一、collection框架
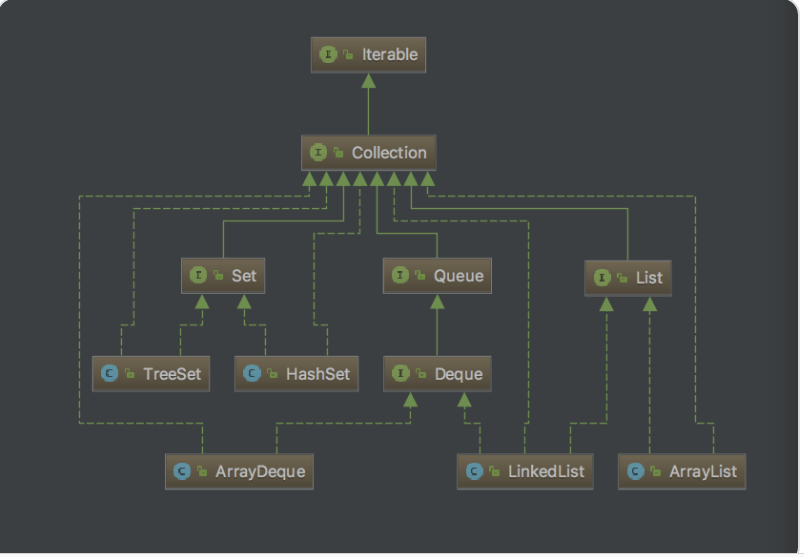
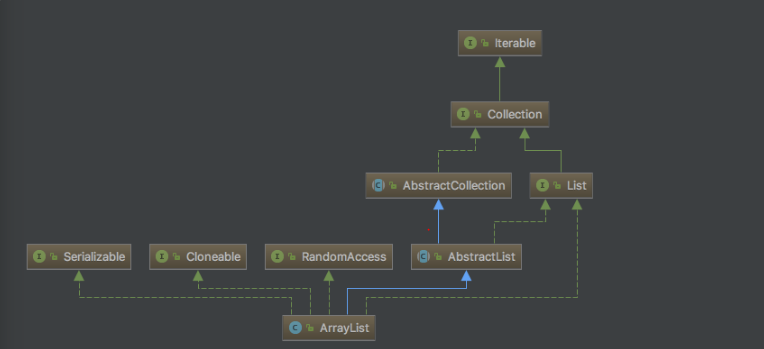
(1)LIST
list是一种collection,作用是收集对象,并以索引的方式保留收集的对象的顺序。其操作类之一就是Java.utl.ArrayList.ArrayList特性:随机查找(list.get[i]),ArrayList内部就是用Object来保存收集的对象。此时就考虑到了数组的特性。根据数据结构内容我们只数组的好处就是随机存储速度快,排序等就可以考虑使用ArrayList

package Learn; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Scanner; public class ListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List name=new ArrayList();//收集信息的list collectNameTo(name);//收集函数 System.out.println("输出访客名单:"); printUpperCase(name);//输出收集到的信息 } /** *@author wbm *@param List *@deprecated通过控制台输入访客的名称,如果遇到quit则退出输入访客名称的循环,每次循环都把收集到的信息通过List.add(信息对象)收集到list中去 */ static void collectNameTo(List names){ Scanner console=new Scanner(System.in);//控制台输入信息 while(true){ System.out.println("访客名称:"); String name=console.nextLine(); if(name.equals("quit")){ break; } names.add(name);//把控制台输入的信息放入到list中去 } } /** *通过for循环把传进来的List通过索引获取list元素并转换为string性,然后通过string的toUpperCase()转为大写 */ static void printUpperCase(List names){ for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); i++) { String name=(String) names.get(i);//通过索引获得收集的信息 System.out.println(name.toUpperCase()); } } }
LinkedList特性:采用链接结构。链接结构简单代码如下。

package Learn; public class LinkListDemo { private class Node{ Object o; Node next; Node(Object o){ this.o=o; } } private Node first; public void add(Object elem){ Node node=new Node(elem); if(first==null){ first=node; } else{ append(node); } } private void append(Node node){ Node last=first; while(first.next!=null){ last=last.next; } last.next=node; } public int size(){ int count=0; Node last=first; while(last.next!=null){ last=last.next; count++; } return count; } public Object get(int index){ checkSize(index); return findElemof(index); } private void checkSize(int index)throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{ int size=size(); if(index>=size){ throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( String.format("index:%d size:%d", index,size)); } } private Object findElemof(int index){ int count=0; Node last=first; while(count<index){ last=last.next; count++; } return last.next; } }
(2)set
也是收集对象,但是对象相同则不重复收集。知道不重复单词个数有几个代码如下。

public static void mian(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入英文"); Set words=tokenSet(scanner.nextLine());//scanner.nextLine()String类型 System.out.printf("不重复的字有%d个:%s%n",words.size(),words); } static Set tokenSet(String line){ String[] tokens=line.split(" ");//根据空白切割字符串 return new HashSet(Arrays.asList(tokens));//使用HashSet收集字符串 }
使用set时得告诉怎样的对象是相同,这时要用对象的hashCode()和equals()来判断对象是够相同。HashSet的操作哦该娘是,在内存中开设空间,每个空间都会有哈希编码,这些空间称为哈希桶,如果对象要加入哈希桶,则要调用对象的hashcode(),并尝试放入对应的哈希桶中,如果哈希桶中没有对象就放入,如果有对象就调用equals()进行比较。有无equals和hashcode的对比代码如下

package Learn; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; class Student { private String name; private String number; Student(String name,String number){ this.name=name; this.number=number; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", number=" + number + "]"; } } package Learn; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class Students { public static void main(String[] args) { Set students=new HashSet(); students.add(new Student("b","c")); students.add(new Student("b","c")); students.add(new Student("q","c")); System.out.println(students); } } 结果: [Student [name=q, number=c], Student [name=b, number=c], Student [name=b, number=c]] package Learn; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; class Student { private String name; private String number; Student(String name,String number){ this.name=name; this.number=number; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((number == null) ? 0 : number.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Student other = (Student) obj; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; if (number == null) { if (other.number != null) return false; } else if (!number.equals(other.number)) return false; return true; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", number=" + number + "]"; } } 结果: [Student [name=b, number=c], Student [name=q, number=c]]
java.util.TreeSet不仅有收集不重复对象的能力,还可以用红黑树的方式排序收集到的对象,条件就是收集到的对象必须是Comparable(否则会抛出ClassCastException),或者是在创建的是后指定comparator对象
(3)quene
支持队列操作,收集的对象加入至尾部,取得的对象时从前部,quene继承自collection所以有add、remove、element等方法然而quene定义了自己的offer、poll、peak等方法主要区别在于,add、remove、element等方法操作失败时会抛出异常,而offer、poll、peak会返回特定的值。对象需要使用队列且长度受限是用通常使用poll、offer、peak方法。从架构图可知linkedList不仅操作了queue的行为也操作了list的行为。所以可以将linkedlist当做队列来使用。
简单的代码实例如下:

package Learn; public interface Request { void execute(); } package Learn; import java.util.*; /** * offer是在队列前端加入对象成功会返回trues失败会返回false。 * poll是去除队列的前端对象,若队列为空则返回null。 * peak是取得前端对象但是不取出若为空则返回null。 * */ public class RequestQuene{ public static void main(String[] args) { Queue requests=new LinkedList(); offerRequestTo(requests); process(requests); } static void offerRequestTo(Queue requests){ //请求加入队列 for(int i=1;i<6;i++){ Request request=new Request(){ @Override public void execute() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.printf("处理数据%f%n",Math.random()); } }; requests.offer(request); System.out.println(requests.offer(request)); } } static void process(Queue requests){ //处理队列中的请求 while(requests.peek()!=null){ Request request=(Request)requests.poll(); request.execute(); } } }
如果想要对队列的前端和尾端进行操作,在前端加入对象和取出对象,在尾端加入对象和取出对象,queue的子接口Deque就定义了该行为。deque中定义addFirst()、removeFirst()、getFirst()、addLast()、
removeLast()、getLast()等方法,操作失败时会抛出异常。而offerFirst()、pollFirst()、peekFirst()、offerLast()、pollLast()、peekLast()操作失败会返回特定的值。java.util.ArrayDeque操作了Deque接口,操作使用容量有限的堆栈的简单实例如下

package Learn; import java.util.*; public class Stack { private Deque elems=new ArrayDeque(); private int capacity; Stack(int capacity){ this.capacity=capacity; } public boolean push(Object elem){ if(isFull()){ return false; } else{ return elems.offerLast(elem); } } private boolean isFull(){ return elems.size()+1>capacity; } public Object pop(){ return elems.pollLast(); } public Object peek(){ return elems.peekLast(); } public int size(){ return elems.size(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Stack stack=new Stack(5); stack.push("justin"); stack.push("wbm"); stack.push("wcy"); System.out.println(stack.pop()); System.out.println(stack.pop()); System.out.println(stack.pop()); } } 结果: wcy wbm justin 堆栈是先进后出
queue的操作类之一java.util.PriorityQueue也是,收集至PriorityQueue的对象,会根据你指定的优先权来决定对象在队列中的顺序,优先的告知,要不是对象必须是comparable,或者是在创建PriorityQueue时指定comparator对象。
(3)Interable与Iterator
iterator方法JDK5之前是定义在collection中在JDK5之后定义在iterable;具体的一些好处和细节如下代码。

//收集LIst对象 static void forEachList(List list){ int size=list.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ System.out.println(list.get(i)); } } //收集set对象 static void forEachSet(Set set){ for(Object o:set.toArray()){ System.out.println(o); } } //收集queue对象 static void forEachQueue(Queue queue){ while(queue.peek()!=null){ System.out.println(queue.poll()); } } //含有这个方法的类是util,那么你就可以指定使用util.<String> elemOf()的方式指定E的实际类型 public static<E> E elemOf(E[] objs,int index){ return objs[index]; } //无论是Queue、List、Set都会有iterator方法JDK5之前是定义在collection中在JDK5之后定义在iterable static void forEachCollection(Collection collection){ Iterator iterator=collection.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } static void forEachIterable(Iterable iterable){ Iterator iterator=iterable.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } }

package Learn; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.List; public class forEach { public static void main(String[] args) { List names=Arrays.asList("ww","bb","mm");//静态方法aslist接收不定长自变量将其指定为List forEach(names);//list是一种Iterable. forEach(new HashSet(names));//List是一种collection,hashSet是一种collection接收collection的构造函数所以list可以用来创建hashset forEach(new ArrayDeque(names));//同理 } static void forEach(Iterable iterable){ for (Object object : iterable) { System.out.println(object); } } }
(4)comparable与comparator
1. comparable(comparaTo())
在收集对象之后,对对象排序是常用的动作,我们不用亲自操作排序算法,java.util.collections

List numbers=Arrays.asList(10,5,1,9,8,9,7);
Collections.sort(numbers);
System.out.println(numbers);
结果为:[1, 5, 7, 8, 9, 9, 10]
如果没有说明list元素的比较会出现错误

package Learn; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; class Student { private String name; private String number; Student(String name,String number){ this.name=name; this.number=number; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", number=" + number + "]"; } } package Learn; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class Students { public static void main(String[] args) { List students=Arrays.asList(new Student("b","c"),new Student("b","c"),new Student("q","c")); Collections.sort(students); System.out.println(students); } } 出现: java.lang.ClassCastException:
collections.sort()的操作对象必须操作java.lang.comparable接口,这个接口有compareTo()方法的返回值必须大于0,等于0或小于0的整数。

package Learn; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { private String name; private String number; Student(String name,String number){ this.name=name; this.number=number; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", number=" + number + "]"; } @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return Integer.parseInt(this.number)-Integer.parseInt(o.number); } } package Learn; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class Students { public static void main(String[] args) { List students=Arrays.asList(new Student("b","1"),new Student("b","3"),new Student("q","2")); Collections.sort(students); System.out.println(students); } } 结果为 [Student [name=b, number=1], Student [name=q, number=2], Student [name=b, number=3]]
2.compatator(compare())
如果对象无法操作comparable的话呢?比如String本身有操作Comparable,所以可以按字母的排序如果我想要把字母排序的顺序反过来呢?String是final的类型不能被继承所以无法重新定义compareTo()方法。Collection有另一个重载版本,可以接受java.lang.Comparator接口的操作对象。流程:1.定义一个comparator:class StringComparator implements<String>{ public int compare(String s1,String s2){ return s1.compareTo(s2);}} 2.调用:Collections.sort(List,new StringComparator());

package Learn; import java.util.Comparator; public class StringComparator implements Comparator <String> { @Override public int compare(String o1, String o2) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return -o1.compareTo(o2); } } package Learn; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class sort { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> words=Arrays.asList("B","A","C"); Collections.sort(words,new StringComparator()); System.out.println(words); } } 结果 [C, B, A]
二、Map框架
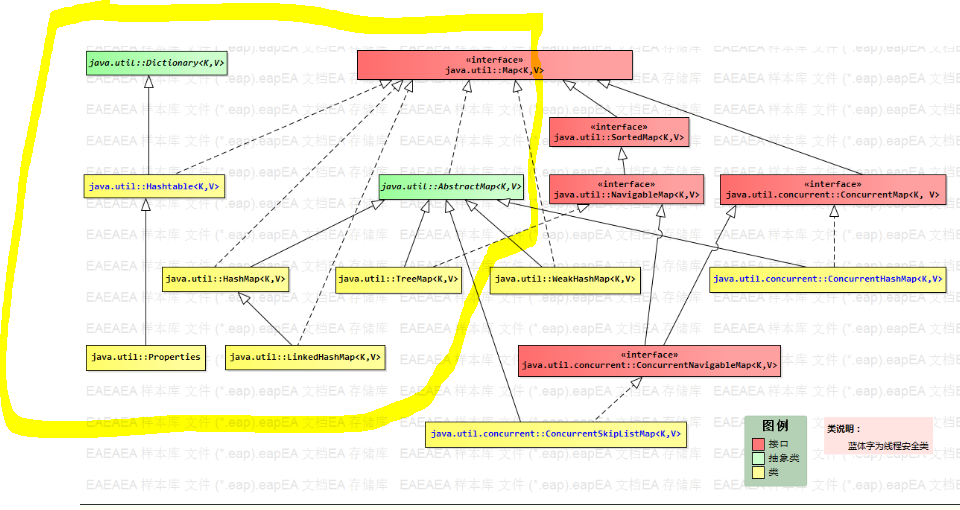
1.hashMap
1)概述
基于哈希表的Map接口的非同步实现。实现所有的可选映射操作,允许使用null键和null值。此类不保证映射的顺序。
2)数据结构

3)简单使用HashMap
对于Map而言键值是不会重复,判断键是否重复式根据hashcode和equals(),所以作为键的对象必须操作hashcode()与equals()

public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> messages=new HashMap<String,String>(); messages.put("1", "one"); messages.put("2", "two"); messages.put("3", "three"); Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); String message=messages.get(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.println(message); System.out.println(messages); } 结果为: 1 one {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
2.TreeMap
键的部分会排序,条件式作为键的对象必须操作Comparable接口,或者是在创建TreeMap时指定Comparator接口的对象。

public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,String> messages=new TreeMap<String,String>(); messages.put("1", "one"); messages.put("2", "two"); messages.put("3", "three"); System.out.println(messages); } } 结果为: {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
3.使用Properties

Properties props=new Properties(); props.setProperty("username", "justin"); props.setProperty("password", "123456"); System.out.println(props.getProperty("username")); System.out.println(props.getProperty("password")); //从文档中读取属性 //文档内容a.properties /* cc.openhome.username=justin cc.openhome.password=123456 */ Properties props=new Properties(); props.load(new FileInputStream("args[0]")); System.out.println(props.getProperty("cc.openhome.username")); System.out.println(props.getProperty("cc.openhome.password"));
三、简单泛型的使用
在使用Collection收集对象时,由于事先不知道对象的形态使用的是Object来收集,取回对象也是Object,所以执行期间失去了形态的信息。所以取回对象之后要记得对象的真正的类型,然后让对象重新扮演
自己的类型。

List names=Array.asList("ww","bb","mm");
String name=(String)name.get(0);
ArrayList<String> names= new ArrayList<String>();
names.add("justin");
names.add("wbm");
names.add(new Long(10));//编译会出错没法通过。
String name1=names.get(0);
string nmae2=names.get(1);
静态方法上定义类型
//含有这个方法的类是util,那么你就可以指定使用util.<String> elemOf()的方式指定E的实际类型 public static<E> E elemOf(E[] objs,int index){ return objs[index]; }
补充:
Utilizes
Collections:是针对集合类的一个帮助类,提供了操作集合的工具方法:一系列静态方法实现对各种集合的搜索、排序、线程
安全化等操作。
Arrays:针对数组的一个帮助类,提供了操作arrays的工具方法:一系列静态方法对各种数组的搜索、排序等操作
