一,MVC将代码分为三个部分,分别为视图(jsp),模型(javaBean),控制部分(servlet);
视图基本为 jsp 文件,主要内容为界面的html代码,负责显示界面;
模型为 javaBean ,负责与数据库交互;
控制部分为 servlet 充当,负责处理业务逻辑与页面切换。
二,MVC包括 Model1 和 Model2 两个模型;
1. Model1 模型程序流程如下图:
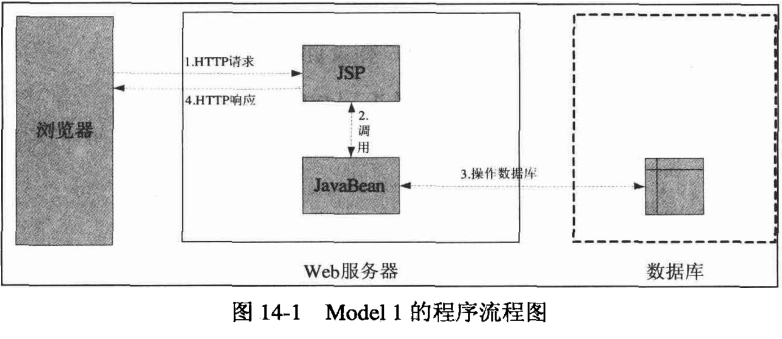
Model1 中界面显示部分与界面跳转,业务逻辑都由 jsp 负责,导致 jsp 中充满大量java脚本代码,
代码重复率高,可用性低,程序功能的微小的修改往往引起大量的修改,优点是容易掌控。
2. Model2 模型程序流程如下图:
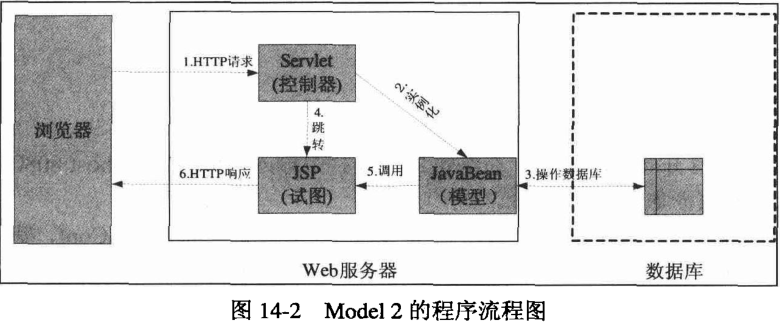
Model2 模型中分层更加明显,jsp 负责页面显示,javaBean负责数据库操作与业务逻辑,servlet
则是核心的调度部分,负责调用 javaBean 来处理业务逻辑,同时负责界面调度切换。优点是程序
执行更加清晰,方便后期功能的添加与修改。
三,基于MVC模型的用户登陆实例:
1.界面部分(login.jsp登陆界面,login_success.jsp登陆成功界面,login_failure.jsp登录失败界面)
login.jsp:

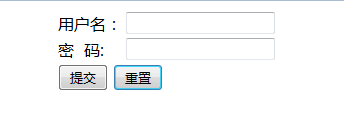
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>用户登录</title> </head> <body> <form action="../loginConf" method="post"> <center> <table> <tr> <td>用户名:</td> <td><input type="text" name="uname" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>密 码:</td> <td><input type="password" name="password" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2"><input type="submit" value="提交" /> <input type="reset" value="重置" /></td> </tr> </table> </center> </form> </body> </html>
效果图:
login_success.jsp:

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>登陆成功</title> </head> <body> <% if(session.getAttribute("login")!=null&&session.getAttribute("login").equals("true")) { %> <center> <h2>登陆成功</h2> </center> <% } else { %> <jsp:forward page="login.jsp"></jsp:forward> <% } %> </body> </html>
效果图:

login_failure.jsp

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>登录失败</title>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h2>登录失败</h2>
</center>
</body>
</html>
效果图:

2.servlet(controller)
loginConf.java

package com.javaweb.mvc; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; /** * Servlet implementation class loginConf */ @WebServlet("/loginConf") public class loginConf extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public loginConf() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //设置编码格式 response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8"); request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); //获取参数 String uname = request.getParameter("uname"); String password = request.getParameter("password"); //获取session HttpSession session = request.getSession(); //业务逻辑判断 loginCheck lc = new loginCheck(); if(lc.isLogin(uname, password)) { session.setAttribute("login", "true"); request.getRequestDispatcher("MVC/login_success.jsp").forward(request, response); } else { request.getRequestDispatcher("MVC/login_failure.jsp").forward(request, response); } } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub doGet(request, response); } }
3.javaBean(业务逻辑Model)

package com.javaweb.mvc; public class loginCheck { public boolean isLogin(String uname,String password) { if(uname.equals("wei")&&password.equals("123")) { return true; } else { return false; } } }
