1 面向对象
一般地, 类是对象的类型模板, 实例是根据类创建的对象
但是在JavaScript中不区分类和实例, 而是通过原型(prototype)来实现面向对象编程
JavaScript不区分类和实例的情况就是, 实例是一个对象, 我们想要创建的类也是一个对象, 用
实例对象.__proto__ = 类对象;
来表明继承, 而且由于是对一个属性进行设定, 因此只能单继承
使用原型相当于继承
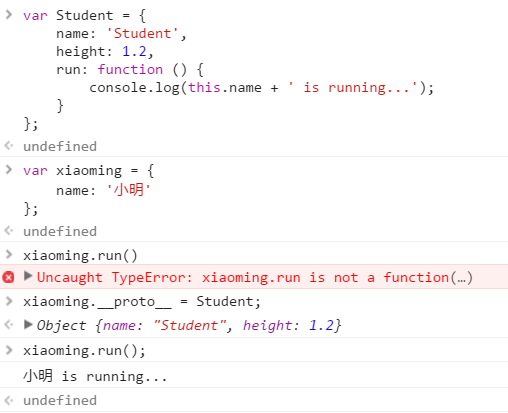
但是如果再给xiaoming绑定一个_proto_, 那原来绑定的东西就没有了(单继承)
使用__proto__并不是一般的使用方式, 一般的时候方式是编写一个类似于new的方法来创建一个对象
可以使用
Object.create(类对象);
来返回一个基于类对象的空的对象, 通过对该对象的属性进行绑定, 可以完成创建一个机遇类对象的对象(实例), 具体如下
// 原型对象(类): var Student = { name: 'Robot', height: 1.2, run: function () { console.log(this.name + ' is running...'); } }; function createStudent(name) { // 基于Student原型创建一个新对象: var s = Object.create(Student); // 初始化新对象: s.name = name; return s; } var xiaoming = createStudent('小明'); xiaoming.run(); // 小明 is running... xiaoming.__proto__ === Student; // true
2 创建对象
对象访问属性的过程:
在当前对象查找, 没有找到就找它原型对象有没有, 再没有就找object的原型上查找, 如果都没查找到, 就返回undefined
xiaoming -> xiaoming.prototype -> object.prototype -> null
constructor
该属性会获得该对象的prototype的源对象
关于prototype和constructor的关系
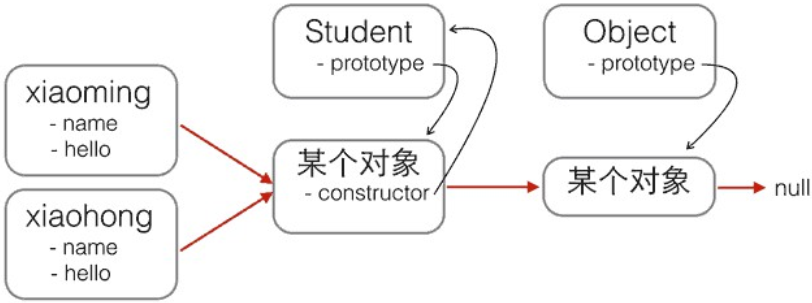
构造函数
由于之前都是类是一个对象, 在创建一个函数来生成一个实例
有没有类似于class类的一步到位既创建了类有可以生成实例的呢, 那就是构造函数了
构造函数实际上就是一个普通的函数, 函数内容就类似于定义一个类, 在生成对象的时候, 是调用new 函数名来创建
但是注意的是, 构造函数中的this指的就是新创建的对象, 而且该函数会默认返回this, 所以不要自己单独写return
由于构造函数与普通函数并没有区别, 因此也可以像普通函数那样直接使用, 但是这样场产生的this会出现异常, 因此为了区分普通函数与构造函数
一般地:
构造函数首字母大写
普通函数首字母小写
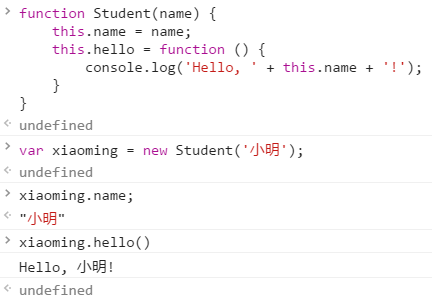
另外, 继承自相同类的不同对象, 得到的方法尽管在功能上是相同的, 但是是不一样的函数, 类似于python中绑定方法
要使不同的对象共享一个函数, 可以针对父类的prototype来绑定原来放在父类中的函数
function Student(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Student.prototype.hello = function () {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
};
在JavaScript中还可以写一个函数来专门封装new, 同时将传入的参数也一并用对象的方式整体传入, 这样就完成了一个封装性更高, 可用性更强的类
function Student(props) {
this.name = props.name || '匿名'; // 默认值为'匿名'
this.grade = props.grade || 1; // 默认值为1
}
Student.prototype.hello = function () {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
};
function createStudent(props) {
return new Student(props || {})
}
var xiaoming = createStudent({
name: '小明'
});
xiaoming.grade;
这样设置有一个很大的好处, 那就是传参十分方便, 因为实际上定义的props是一个对象数据类型, 绑定好了就不需要顺序对应, 想什么时候取值就什么时候取值
3 原型继承
由于JavaScript采用原型继承, 不存在Class这种类型, 因此无法像Java那样使用类的扩展来继承
要想继承一个类, 需要想办法把原型链修改为
new PrimaryStudent() ----> PrimaryStudent.prototype ----> Student.prototype ----> Object.prototype ----> null
可以参考道格拉斯的方法, 在中间创建一个空的函数来桥接
// PrimaryStudent构造函数:
function PrimaryStudent(props) {
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}
// 空函数F:
function F() {
}
// 把F的原型指向Student.prototype:
F.prototype = Student.prototype;
// 把PrimaryStudent的原型指向一个新的F对象,F对象的原型正好指向Student.prototype:
PrimaryStudent.prototype = new F();
// 把PrimaryStudent原型的构造函数修复为PrimaryStudent:
PrimaryStudent.prototype.constructor = PrimaryStudent;
// 继续在PrimaryStudent原型(就是new F()对象)上定义方法:
PrimaryStudent.prototype.getGrade = function () {
return this.grade;
};
// 创建xiaoming:
var xiaoming = new PrimaryStudent({
name: '小明',
grade: 2
});
xiaoming.name; // '小明'
xiaoming.grade; // 2
// 验证原型:
xiaoming.__proto__ === PrimaryStudent.prototype; // true
xiaoming.__proto__.__proto__ === Student.prototype; // true
// 验证继承关系:
xiaoming instanceof PrimaryStudent; // true
xiaoming instanceof Student; // true
可以简化为
function inherits(Child, Parent) {
var F = function () {};
F.prototype = Parent.prototype;
Child.prototype = new F();
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
}
复用方式为
function Student(props) {
this.name = props.name || 'Unnamed';
}
Student.prototype.hello = function () {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}
function PrimaryStudent(props) {
Student.call(this, props);
this.grade = props.grade || 1;
}
// 实现原型继承链:
inherits(PrimaryStudent, Student);
// 绑定其他方法到PrimaryStudent原型:
PrimaryStudent.prototype.getGrade = function () {
return this.grade;
};
4 class继承
由于原型继承尽管简单, 但是理解起来困难, 因此ES6提供了class继承
编写类基本格式如下
class 类名{
constructor(参数列表){
构造函数函数体;
}
函数名(参数列表){
一般函数的函数体;
}
}
具体定义和使用如
class Student {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
hello() {
alert('Hello, ' + this.name + '!');
}
}
var xiaoming = new Student('小明');
xiaoming.hello();
继承的基本格式如下
class 子类名 extends 父类名{
constructor(参数列表){
super(参数列表);
子类构造方法体;
}
方法名(参数列表){
函数体;
}
}
具体代码为
class PrimaryStudent extends Student {
constructor(name, grade) {
super(name); // 记得用super调用父类的构造方法!
this.grade = grade;
}
myGrade() {
alert('I am at grade ' + this.grade);
}
}
由于现在不是全面支持ES6, 因此现在还不普及, 但是如果真的要使用的话, 可以使用Babel工具来将写好的class继承转化为原型继承