Given a binary tree root and an integer target, delete all the leaf nodes with value target.
Note that once you delete a leaf node with value target, if it's parent node becomes a leaf node and has the value target, it should also be deleted (you need to continue doing that until you can't).
Example 1:
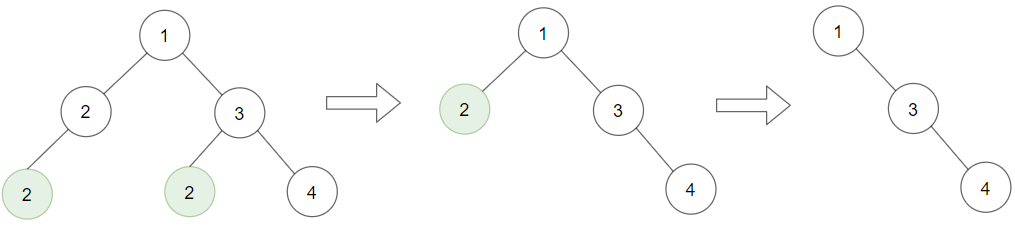
Input: root = [1,2,3,2,null,2,4], target = 2 Output: [1,null,3,null,4] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed (Picture in left). After removing, new nodes become leaf nodes with value (target = 2) (Picture in center).
Example 2:
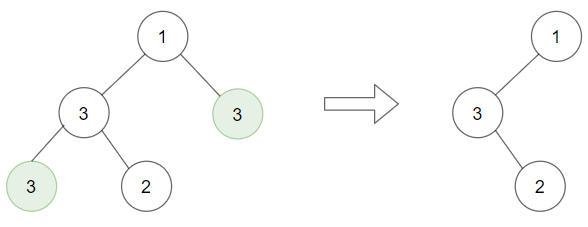
Input: root = [1,3,3,3,2], target = 3 Output: [1,3,null,null,2]
Example 3:
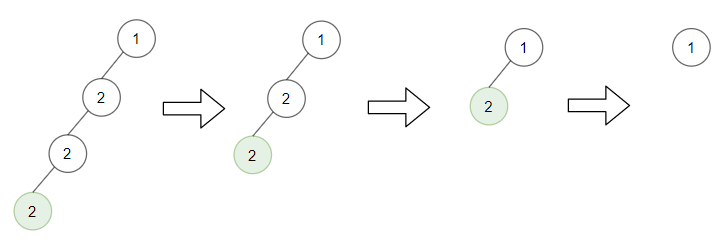
Input: root = [1,2,null,2,null,2], target = 2 Output: [1] Explanation: Leaf nodes in green with value (target = 2) are removed at each step.
Example 4:
Input: root = [1,1,1], target = 1 Output: []
Example 5:
Input: root = [1,2,3], target = 1 Output: [1,2,3]
Constraints:
1 <= target <= 1000- Each tree has at most
3000nodes. - Each node's value is between
[1, 1000].
class Solution { public TreeNode removeLeafNodes(TreeNode root, int target) { // use a temporary node as the parent of root TreeNode head = new TreeNode(0); head.left = root; helper(root, head, target); return head.left; } // post-order with reference to root's parent for easy removal private void helper(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent, int target) { if (node == null) return; helper(node.left, node, target); helper(node.right, node, target); // post-order: if the leaf value equals target, remove it from its parent if (node.left == null && node.right == null && node.val == target) { if (parent.left == node) parent.left = null; else parent.right = null; } } }
postorder,很巧妙,用parent监视子节点,省很多事情。
class Solution { public TreeNode removeLeafNodes(TreeNode root, int target) { if (root.left != null) root.left = removeLeafNodes(root.left, target); if (root.right != null) root.right = removeLeafNodes(root.right, target); return root.left == root.right && root.val == target ? null : root; } }
还有大佬的recursion方法,屌