一、数据类型:
1)数据类型
1、整数(int)
2、浮点数(float)
3、字符串(string)
4、列表(list)
5、 元组(tuple)
6、字典(dict): key和value是一一对应的,key必须是唯一的,字典是无序的
元组和列表的区别:
区别一:元组定义是() / list 定义是[]
区别二:元组里面的元素只能读,无法增删改
字典:
dict = {}
dict['one'] = "This is one"
dict[2] = "This is second"
apndict = {'apn': 'cmnet', 'username':'test', 'password': 1234}
print(dict['one'] ) # 输出键为'one' 的值
print(dict[2]) # 输出键为 2 的值
print(apndict) # 输出完整的字典
print(apndict.keys()) # 输出所有键
print(apndict.values() ) # 输出所有值
运行结果:
》》
This is one
This is second
{'apn': 'cmnet', 'username': 'test', 'password': 1234}
dict_keys(['apn', 'username', 'password'])
dict_values(['cmnet', 'test', 1234])
2)字符串切片:
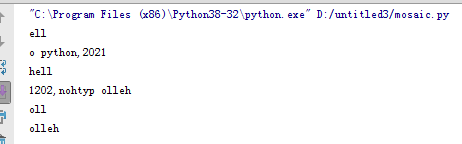
'''字符串的切片'''
h = 'hello python,2021'
print(h[1:4]) # 丛1 到4
print(h[4:]) # 丛4开始往后
print(h[:4]) # 丛前面开始到4
print(h[::-1]) #字符串反转
print(h[4:1:-1])# 丛1到4反着取
print(h[4::-1]) # 丛4往前反着取
字符串的简单函数:
计算字符串的长度:len()
print(len(h))
》17
统计某个字符出现的次数:.count()
print(h.count('o'))
》2
3)布尔值:bool (True,False),在编程的世界里,非0为真,0为假
a = None
b = ''
c = 0
print(bool(a)) # False
print(bool(b)) # False
print(bool(c)) #False
d = 1
e = -1
f = '0'
print(bool(d)) # True
print(bool(e)) # True
print(bool(f)) # True
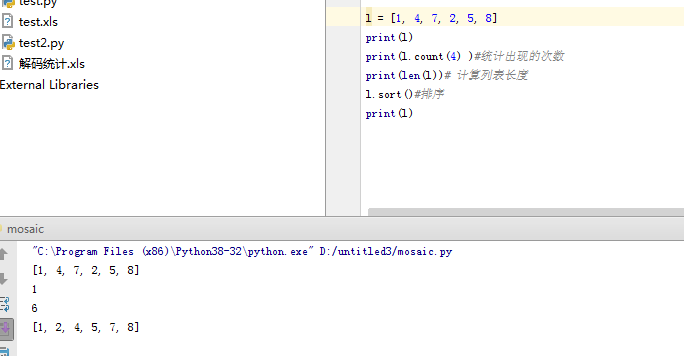
4)列表:list(常用操作:增删改)
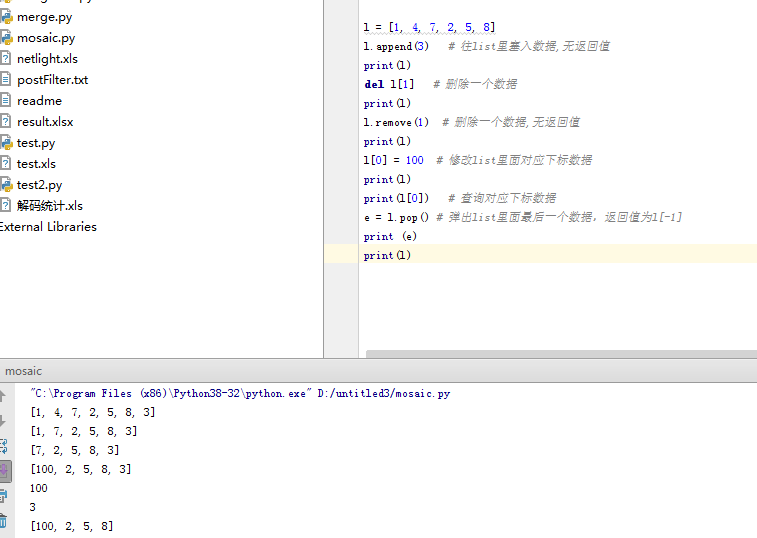
list的常用函数:len()计算长度,sort()排序,count()统计某个字符出现的次数
二、控制语句:
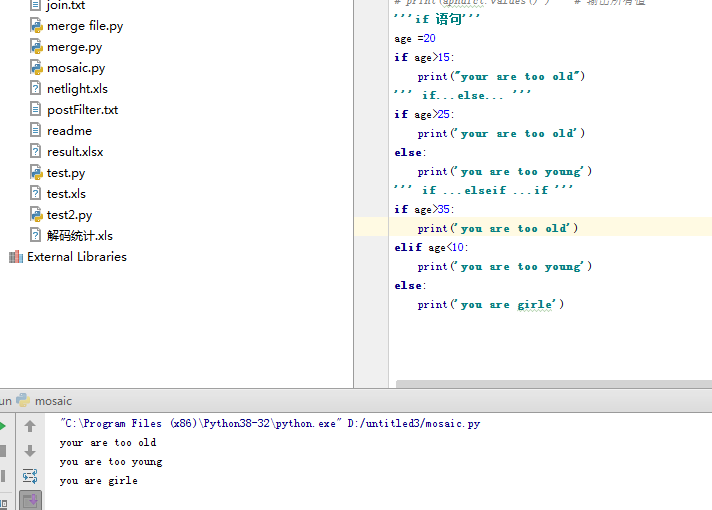
1) if
2) for 语句
a、 遍历字符串:
str = "this is test"
for i in str:
print(i)
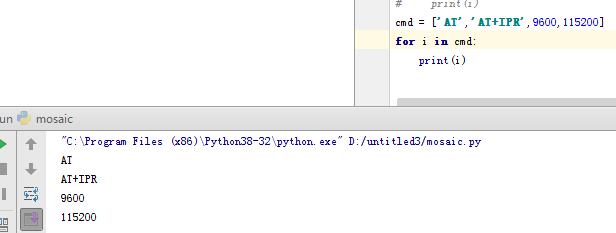
b、遍历list:
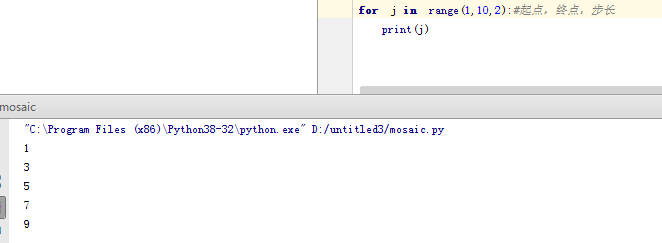
c、range 的应用,通常可以用来设置某个流程循环几次


while
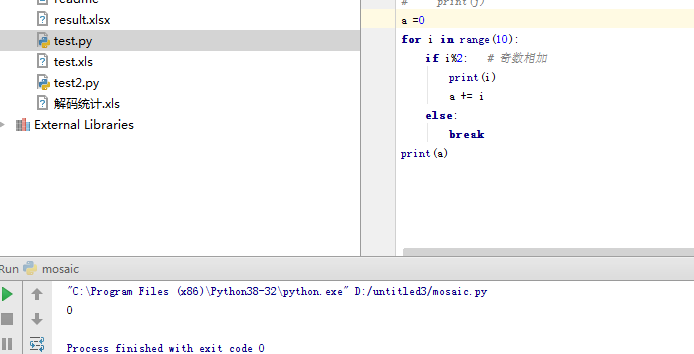
循环中break 和continue 的应用:
break:结束for循环
continue:跳出本次循环继续下一个
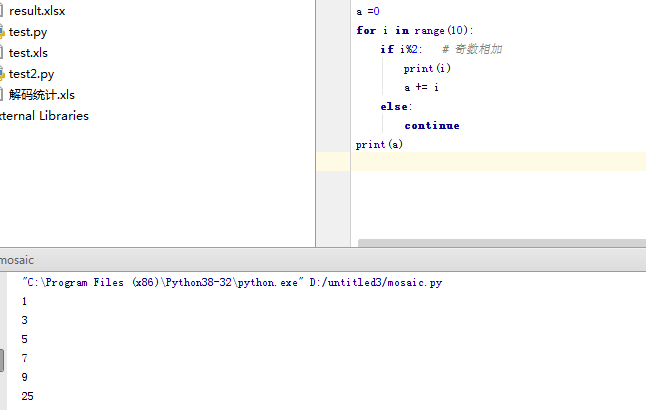
break:直接退出for循环
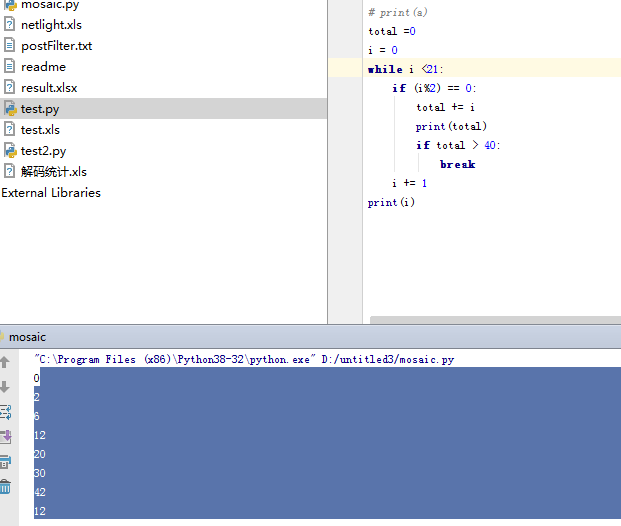
while 循环:

例如:实现1~20的偶数相加,当总和大于40时退出循环