1:事件驱动
1)事件:所谓事件就是js侦测到的用户的操作或是页面的一些行为(怎么发生的)
2)事件源对象:引发事件的元素。(发生在谁的身上)
3)事件处理程序:对事件处理的程序或是函数 (发生了什么事)
4)事件对象:当事件发生的时候,具体发生了哪些信息,(当按键盘的时候按的哪个键或者鼠标光标在页面的哪个位置等等)。
2:事件分类
1.鼠标事件
onclick 点击鼠标
ondblclick 双击鼠标
onmousedown 鼠标按下
onmouseup 鼠标抬起
onmousemove 鼠标移动
onmouseover 鼠标放上去
onmouseout 鼠标离开
onmouseenter 鼠标进入
onmouseleave 鼠标离开
onmouseover、onmouseout/onmouseenter、onmouseleave的区别:
onmouseenter、onmouseleave不触发事件的冒泡
onmouseover、onmouseout触发事件的冒泡
2.键盘事件
onkeyup 键盘抬起
onkeydown 键盘按下
onkeypress 键盘按下或按住
释义:onkeydown和onkeypress二者的区别
onkeypress支持的是可在文本区域输入内容的键按下出发事件;
onkeydown所有键盘的吉安按下都触发事件
3. 表单事件(详解见Dom)
onsubmit 提交
onblur 失去焦点(内容发生变化,失去焦点触发)
onfocus 获得焦点
oninput 输入事件(根据长度限制文本框输入的内容)
onchange 改变文本区域的内容(发生条件:1.内容发生变化2.失去焦点)
4.页面事件
onload 当页面加载完成
onbeforeunload 当页面卸载完成之前
3:绑定事件
1)绑定一个事件处理程序:
1.在脚本中绑定。(通过获取元素绑定相应的事件)
2.直接在HTML元素中绑定。(标签属性中加调用事件,具体的实现放到js文件或内部脚本区域)(不建议使用:结构,样式,行为分离)
2)绑定多个事件处理程序:
1.自己写的。
2.IE:(多个函数执行顺序:IE9/10按照绑定的顺序执行,IE7/8顺序相反。)
对象.attachEvent("事件(on)","处理程序") 添加事件监听
对象.detachEvent("事件(on)","处理程序") 删除事件监听
火狐:(多个函数执行顺序:按照绑定的顺序执行。)
对象.addEventListener("事件"(不加on),"处理程序",布尔值(false:事件冒泡true:事件的捕获)) 添加
对象.removeEventListener("事件"(不加on),"处理程序",布尔值) 删除
易错用点:
//事件处理程序通过调用声明式函数卸载监听
//错误用法
对象.addEventListener("click",function(){},false);
对象.removeEventListener("click",function(){},false)
//无法删除监听事件,function(){}新创建的函数与添加监听调用的函数指向不一
//正确用法
对象.addEventListener("click",fun(),false);
对象.removeEventListener("click",fun(),false);
function fun(){
}
//通过函数名调用声明式的函数
兼容性写法:
function bindEvent(obj,type,fun){
if(obj.addEventListener){
//三个参数,按照绑定顺序执行
obj.addEventListener("事件不加on,eg:click",fun(),false(默认值false,可不写))
}
else{
//两个参数,按照绑定相反顺序执行
obj.attachEvent("事件加on;eg:onclick",func)
}
}
4:事件对象
用来记录一些事件发生时的相关信息的对象。
1.只有当事件发生的时候才产生,只能在处理函数内部访问。
2.处理函数运行结束后自动销毁。
如何获取事件对象:
IE:window.event
火狐:对象.on事件=function(ev){}
5:关于鼠标事件对象属性
1)相对于浏览器位置的:
clientX 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于浏览器X轴的位置。
clientY 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于浏览器Y轴的位置。
2)相对于文档位置的:
pageX 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于文档X轴的位置。(IE7/8无)
pageY 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于文档Y轴的位置。(IE7/8无)
3)相对于屏幕位置的:
screenX 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于屏幕X轴的位置。
screenY 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于屏幕Y轴的位置。
4)相对于事件源的位置:
offsetX 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于事件源X轴的位置。
offsetY 当鼠标事件发生的时候,鼠标相对于事件源Y轴的位置。

event.button:返回一个整数,指示当事件被触发时哪个鼠标按键被点击。0规定鼠标左键,1规定鼠标滚轮,2规定鼠标右键。不过老版本的IE并没有遵守W3C的规范,它的button属性含义如下:1鼠标左键 2鼠标右键 3左右同时按 4滚轮 5左键加滚轮 6右键加滚轮 7三个同时。目前IE11.0版本,无兼容性问题。
6:关于键盘事件对象的属性
keyCode:获得键盘码。空格:32 回车13 左上右下:37 38 39 40。which属性有兼容性问题。
ctrlKey:判断ctrl键是否被按下,按下是true,反之是false 布尔值。还有shiftKey altKey CtrKey。
type:用来检测事件的类型。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件测试</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
//键盘事件对象的属性
document.onkeydown = function (ev) {
var e = ev || window.event;//兼容性写法
console.log(e.type);//输出检测事件类型
console.log(e.keyCode);输出键盘码
//单独建是否按下
console.log(e.ctrlKey);
console.log(e.shiftKey);
console.log(e.altKey);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
7:目标事件源对象
事件源对象:事件源对象与绑定的元素没关系,事件由哪个元素触发,则触发事件的元素为事件源对象。
IE:事件对象.srcElement
火狐:事件对象.target
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件测试</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
//键盘事件对象的属性
window.onload=function(){
document.body.onclick = function (ev) {
var e = ev || window.event;
// 获取目标事件源对象
console.log(e.srcElement)
// 前者兼容标准浏览器,后者兼容低版本的IE浏览器
var target = e.target || e.srcElement;
console.log(target)
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body style="height: 500px;">
</body>
</html>
8:事件流
当页面元素触发事件的时候,该元素的容器以及整个页面都会按照特定顺序响应该元素的触发事件,事件传播的顺序叫做事件流程。
1)事件流的分类
1.冒泡型事件(所有的浏览器都支持)
由明确的事件源到最不确定的事件源依次向上触发。

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>事件流</title> <style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .outer{ height: 500px; 500px; background: #f3f3f3; } .inner{ height: 400px; 400px; background: #f6f6f6; } .parent{ height: 300px; 300px; background: #f9f9f9; } .son{ height: 200px; 200px; background: #ffffff; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="outer" class="outer"> <div id="inner" class="inner"> <div id="parent" class="parent"> <div id="son" class="son"></div> </div> </div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id); } var outer = $('outer'), inner = $('inner'), parent = $('parent'), son = $('son'); outer.onclick = function () { console.log('this is outer') } inner.onclick = function () { console.log('this is inner') } parent.onclick = function () { console.log('this is parent') } son.onclick = function () { console.log('this is son') } </script> </html>

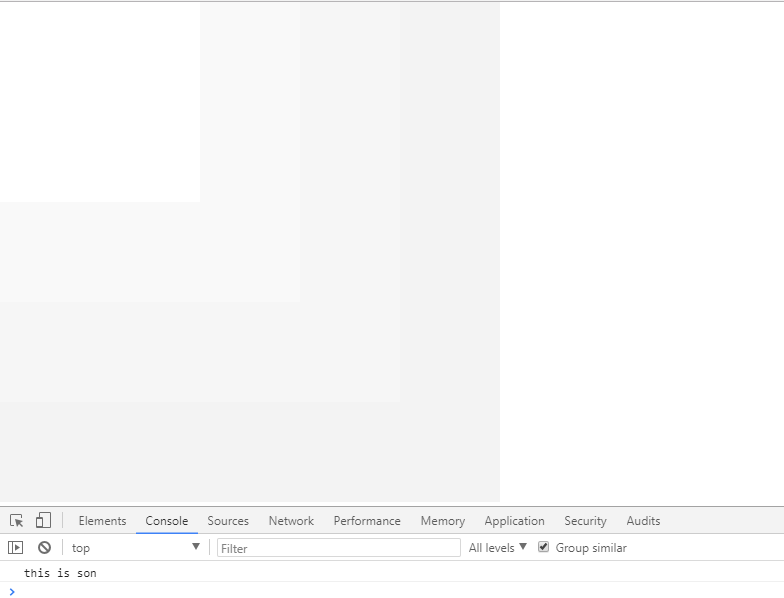
2.捕获型事件(IE不支持 支持w3c标准的浏览器 火狐)

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>事件流</title> <style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .outer{ height: 500px; 500px; background: #f3f3f3; } .inner{ height: 400px; 400px; background: #f6f6f6; } .parent{ height: 300px; 300px; background: #f9f9f9; } .son{ height: 200px; 200px; background: #ffffff; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="outer" class="outer"> <div id="inner" class="inner"> <div id="parent" class="parent"> <div id="son" class="son"></div> </div> </div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id); } var outer = $('outer'), inner = $('inner'), parent = $('parent'), son = $('son'); //添加监听事件(正常浏览器支持的方式,第三个参数就是控制事件流,默认false,即冒泡型事件,反之捕获型事件(IE不支持)) outer.addEventListener("click",function () { console.log('this is outer') },true); inner.addEventListener("click",function () { console.log('this is inner') },true); parent.addEventListener("click",function () { console.log('this is parent') },true); son.addEventListener("click",function () { console.log('this is son') },true); </script> </html>
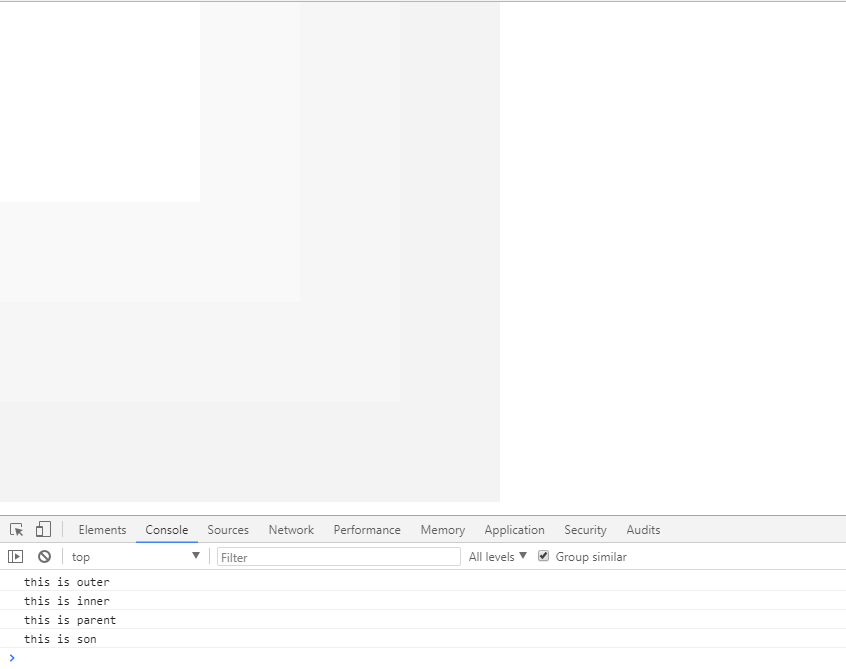
不确定的事件源到明确的事件源依次向下触发。
addEventListener(事件,处理函数,false); 事件在冒泡阶段执行。
addEventListener(事件,处理函数,true) ; 事件在捕获阶段执行。
2)阻止事件流
IE:事件对象.cancelBubble=true;
火狐:事件对象.stopPropagation();
捕获型事件流和冒泡型事件流都可以阻止。

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>事件流</title> <style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .outer{ height: 500px; 500px; background: #f3f3f3; } .inner{ height: 400px; 400px; background: #f6f6f6; } .parent{ height: 300px; 300px; background: #f9f9f9; } .son{ height: 200px; 200px; background: #ffffff; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="outer" class="outer"> <div id="inner" class="inner"> <div id="parent" class="parent"> <div id="son" class="son"></div> </div> </div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id); } var outer = $('outer'), inner = $('inner'), parent = $('parent'), son = $('son'); // 阻止事件流 // outer.addEventListener('click', function (ev) { // console.log('this is outer'); // // ev.stopPropagation(); // }, false); // inner.addEventListener('click', function () { // console.log('this is inner'); // }, false); // parent.addEventListener('click', function (ev) { // console.log('this is parent'); // // ev.stopPropagation(); // }, false); // son.addEventListener('click', function (ev) { // console.log('this is son'); // // ev.stopPropagation(); // }, false); // 低版本的IE阻止事件流 // outer.attachEvent('onclick', function () { // console.log('this is outer'); // }); // inner.attachEvent('onclick', function () { // console.log('this is inner'); // }); // parent.attachEvent('onclick', function () { // console.log('this is parent'); // }); // son.attachEvent('onclick', function () { // var e = window.event; // console.log('this is son'); // e.cancelBubble = true; // }); // 兼容各个浏览器实现阻止事件冒泡 function noBubbleEvent(obj, event, fn) { //兼容式添加监听,注意传参 if(obj.addEventListener) { obj.addEventListener(event, fn); } else { obj.attachEvent('on' + event, fn); } } noBubbleEvent(outer, 'click', function () { console.log('this is outer'); }) noBubbleEvent(inner, 'click', function () { console.log('this is inner'); }) noBubbleEvent(parent, 'click', function () { console.log('this is parent'); }) noBubbleEvent(son, 'click', function (ev) { // 兼容各个浏览器获取事件对象 var e = ev || window.event; console.log('this is son'); // 兼容各个浏览器阻止冒泡 if(e.stopPropagation) { e.stopPropagation(); } else { e.cancelBubble = true; } }) </script> </html>
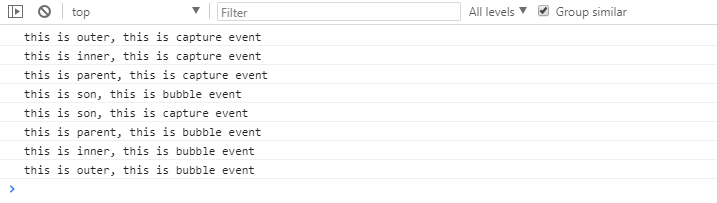
3)执行顺序
当元素即绑定捕获型事件又绑定冒泡型事件执行顺序:捕获阶段、目标阶段、冒泡阶段。
如果该元素是目标事件源对象,则谁绑定在前就先执行谁。

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>事件流</title> <style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .outer{ height: 500px; 500px; background: #f3f3f3; } .inner{ height: 400px; 400px; background: #f6f6f6; } .parent{ height: 300px; 300px; background: #f9f9f9; } .son{ height: 200px; 200px; background: #ffffff; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="outer" class="outer"> <div id="inner" class="inner"> <div id="parent" class="parent"> <div id="son" class="son"></div> </div> </div> </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id); } var outer = $('outer'), inner = $('inner'), parent = $('parent'), son = $('son'); // 元素身上即绑定了冒泡性事件,又绑定了捕获型事件 // 事件执行的顺序:捕获阶段、目标阶段(执行顺序与事件类型无关,哪个绑定谁先执行)、冒泡阶段 outer.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is outer, this is bubble event'); }) outer.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is outer, this is capture event'); }, true) inner.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is inner, this is bubble event'); }) inner.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is inner, this is capture event'); }, true) parent.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is parent, this is bubble event'); }) parent.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is parent, this is capture event'); }, true) son.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is son, this is bubble event'); }) son.addEventListener('click', function () { console.log('this is son, this is capture event'); }, true) </script> </html>
9:浏览器菜单
1)阻止右键菜单 ,建议阻止浏览器默认行为用此方案
document.oncontextmenu = function(){
alert("右键被按下");
return false;
}
2)阻止浏览器的默认行为(以下两种方法做了解,要用须兼容性写法进行支持)
非IE:ev.preventDefault();
IE:ev.returnValue = false;

<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>事件流</title> <style type="text/css"> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } #menu{ list-style: none; padding: 20px; border: 1px solid #f0f0f0; display: inline-block; position: absolute; left: -1000px; top: 0; } #menu li{ border-bottom: 1px dashed #f3f3f3; padding: 5px; } #menu li a{ display: block; text-decoration: none; font-size: 14px; line-height: 30px; } </style> </head> <body> <ul id="menu"> <li><a target="_blank" href="https://www.baidu.com">复制</a></li> <li><a target="_blank" href="http://www.taobao.com">剪切</a></li> <li><a target="_blank" href="http://www.pdmall.net">粘贴</a></li> <li><a target="_blank" href="http://www.smallrain.com">查看源码</a></li> </ul> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id); } document.oncontextmenu=function(ev) { var e=ev||window.event; var leftdistinct=e.clientX; var topdistinct=e.clientY; $('menu').style.left=leftdistinct+"px"; $('menu').style.top=topdistinct+"px"; //阻止浏览器默认效果(在此阻止默认菜单效果) //方式一:返回fasle阻止 return false; //方式二:利用浏览器支持的方式去阻止(兼容性差) // 只针对低版本的IE(测试高版本的浏览器也有效果) //e.returnValue = false; // 针对标准浏览器 //e.preventDefault(); //兼容性写法 /* if ( e && e.preventDefault){ e.preventDefault(); } else { e.returnValue = false; } */ } document.onclick=function() { $('menu').style.left="-1000px"; } </script> </html>
10:事件委托
利用冒泡机制,将子元素事件委托给父元素(此父元素是表义,表示包含该元素的元素,最好选择不是动态创建的元素)执行。
11:拖拽效果
1)拖拽原理
三个事件:onmousedown、onmousemove、onmouseup
实现思路:
1:给目标元素添加onmousedown事件,拖拽的前提是在目标元素按下鼠标左键。
2:当onmousedown发生以后,此刻给document添加onmousemove事件,意味着此刻鼠标在网页的移动都将改变目标元素的位置。
3:在onmousemove事件中,设定目标元素的left和top,公式:
目标元素的left = 鼠标的clientX – (鼠标和元素的横坐标差,即offsetX)
目标元素的top = 鼠标的clientY– (鼠标和元素的纵坐标差,即offsetY)。
4:当onmousedown发生以后,此刻给document添加onmouseup事件,意味着此刻鼠标在网页的任意位置松开鼠标,都会放弃拖拽的效果。
5:在onmouseup事件中,取消document的onmousemove事件即可。
2)注意事项
1:拖拽过程中,会选中文字,应阻止浏览器的默认行为(return false)。
2:低版本IE下,应使用事件捕获obj.setCapture(),在mouseup时取消事件捕获obj.releaseCapture()。
3)限定拖拽范围。
