参考文章:http://www.runoob.com/css/css-intro.html
id和class:

<!DOCTYPE html> <!--CSS 规则由两个主要的部分构成:选择器,以及一条或多条声明--> <html> <head> <style> #para1{ <!--HTML元素以id属性来设置id选择器,CSS 中 id 选择器以 "#" 来定义--> color:red; font-familly:arial; } .center{ <!--class 选择器在HTML中以class属性表示, 在 CSS 中,类选择器以一个点"."号显示--> text-align:center; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 class="center">hello world</h1> <p class="center">this is a paragraph</p> </body> </html>
背景:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> body { background-image: url(image/1.jpg); background-repeat:no-repeat; background-position:right top; } <!-- body{ background:#ffffff url(image/0.jpg) no-repeat right top; } 当使用简写属性时,属性值得顺序为:: background-color background-image background-repeat background-attachment background-position 以上属性无需全部使用,你可以按照页面的实际需要使用. --> </style> </head> <body> <p>whats</p> </body> </html>
text文本:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <style> p.main { text-align:justify; text-indent:50px; } a{text-decoration:none;} p.uppercase{text-transform:uppercase;} p.lowercase{text-transform:lowercase;} #capitalize{text-transform:capitalize;} </style> </head> <body> <h1 style="text-decoration:overline;">whats</h1> <h2 style="text-decoration:line-through;">whats</h2> <h3 style="text-decoration:underline;">whats</h3> <p class="main">“当我年轻的时候,我梦想改变这个世界;当我成熟以后,我发现我不能够改变这个世界,我将目光缩短了些,决定只改变我的国家;当我进入暮年以后,我发现我不能够改变我们的国家,我的最后愿望仅仅是改变一下我的家庭,但是,这也不可能。当我现在躺在床上,行将就木时,我突然意识到:如果一开始我仅仅去改变我自己,然后,我可能改变我的家庭;在家人的帮助和鼓励下,我可能为国家做一些事情;然后,谁知道呢?我甚至可能改变这个世界。”</p> <p>link to: <a href="www.cnblogs.com">cnblogs</a></p> <p class="uppercase">This is some text.</p> <p class="lowercase">This is some text.</p> <p id="capitalize">This is some text.</p> </body> </html>
font字体:

<!--font-family 属性设置文本的字体系列。 font-family 属性应该设置几个字体名称作为一种"后备"机制,如果浏览器不支持第一种字体,他将尝试下一种字体。 注意: 如果字体系列的名称超过一个字,它必须用引号,如Font Family:"宋体"。 多个字体系列是用一个逗号分隔指明--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> p.test1{font-family:"Times New Roman",Times,serif;font-weight:bold;} p.test2{font-family:Arial,Helvetica,sans-serif;font-weight:800;} p.normal{font-style:normal;font-size:40px;font-variant:small-caps;} <!--正常--> p.italic{font-style:italic;font-size:2.5em;} <!--斜体--> p.oblique{font:oblique bold 12px/30px Georgia,serif;} <!--倾斜的文字,文字向一边倾斜(和斜体非常类似,但不太支持--> </style> </head> <body> <p class="test1">This is some text.</p> <p class="test2">there are some flowers.</p> <p class="normal">the first font-family</p> <p class="italic">the second font-family</p> <p class="oblique">the third font-family</p> </body> </html>
link链接:

<!--链接的样式,可以用任何CSS属性(如颜色,字体,背景等)。 特别的链接,可以有不同的样式,这取决于他们是什么状态。 这四个链接状态是: a:link - 正常,未访问过的链接 a:visited - 用户已访问过的链接 a:hover - 当用户鼠标放在链接上时 a:active - 链接被点击的那一刻 当设置为若干链路状态的样式,也有一些顺序规则: a:hover 必须跟在 a:link 和 a:visited后面 a:active 必须跟在 a:hover后面--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> a.one:link{color:#ff0000;text-decoration:none;background-color:#b2ff99;} a.one:visited{color:#00ff00;text-decoration:none;background-color:#ffff85} a.one:hover{color:#ff00ff;text-decoration:underline;background-color:#ff704d;font-size:150%;} a.one:active{color:#0000ff;text-decoration:underline;background-color:#ff704d;} a.two:link{color:#00ff00;background-color:b2ff99;text-decoration:none;} a.two:visited{color:0000ff;text-decoration:none;} a.two:hover{background-color:#66ff66;font-family:monospace;} </style> </head> <body> <p><a class="one" href="http://www.runoob.com/css" target="_blank">this is a link</a></p> <p><a class="two" href="www.cnblogs.com" target="_blank">cnblogs</a></p> </body> </html>
列表:

<!--list-style 简写属性。用于把所有用于列表的属性设置于一个声明中 list-style-image 将图象设置为列表项标志。 list-style-position 设置列表中列表项标志的位置。 list-style-type 设置列表项标志的类型。--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> ul.a{list-style-type:circle;} ol.b{list-style-type:upper-roman;} </style> </head> <body> <ul class="a"> <li>apple</li> <li>banana</li> <li>orange</li> </ul> <ol class="b"> <li>milk</li> <li>coffee</li> <li>tea</li> </ol> </body> </html>
表格:

<!--list-style 简写属性。用于把所有用于列表的属性设置于一个声明中 list-style-image 将图象设置为列表项标志。 list-style-position 设置列表中列表项标志的位置。 list-style-type 设置列表项标志的类型。--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> table{border-collapse:collapse;} table,th,td{border:1px solid green;} table{width:100%;} th{height:50px;background-color:green;color:white;vertical-align:bottom;} td{text-align:left;height:50px;vertical-align:bottom;padding:5px;} </style> </head> <body> <table> <tr> <th>name</th> <th>age</th> </tr> <tr> <td>whats</td> <td>lily</td> </tr> <tr> <td>23</td> <td>19</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
框模型:
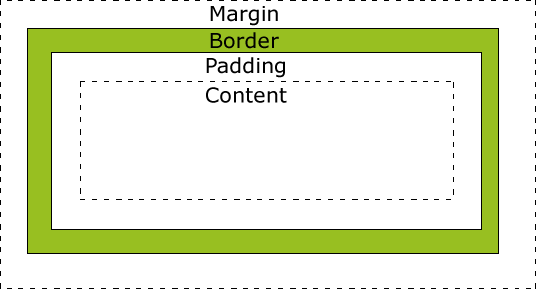

<!--所有HTML元素可以看作盒子,在CSS中,"box model"这一术语是用来设计和布局时使用。 CSS盒模型本质上是一个盒子,封装周围的HTML元素,它包括:边距,边框,填充,和实际内容。 盒模型允许我们在其它元素和周围元素边框之间的空间放置元素。 Margin - 清除边框区域。Margin没有背景颜色,它是完全透明 Border - 边框周围的填充和内容。边框是受到盒子的背景颜色影响 Padding - 清除内容周围的区域。会受到框中填充的背景颜色影响 Content - 盒子的内容,显示文本和图像 最终元素的总宽度计算公式是这样的: 总元素的宽度=宽度+左填充+右填充+左边框+右边框+左边距+右边距 元素的总高度最终计算公式是这样的: 总元素的高度=高度+顶部填充+底部填充+上边框+下边框+上边距+下边距--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> div.ex{width:200px;padding:5px;border:5px solid gray;margin:0px;} </style> </head> <body> <img src="image/0.jpg" width="220" height="123"> <div class="ex">The picture above is 220px wide. The total width of this element is also 220px</div> </body> </html>
边框:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> p.none{border-style:none;} p.dotted{border-style:dotted;} p.dashed{border-style:dashed;} p.solid{border-style:solid;} p.double{border-style:double;} p.groove{border-style:groove;border-width:10px;border-color:green blue;} p.ridge{border-style:ridge;border-width:10px;border-color:green yellow;} p.inset{border-style:inset;border-width:10px;border-color:grey green;} p.outset{border-style:outset;border-width:10px;border-color:pink green;} p.hidden{border-style:hidden;} p.four{ border-top-style:dotted; border-right-style:solid; border-bottom-style:double; border-left-style:dashed; border-color:#ff0000 #00ff00 #0000ff rgb(255,0,255); } p.two{ border-style:dotted solid; } p.one{border:10px solid grey;} </style> </head> <body> <body> <p class="none">No border.</p> <p class="dotted">A dotted border.</p> <p class="dashed">A dashed border.</p> <p class="solid">A solid border.</p> <p class="double">A double border.</p> <p class="groove">A groove border.</p> <p class="ridge">A ridge border.</p> <p class="inset">An inset border.</p> <p class="outset">An outset border.</p> <p class="hidden">A hidden border.</p> <p class="four">four side.</p> <p class="two">two side.</p> <p class="one">one method.</p> </body> </html>
轮廓:

<!--轮廓(outline)是绘制于元素周围的一条线,位于边框边缘的外围,可起到突出元素的作用。 轮廓(outline)属性指定了样式,颜色和外边框的宽度。--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> p{ border:2px solid pink; outline:green dotted 8px; } </style> </head> <body> <p><b>note:</b>whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!It's important things to said three times.</p> </body> </html>
margin:

<!--margin清除周围的元素(外边框)的区域。margin没有背景颜色,是完全透明的 margin可以单独改变元素的上,下,左,右边距。也可以一次改变所有的属性。--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> p{background-color:yellow;} p.margin{ margin-top:100px; margin-bottom:100px; margin-right:50px; margin-left:50px; } </style> </head> <body> <p>this is a paragraph with no specified margins.</p> <p class="margin">this is a paragraph with specified margins.</p> </body> </html>
padding填充:

<!--CSS Padding(填充)属性定义元素边框与元素内容之间的空间--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> p{ background-color:pink; } p.padding{ padding-top:25px; padding-bottom:25px; padding-left:50px; padding-right:50px; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="padding"><b>note:</b>whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!It's important things to said three times.</p> </body> </html>
分组和嵌套:

<!----> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> h1,h2,p{ color:green; } p{text-align:center;} .marked{background-color:pink;} .marked{color:white;} </style> </head> <body> <h1>whats</h1> <h2>whats</h2> <p class="marked"><b>note:</b>whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!It's important things to said three times.</p> </body> </html>
尺寸:

<!----> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> img.normal{height:130px;} p.ex{max-heith:50px;background-color:pink;} </style> </head> <body> <h1 class="h">whats</h1> <img class="normal" src="image/0.jpg" width="220" height="123"><br> <p class="ex"><b>note:</b>whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!It's important things to said three times.</p> </body> </html>
display显示:

<!--隐藏一个元素可以通过把display属性设置为"none",或把visibility属性设置为"hidden"。但是请注意,这两种方法会产生不同的结果。 visibility:hidden可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。 display:none可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失。--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> h1.display{display:none;} img.hidden{visibility:hidden;} li{display:inline;} span{display:block;} </style> </head> <body> <h1 class="display">whats</h1> <img class="hidden" src="image/0.jpg" width="220" height="123"><br> <img class="none" src="image/1.jpg" width="220" height="123"><br> <img class="hidden" src="image/2.jpg" width="220" height="123"><br> <ul> <li>milk</li> <li>coffee</li> <li>tea</li> </ul> <h2>Nirvana</h2> <span>Record: MTV Unplugged in New York</span> <span>Year: 1993</span> <h2>Radiohead</h2> <span>Record: OK Computer</span> <span>Year: </span> <span>2015</span> </body> </html>
positioning定位:

<!----> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> p.fixed{ position:fixed; top:30px; right:5px; } img{ position:absolute; left:0px; top:0px; z-index:-1; } p.absolute{ position:absolute; left:100px; top:150px; } p.relative{ position:relative; left:50px; } img.one{ position:absolute; left:200px; top:300px; clip:rect(0px,100px,200px,0px); } p.two{ position:absolute; left:330px; top:300px; width:100px; height:100px; overflow:scroll; } p.three{ position:absolute; left:400px; top:400px; width:100px; height:100px; overflow:auto; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="fixed" style="cursor:pointer" >some more text.</p> <img src="image/2.jpg" height="123" width="220"> <p class="absolute">whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!</p> <p class="relative">whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!</p> <img class="one" src="image/3.jpg" height="150" width="220" > <p class="two">whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!</p> <p class="three">whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!</p> <p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p><p>some text</p> </body> </html>
float:

<!--CSS 的 Float(浮动),会使元素向左或向右移动,其周围的元素也会重新排列。 Float(浮动),往往是用于图像,但它在布局时一样非常有用--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> span{ float:left; width:0.7em; font-family:algerian,courier; line-height:80%' } img{float:left; width:150px; height:200px; border:1px solid pink; margin:5px; } .text_line{ clear:both; } </style> </head> <body> <h2>this is whats's mm.</h2> <p><span>W</span>hats is a handsome boy!<br> whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!<br> whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!<br> whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!<br> whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy! </p> <img src="image/1.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/2.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/3.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/4.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/5.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/6.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/7.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <h3 class="text_line">second row.</h3> <img src="image/1.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/2.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/3.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/4.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/5.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/6.jpg" width="350" height="500"> <img src="image/7.jpg" width="350" height="500"> </body> </html>


<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> div.container { width:100%; margin:0px; border:1px solid gray; line-height:150%; } div.header,div.footer { padding:0.5em; color:white; background-color:gray; clear:left; } h1.header { padding:0; margin:0; } div.left { float:left; width:160px; margin:0; padding:1em; } div.content { margin-left:190px; border-left:1px solid gray; padding:1em; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="header"><h1 class="header">this is header.</h1></div> <div class="left"><p>menu:</p></div> <div class="content"><p><b>note:</b>whats is a handsome boy!</p></div> <div class="footer">copyright by whats 2015-11-26.</div> </div> </body> </html>
align对齐:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> .center { margin:auto; width:80%; background-color:pink; } #position{ position:absolute; right:0px; width:600px; border:1px solid blue; background-color:gray; } .float{ float:left; width:300px; background-color:gray; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="center"> <p>In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I've been turning over in my mind ever since.</p> <p>'Whenever you feel like criticizing anyone,' he told me, 'just remember that all the people in this world haven't had the advantages that you've had.'</p> </div> <p id="position"><b>Note: </b>Using margin:auto will not work in IE8, unless a !DOCTYPE is declared.</p> <p class="float"><b>Note: </b>Using margin:auto will not work in IE8, unless a !DOCTYPE is declared.</p> </body> </html>
组合选择符:

<!--在 CSS3 中包含了四种组合方式: 后代选取器(以空格分隔) 子元素选择器(以大于号分隔) 相邻兄弟选择器(以加号分隔) 普通兄弟选择器(以破折号分隔)--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> div.one p { <!--后代选取器匹配所有值得元素的后代元素。--> background-color:pink; } div.two>p{ background-color:gray; } div.two+p{ background-color:green; } div.three~p{ background-color:yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="one"> <p>paragraph1.</p> <p>paragraph2.</p> </div> <div class="two"> <p>paragraph3.</p> <p>paragraph4.</p> </div> <p>paragraph5.</p> <p>paragraph6.</p> <div class="three"> <p>paragraph7.</p> </div> <p>paragraph8.</p> <p>paragraph9.</p> <p>paragraph10.</p> <p>paragraph11.</p> </body> </html>
伪类:

<!--CSS伪类是用来添加一些选择器的特殊效果。--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> input:focus{background-color:yellow;} p>i:first-child{color:pink;} p:first-child{color:blue;} q:lang(no) {quotes:"~""~";} a:link{color:#00ff00;} a:visited{color:#ff0000;} a:hover{color:#ff00ff;} a:active{color:#0000ff;} </style> </head> <body> <form> name:<input type="text" name="username"/><br> password:<input type="text" name="pwd"/><br> <input type="button" value="submit"/> </form> <p>this is <i>some</i> text.this is <i>some</i> text.</p> <p>this is <i>some</i> text.this is <i>some</i> text.</p> <p>this is some <q lang="no">text.this is</q> some text.</p> <p><a class="red" href="www.cnblogs.com" target="_blank">cnblogs</a></p> </body> </html>
伪元素:

<!--CSS伪元素是用来添加一些选择器的特殊效果。--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> h1:before{content:url(image/1.jpg);} h1:after{content:url(image/2.jpg);} p.article:first-letter{color:blue;} p:first-letter{color:red;font-size:xx-large;} p:first-line{color:pink;font-variant:small-caps;} </style> </head> <body> <h1>aha,amazing</h1> <p class="article">this is some text.this is some text.<br> this is some text.this is some text.</p> <p>this is some text.this is some text.</p> <p><a class="red" href="www.cnblogs.com" target="_blank">cnblogs</a></p> </body> </html>
导航栏:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> ul{ list-style-tyle:none; <!--list-style-type:none - 移除列表前小标志。一个导航栏并不需要列表标记--> margin:0; padding:0; } a:link,a:visited{ display:block; font-weight:bold; color:#ffffff; background-color:#98bf21; width:120px; text-align:center; padding:4px; text-decoration:none; text-transform:uppercase; } a:hover,a:active{ background-color:#7a991a; } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">home</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">news</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">contact</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">about</a></li> </ul> </body> </html> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> ul{ list-style-type:none; margin:0; padding:0; overflow:hidden; } li{ float:left; } a:link,a:visited{ display:block; width:120px; font-weight:bold; color:#ffffff; background-color:#98bf21; text-align:center; padding:4px; text-decoration:none; text-transform:uppercase; } a:hover,a:active{ background-color:#7a991a; } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">home</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">news</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">contact</a></li> <li><a href="http://www.cnblogs.com">about</a></li> </ul> </body> </html> <!--float:left - 使用浮动块元素的幻灯片彼此相邻 display:block - 显示块元素的链接,让整体变为可点击链接区域(不只是文本),它允许我们指定宽度 60px - 块元素默认情况下是最大宽度。我们要指定一个60像素的宽度-->
图像透明/不透明:

<!--CSS3中属性的透明度是 opacity.--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> img{ opacity:0.4; filter:alpha(opacity=40); } img:hover{ opacity:1.0; filter:alpha(opacity=100); } </style> </head> <body> <img src="image/1.jpg" width="120" height="200"> <img src="image/2.jpg" width="120" height="200"> </body> </html> <!--CSS3中属性的透明度是 opacity.--> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> div.one{ width:500px; height:250px; background:url(image/3.jpg) repeat; border:2px solid black; } div.two{ width:400px; height:200px; margin:30px 50px; background-color:#ffffff; border:1px solid black; opacity:0.6; filter:alpha(opacity=60); } div.two p{ margin:30px 40px font-weight:bold; color:#000000; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="one"> <div class="two"> <p>whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy!whats is a handsome boy! It is important thing to said three times.</p> </div> </div> </body> </html>
