1.简单数学
1008 Elevator (20分)
模拟题

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <cmath> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e4+100; int n, sum, now, tmp; int main(){ scanf("%d", &n); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ scanf("%d", &tmp); int num = tmp-now; sum += num > 0 ? num*6 : num*(-4); now = tmp; } sum += 5*n; printf("%d", sum); }
1049 Counting Ones (30 分)
1的个数等于各个位出现1的次数的累加和,因此我们计算各个位上对答案的贡献即可。
那么关键的问题就在如何计算某一位上的贡献,当然就是求这一位为1时数的个数,如下:
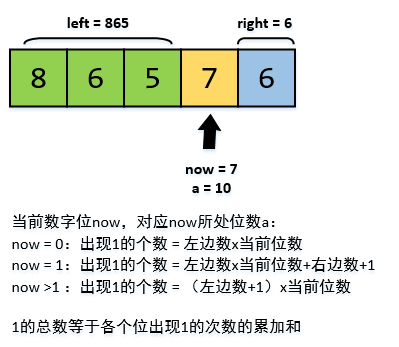 (具体为什么是这样可以在脑子或者纸上演算一下)
(具体为什么是这样可以在脑子或者纸上演算一下)
我一开始的思路是对的,但是那会想不出来具体的做法,考试时暴力骗个分还是可以的。另外上机指南中提到可以对程序进行边界测试,确实应当如此,以后多使用几种方法来测试自己的代码

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pb push_back #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; const int maxn = 2e6+100; int n, res; int main(){ scanf("%d", &n); int left = n, right, a = 1, now; while(left){ now = left%10, right = n-left*a, left /= 10; if(now==0) res += left*a; else if(now==1) res += left*a+right+1; else res += (left+1)*a; a *= 10; } printf("%d", res); }
Reference:
https://blog.csdn.net/CV_Jason/article/details/85112495
1069 The Black Hole of Numbers (20 分)
按照题目要求模拟即可,不过要注意要考虑全面:
1.所有输出都要求4位数
2.考虑特殊样例如6174、2222、1情况下的处理。如输入为1的时候要补充前导0;输入为6174的时候要输出一行而不能直接退出

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pb push_back #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5+100; string a, b, c, last, s; int tmp; int main(){ cin >> c; while(1){ for(int i = 0; i < 4-c.length(); i++) s += "0"; s += c, a = b = s, last = c; sort(a.begin(), a.end()), sort(b.rbegin(), b.rend()); c = to_string(stoi(b) - stoi(a)), s.clear(); printf("%04d - %04d = %04d ", stoi(b), stoi(a), stoi(c)); if(c=="6174"||c=="0") break; } }
1104 Sum of Number Segments (20分)
常规思路, 仍然是计算每个数的贡献。不过还是调试了一会,开始发现必须要用double,仔细观察运算过程就能发现这点,改后又过了部分样例,但是卡在测试样例2过不了。题目下面说测试样例被更新过,去网上查博客才发现,大概意思是:n比较大时,double类型的值多次累加导致的精度误差,建议不要使用double类型进行多次累加的精确计算,而是转为能够精确存储的整型,具体原因可以在Reference中查看。有种简单的解决办法是乘以1000转化成long long,输出的时候再还原,显然这个做法看来是不够严谨的,不过已经够用了。
有个细节需要注意,就是C语言中强制类型的转化。以这道题为例,1ll*1000*tmp,*有左结合性,ll*double最后的结果还是double,显然使用%lld输出就会有问题。因此需要加上括号更改来提高优先级,将double强制转化为ll才可以,这也是不能使用1ll相乘的原因。
专业知识是值得认真去学习的,这样出了问题才知道出在什么地方以及如何去解决

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pb push_back #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5+100; int n; int main(){ scanf("%d", &n); double tmp; ll sum = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%lf", &tmp); sum += (ll)(1000*tmp)*i*(n-i+1); } printf("%.2lf", sum/1000.0); }
Reference:
https://www.liuchuo.net/archives/1921
https://blog.csdn.net/u011277123/article/details/95774544(Double精度问题)
https://www.cnblogs.com/gaoshanxiaolu/p/3601038.html(强制转化)
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinanweike/p/10630260.html(强制转化)
https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E8%BF%90%E7%AE%97%E7%AC%A6%E4%BC%98%E5%85%88%E7%BA%A7/4752611(符号优先级)
2.素数
1015 Reversible Primes (20分)
WA一发后,想了几个样例测试了一下,发现自己漏掉了一个点:1不是素数。另外这题竟然不用素数筛和快速幂,惊了,当时想着先暴力试试,不行再优化,结果就过了。不过说实话素数筛和快速幂每次套板子,自己都已经不会写了,这位杨感觉不太行的样子

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <cmath> #define ll long long #define pb push_back #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pii pair<int, int> using namespace std; const int maxn = 2e3+100; bool judge(int n){ if(n==1) return false; for(int i = 2; i <= n/i; i++) if(n%i==0) return false; return true; } int change(int n, int d){ int res = 0, a[100], t = 0; while(n){ a[++t] = n%d; n /= d; } for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++) res += a[i]*pow(d, t-i); return res; } int main(){ int n, d; while(scanf("%d", &n)&&n>0){ scanf("%d", &d); if(judge(n)&&judge(change(n, d))) printf("Yes "); else printf("No "); } }
3.质因子分解
1059 Prime Factors (25 分)
可能之前做过类似的,一觉起来后就直接敲了,单独特判了n==1的情况后就过了,方法就是按照代码那样去写的,至于为什么(即证明)暂时还去推论

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pb push_back #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5+100; ll n, sta[maxn], t, cnt[maxn]; int main(){ scanf("%lld", &n); if(n==1){ printf("1=1"); return 0; } ll tmp = n; for(ll fac = 2; fac <= tmp; fac++){ if(tmp%fac==0) sta[++t] = fac; while(tmp%fac==0) tmp /= fac, cnt[fac]++; } printf("%lld=", n); for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++){ printf("%lld", sta[i]); if(cnt[sta[i]]>1) printf("^%lld", cnt[sta[i]]); if(i!=t) printf("*"); } }
1096 Consecutive Factors (20 分)
注意到 2^31 值在 12!~13! 之间,可以循环暴力计算,按照题目要求不断寻找连续并且能整除的数即可。注意每次遍历的数的范围是小于sqrt(n)的,否则和下个连续的数相乘大与n,最后特判n为质数即可

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pb push_back #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5+100; ll n, last, res, id; int main(){ scanf("%lld", &n); for(ll i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); i++){ ll cnt = 0, tmp = n, now = i; while(tmp%now==0) tmp /= now, cnt++, now++; if(cnt>res) res = cnt, id = i; } if(res==0) printf("1 %lld", n); else{ printf("%lld ", res); while(res--){ printf("%lld", id++); if(res) printf("*"); } } }
Reference:
https://blog.csdn.net/liuchuo/article/details/52139124
4.分数的四则运算
1081 Rational Sum (20 分)
按照要求迭代模拟即可,需要注意的是如何将输入转化为数字。最开始的时候我只是读入字符串的一位,有了之前的经验发现数字显然不止一位,就换了个思路结合string和stoi提取数字。最后修改下格式错误就AC了

#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #define ll long long #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define pb push_back #define pii pair<int,int> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5+100; int n; ll a[maxn], b[maxn]; string s; ll gcd(ll a, ll b){ return b==0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b); } int main(){ scanf("%d", &n); ll x, y, now = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ cin >> s; int pos = s.find('/'); x = stoi(s.substr(0, pos)), y = stoi(s.substr(pos+1)); ll fac = gcd(abs(x), y); a[i] = x/fac, b[i] = y/fac, now = now*b[i]/gcd(now, b[i]); } ll res = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) res += (now/b[i])*a[i]; x = res/gcd(abs(res), now), y = now/gcd(abs(res), now); if(x/y!=0&&x%y==0) printf("%lld", x/y); else if(x/y!=0&&x%y!=0) printf("%lld %lld/%lld", x/y, x%y, y); else if(x/y==0&&x%y!=0) printf("%lld/%lld", x%y, y); else printf("0"); }
1088 Rational Arithmetic (20 分)
细心的话一遍就能AC,不过回头看代码发现还是没有柳婼的代码简洁,输入写的过于复杂,使用%lld/%lld就能输入,1081中的那种做法很明显麻烦很多,大可不必那样。除此外1081的代码还有个点应该错误的,比如-4/3按照题目的意思应该写是-1 1/3而不是-1/ -1/3,因为这个点在1088中就是它的测试样例。在有限个枚举中有时候没必要写for循环去判断,这样可能反而会使代码更加复杂

#include <cstdio> #include <string> #define ll long long using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5+100; int n; ll a[maxn], b[maxn]; ll x, y, now = 1; string s; char sym[6] = {'+', '-', '*', '/'}; ll gcd(ll a, ll b){ return b==0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b); } void out(ll x, ll y){ if(x>0&&y<0) x = -x, y = -y; if(x<0&&y!=0) printf("("); if(y==0) printf("Inf"); else if(x/y!=0&&x%y==0) printf("%lld", x/y); else if(x/y!=0&&x%y!=0) printf("%lld %lld/%lld", x/y, abs(x%y), y); else if(x/y==0&&x%y!=0) printf("%lld/%lld", x%y, y); else printf("0"); if(x<0&&y!=0) printf(")"); } void cal(char s){ ll res; if(s=='+'||s=='-') { res = (now/b[1])*a[1]; s=='+' ? res += (now/b[2])*a[2] : res -= (now/b[2])*a[2]; } else if(s=='*') res = a[1]*a[2]; else res = a[1]*b[2], now = b[1]*a[2]; x = res/gcd(abs(res), now), y = now/gcd(abs(res), now); printf(" = "), out(x, y), printf(" "); } int main(){ for(int i = 1; i <= 2; i++){ scanf("%lld/%lld", &x, &y); ll fac = gcd(abs(x), y); a[i] = x/fac, b[i] = y/fac, now = now*b[i]/gcd(now, b[i]); } for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ for(int j = 1; j <= 2; j++){ out(a[j], b[j]); if(j==1) printf(" %c ", sym[i]); else cal(sym[i]); } } }
Reference:
