MSE(list_groups,list_total)
ratio=msa/mse*1.0
return ratio
'''
>>> F(list_groups,list_total)
22.592592592592595
'''
#LSD检验有问题,需要核对,不如配对T检验准确
#LSD(least significant difference)最小显著差异
def LSD(list_groups,list_total,sample1,sample2):
mean1=np.mean(sample1)
mean2=np.mean(sample2)
distance=abs(mean1-mean2)
print"distance:",distance
#t检验的自由度
df=len(list_total)-1*len(list_groups)
mse=MSE(list_groups,list_total)
print"MSE:",mse
t_value=stats.t(df).isf(a/2)
print"t value:",t_value
lsd=t_value*math.sqrt(mse*(1.0/len(sample1)+1.0/len(sample2)))
print "LSD:",lsd
if distance<lsd:
print"no significant difference between:",sample1,sample2
else:
print"there is significant difference between:",sample1,sample2
#正态分布测试
def check_normality(testData):
#20<样本数<50用normal test算法检验正态分布性
if 20<len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.normaltest(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print"use normaltest"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print"use normaltest"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
#样本数小于50用Shapiro-Wilk算法检验正态分布性
if len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.shapiro(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use shapiro:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use shapiro:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
if 300>=len(testData) >=50:
p_value= lillifors(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use lillifors:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use lillifors:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
if len(testData) >300:
p_value= stats.kstest(testData,'norm')[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use kstest:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use kstest:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
#对所有样本组进行正态性检验
def NormalTest(list_groups):
for group in list_groups:
#正态性检验
status=check_normality(group1)
if status==False :
return False
#排列组合函数
def Combination(list_groups):
combination= []
for i in range(1,len(list_groups)+1):
iter = itertools.combinations(list_groups,i)
combination.append(list(iter))
#需要排除第一个和最后一个
return combination[1:-1][0]
'''
Out[57]:
[[([2, 3, 7, 2, 6], [10, 8, 7, 5, 10]),
([2, 3, 7, 2, 6], [10, 13, 14, 13, 15]),
([10, 8, 7, 5, 10], [10, 13, 14, 13, 15])]]
'''
#多重比较
def Multiple_test(list_groups):
combination=Combination(list_groups)
for pair in combination:
LSD(list_groups,list_total,pair[0],pair[1])
#discriptive statistcs
print "discriptive statistcs----------------------------------------------"
print "group1 mean",np.mean(group1)
print "group2 mean",np.mean(group2)
print "group3 mean",np.mean(group3)
#对所有样本组进行正态性检验
print"M=Normality test:-----------------------------------"
NormalTest(list_groups)
#方差齐性检测
print"levene test:-----------------------------------"
leveneResult=scipy.stats.levene(group1,group2,group3)
leveneScore=leveneResult[0]
p_levene=leveneResult[1]
if p_levene<0.05:
print"levene test is not fit,be attention!"
else:
print"levene test is ok"
'''
H0成立,三组数据方差无显著差异
Out[9]: LeveneResult(statistic=0.24561403508771934, pvalue=0.7860617221429711)
'''
print "result--------------------------------------------------"
f_score=F(list_groups,list_total)
print"F score:",f_score
#sf 为生存函数survival function
#组数自由度
df1=len(list_groups)-1
#所有样本的自由度
df2=len(list_total)-1*len(list_groups)
probability=f.sf(f_score,df1,df2)
print"p value:",probability
'''
Out[28]: 8.5385924542746692e-05
'''
if probability<0.05:
print"there is significance,H1 win"
else:
print"there is no significance,H0 win"
#多重比较
print"multiple test----------------------------------------------"
print"Multiple test",Multiple_test
Multiple_test(list_groups)
贾俊平书里的例子,综合多重检验和LSD方法结果一致
#居民区
group1=[265,310,220,290,350,300,445,480,500,430,428,530]
#商业区
group2=[410,305,450,380,310,390,590,480,510,470,415,390]
#写字楼
group3=[180,290,330,220,170,256,290,283,260,246,275,320]

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Import standard packages
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
import pandas as pd
import os
# additional packages
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.join('..', '..', 'Utilities'))
try:
# Import formatting commands if directory "Utilities" is available
from ISP_mystyle import showData
except ImportError:
# Ensure correct performance otherwise
def showData(*options):
plt.show()
return
# Other required packages
from statsmodels.stats.multicomp import (pairwise_tukeyhsd,
MultiComparison)
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
from statsmodels.stats.anova import anova_lm
from statsmodels.stats.libqsturng import psturng
def setData():
''' Set up the data, as a structured array. '''
# The first and last field are 32-bit intergers; the second field is an
# 8-byte string. Note that here we can also give names to the individual
# fields!
data = np.rec.array([
( 1, 'resident', 265 ),
( 2, 'resident', 310 ),
( 3, 'resident', 220 ),
( 4, 'resident', 290 ),
( 5, 'resident', 350 ),
( 6, 'resident', 300 ),
( 7, 'resident', 445 ),
( 8, 'resident', 480 ),
( 9, 'resident', 500 ),
( 10, 'resident', 430),
( 11, 'resident', 428),
( 12, 'resident', 530 ),
( 13, 'commercial', 410 ),
( 14, 'commercial', 305 ),
( 15, 'commercial', 450 ),
( 16, 'commercial', 380 ),
( 17, 'commercial', 310 ),
( 18, 'commercial', 390 ),
( 19, 'commercial', 590 ),
( 20, 'commercial', 480 ),
( 21, 'commercial', 510 ),
( 22, 'commercial', 470 ),
( 23, 'commercial', 415 ),
( 24, 'commercial', 390 ),
( 25, 'officeBuilding', 180 ),
( 26, 'officeBuilding', 290 ),
( 27, 'officeBuilding', 330 ),
( 28, 'officeBuilding', 220 ),
( 29, 'officeBuilding', 170),
( 30, 'officeBuilding', 256),
( 31, 'officeBuilding', 290 ),
( 32, 'officeBuilding', 283 ),
( 33, 'officeBuilding', 260),
( 34, 'officeBuilding', 246),
( 35, 'officeBuilding', 275),
( 36, 'officeBuilding', 320),
], dtype=[('idx', '<i4'),
('Treatment', '|S8'),
('StressReduction', '<i4')])
return data
def doAnova(data):
'''one-way ANOVA'''
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
model = ols('StressReduction ~ C(Treatment)',df).fit()
anovaResults = anova_lm(model)
print(anovaResults)
if anovaResults['PR(>F)'][0] < 0.05:
print('One of the groups is different.')
def doTukey(data, multiComp):
'''Do a pairwise comparison, and show the confidence intervals'''
print((multiComp.tukeyhsd().summary()))
# Calculate the p-values:
res2 = pairwise_tukeyhsd(data['StressReduction'], data['Treatment'])
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
numData = len(df)
numTreatments = len(df.Treatment.unique())
dof = numData - numTreatments
# Show the group names
print((multiComp.groupsunique))
# Generate a print -------------------
# Get the data
xvals = np.arange(3)
res2 = pairwise_tukeyhsd(data['StressReduction'], data['Treatment'])
errors = np.ravel(np.diff(res2.confint)/2)
# Plot them
plt.plot(xvals, res2.meandiffs, 'o')
plt.errorbar(xvals, res2.meandiffs, yerr=errors, fmt='o')
# Put on labels
pair_labels = multiComp.groupsunique[np.column_stack(res2._multicomp.pairindices)]
plt.xticks(xvals, pair_labels)
# Format the plot
xlim = -0.5, 2.5
plt.hlines(0, *xlim)
plt.xlim(*xlim)
plt.title('Multiple Comparison of Means - Tukey HSD, FWER=0.05' +
'
Pairwise Mean Differences')
# Save to outfile, and show the data
outFile = 'multComp.png'
showData(outFile)
def Holm_Bonferroni(multiComp):
''' Instead of the Tukey's test, we can do pairwise t-test '''
# First, with the "Holm" correction
rtp = multiComp.allpairtest(stats.ttest_rel, method='Holm')
print((rtp[0]))
# and then with the Bonferroni correction
print((multiComp.allpairtest(stats.ttest_rel, method='b')[0]))
# Any value, for testing the program for correct execution
checkVal = rtp[1][0][0,0]
return checkVal
def main():
# Get the data
data = setData()
# Do a one-way ANOVA
doAnova(data)
#Then, do the multiple testing
multiComp = MultiComparison(data['StressReduction'], data['Treatment'])
doTukey(data, multiComp) # Tukey's HSD test
checkVal = Holm_Bonferroni(multiComp) # Alternatives to Tukey's HSD test
return checkVal # this is only for regression testing of the program
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
贾俊平书里的例子,综合多重检验和LSD方法结果一致
#居民区
group1=[265,310,220,290,350,300,445,480,500,430,428,530]
#商业区
group2=[410,305,450,380,310,390,590,480,510,470,415,390]
#写字楼
group3=[180,290,330,220,170,256,290,283,260,246,275,320]

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scipy,math
from scipy.stats import f
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.stats as stats
# additional packages
from statsmodels.stats.diagnostic import lillifors
#多重比较
from statsmodels.sandbox.stats.multicomp import multipletests
#用于排列组合
import itertools
#独立T检验
from scipy.stats import ttest_ind
#配对T检验
from scipy.stats import ttest_rel
#居民区
group1=[265,310,220,290,350,300,445,480,500,430,428,530]
#商业区
group2=[410,305,450,380,310,390,590,480,510,470,415,390]
#写字楼
group3=[180,290,330,220,170,256,290,283,260,246,275,320]
list_groups=[group1,group2,group3]
list_total=group1+group2+group3
a=0.05
#one within group error,also know as random error
def SE(group):
se=0
mean1=np.mean(group)
for i in group:
error=i-mean1
se+=error**2
return se
'''
>>> SE(group1)
22.0
>>> SE(group2)
18.0
>>> SE(group3)
14.0
'''
#sum of squares within group error,also know as random error
def SSE(list_groups):
sse=0
for group in list_groups:
se=SE(group)
sse+=se
return sse
#误差总平方和
def SST(list_total):
sst=0
mean1=np.mean(list_total)
for i in list_total:
error=i-mean1
sst+=error**2
return sst
#SSA,between-group sum of squares 组间平方和,公式1:ssa=sst-sse
def SSA(list_groups,list_total):
sse=SSE(list_groups)
sst=SST(list_total)
ssa=sst-sse
return ssa
#SSA,between-group sum of squares 组间平方和
def SSA1(list_groups,list_total):
mean_total=np.mean(list_total)
ssa=0
for group in list_groups:
group_mean=np.mean(group)
distance=(mean_total-group_mean)**2
ssa+=distance
ssa=ssa*5
return ssa
#处理效应均方
def MSA(list_groups,list_total):
ssa=SSA(list_groups,list_total)
msa=ssa/(len(list_groups)-1)*1.0
return msa
# 误差均方
def MSE(list_groups,list_total):
sse=SSE(list_groups)
mse=sse/(len(list_total)-1*len(list_groups))*1.0
return mse
#F score
def F(list_groups,list_total):
msa=MSA(list_groups,list_total)
mse=MSE(list_groups,list_total)
ratio=msa/mse*1.0
return ratio
'''
>>> F(list_groups,list_total)
22.592592592592595
'''
#LSD检验有问题,需要核对,不如配对T检验准确
#LSD(least significant difference)最小显著差异
def LSD(list_groups,list_total,sample1,sample2):
mean1=np.mean(sample1)
mean2=np.mean(sample2)
distance=abs(mean1-mean2)
print"distance:",distance
#t检验的自由度
df=len(list_total)-1*len(list_groups)
mse=MSE(list_groups,list_total)
print"MSE:",mse
t_value=stats.t(df).isf(a/2)
print"t value:",t_value
lsd=t_value*math.sqrt(mse*(1.0/len(sample1)+1.0/len(sample2)))
print "LSD:",lsd
if distance<lsd:
print"no significant difference between:",sample1,sample2
else:
print"there is significant difference between:",sample1,sample2
#正态分布测试
def check_normality(testData):
#20<样本数<50用normal test算法检验正态分布性
if 20<len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.normaltest(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print"use normaltest"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print"use normaltest"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
#样本数小于50用Shapiro-Wilk算法检验正态分布性
if len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.shapiro(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use shapiro:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use shapiro:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
if 300>=len(testData) >=50:
p_value= lillifors(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use lillifors:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use lillifors:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
if len(testData) >300:
p_value= stats.kstest(testData,'norm')[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use kstest:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use kstest:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True
#对所有样本组进行正态性检验
def NormalTest(list_groups):
for group in list_groups:
#正态性检验
status=check_normality(group1)
if status==False :
return False
#排列组合函数
def Combination(list_groups):
combination= []
for i in range(1,len(list_groups)+1):
iter = itertools.combinations(list_groups,i)
combination.append(list(iter))
#需要排除第一个和最后一个
return combination[1:-1][0]
'''
Out[57]:
[[([2, 3, 7, 2, 6], [10, 8, 7, 5, 10]),
([2, 3, 7, 2, 6], [10, 13, 14, 13, 15]),
([10, 8, 7, 5, 10], [10, 13, 14, 13, 15])]]
'''
#多重比较
def Multiple_test(list_groups):
combination=Combination(list_groups)
for pair in combination:
LSD(list_groups,list_total,pair[0],pair[1])
#discriptive statistcs
print "discriptive statistcs----------------------------------------------"
print "group1 mean",np.mean(group1)
print "group2 mean",np.mean(group2)
print "group3 mean",np.mean(group3)
#对所有样本组进行正态性检验
print"M=Normality test:-----------------------------------"
NormalTest(list_groups)
#方差齐性检测
print"levene test:-----------------------------------"
leveneResult=scipy.stats.levene(group1,group2,group3)
leveneScore=leveneResult[0]
p_levene=leveneResult[1]
if p_levene<0.05:
print"levene test is not fit,be attention!"
else:
print"levene test is ok"
'''
H0成立,三组数据方差无显著差异
Out[9]: LeveneResult(statistic=0.24561403508771934, pvalue=0.7860617221429711)
'''
print "result--------------------------------------------------"
f_score=F(list_groups,list_total)
print"F score:",f_score
#sf 为生存函数survival function
#组数自由度
df1=len(list_groups)-1
#所有样本的自由度
df2=len(list_total)-1*len(list_groups)
probability=f.sf(f_score,df1,df2)
print"p value:",probability
'''
Out[28]: 8.5385924542746692e-05
'''
if probability<0.05:
print"there is significance,H1 win"
else:
print"there is no significance,H0 win"
#多重比较
print"multiple test----------------------------------------------"
print"Multiple test",Multiple_test
Multiple_test(list_groups)