题目:
From beginning till end, this message has been waiting to be conveyed.
For a given unordered multiset of n lowercase English letters ("multi" means that a letter may appear more than once), we treat all letters as strings of length 1, and repeat the following operation n - 1 times:
- Remove any two elements s and t from the set, and add their concatenation s + t to the set.
The cost of such operation is defined to be 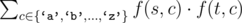 , where f(s, c) denotes the number of times character cappears in string s.
, where f(s, c) denotes the number of times character cappears in string s.
Given a non-negative integer k, construct any valid non-empty set of no more than 100 000 letters, such that the minimum accumulative cost of the whole process is exactly k. It can be shown that a solution always exists.
The first and only line of input contains a non-negative integer k (0 ≤ k ≤ 100 000) — the required minimum cost.
Output a non-empty string of no more than 100 000 lowercase English letters — any multiset satisfying the requirements, concatenated to be a string.
Note that the printed string doesn't need to be the final concatenated string. It only needs to represent an unordered multiset of letters.
12
abababab
3
codeforces
For the multiset {'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b'}, one of the ways to complete the process is as follows:
- {"ab", "a", "b", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 0;
- {"aba", "b", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "ab", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 0;
- {"abab", "aba", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "abab"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abababab"}, with a cost of 8.
The total cost is 12, and it can be proved to be the minimum cost of the process.
思路:
观察样例1很容易发现对于同一种字母,最小花费显然是是n*(n-1)/2,所以可以尝试用几个n*(n-1)/2去构造k。
具体怎么证明没多想,用代码测了下发现都是对的,就写了一发。
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 #define MP make_pair 6 #define PB push_back 7 typedef long long LL; 8 typedef pair<int,int> PII; 9 const double eps=1e-8; 10 const double pi=acos(-1.0); 11 const int K=1e6+7; 12 const int mod=1e9+7; 13 14 int k,cnt,ls,num,sum; 15 int main(void) 16 { 17 cin>>k; 18 if(k==0) 19 { 20 printf("a "); 21 return 0; 22 } 23 while(k>0) 24 { 25 ls=num=sum=0; 26 while(k>=sum) 27 ls=sum,num++,sum+=num; 28 k-=ls; 29 for(int i=1; i<=num; i++) 30 printf("%c",'a'+cnt); 31 if(k<=0)break; 32 cnt++; 33 } 34 return 0; 35 }