You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1) (i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a route that requires the minimum effort.
A route's effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route.
Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
Example 1:
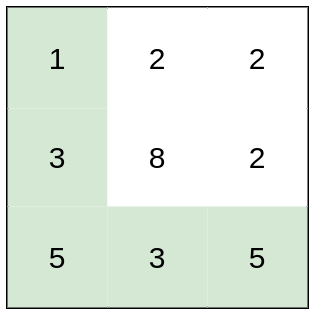
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] Output: 2 Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells. This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Example 2:
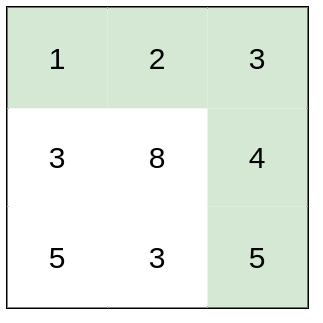
Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells, which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5].
Example 3:
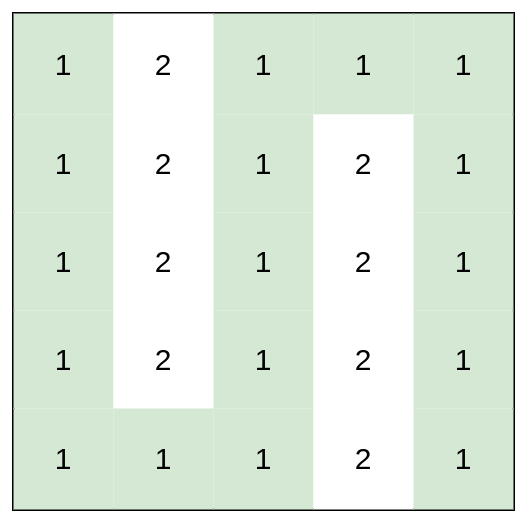
Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] Output: 0 Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
Constraints:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
class Solution { int[] DIR = new int[]{0, 1, 0, -1, 0}; public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) { int m = heights.length, n = heights[0].length; int[][] dist = new int[m][n]; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) Arrays.fill(dist[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE); PriorityQueue<int[]> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])); minHeap.offer(new int[]{0, 0, 0}); // distance, row, col while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) { int[] top = minHeap.poll(); int d = top[0], r = top[1], c = top[2]; if (d > dist[r][c]) continue; if (r == m - 1 && c == n - 1) return d; // Reach to bottom right for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int nr = r + DIR[i], nc = c + DIR[i + 1]; if (nr >= 0 && nr < m && nc >= 0 && nc < n) { int newDist = Math.max(d, Math.abs(heights[nr][nc] - heights[r][c])); if (dist[nr][nc] > newDist) { dist[nr][nc] = newDist; minHeap.offer(new int[]{dist[nr][nc], nr, nc}); } } } } return 0; // Unreachable code, Java require to return interger value. } }
https://leetcode.com/problems/path-with-minimum-effort/discuss/909017/JavaPython-Dijikstra-Clean-and-Concise-O(MNlogMN)