这是小编整理的笔试题,当然有些比较难,但是也是Python面试中出现频率比较高的知识点,以便复习和练习。
1,两个队列生成一个栈,如何做?
(听说是阿里问过的面试题)
那想要实现两个队列生成一个栈,我们需要先了解队列和栈的特性:
队列(先进先出),即只能在队列的尾部插入元素,头部删除元素,根据该特性,实现队列时候使用链表比较好。
栈(先进后出),即只能在该线性表的一头进行数据的插入和删除,该位置称为“栈顶”,而另一头称为“栈底”;根据特性,实现栈时使用顺序表比较好。
栈和队列
使用两个队列生成一个栈的实现思路为:
两个队列,队列1和队列2在任意时刻至少有一个为空,即如果有元素,所有元素只能在一个队列中,当有元素需要插入时,将元素插入到空队列中,并将另一非空队列的所有元素全部转移到该队列中,于是,插入的元素添加到了队列的最前面。
首先是入栈:

然后是出栈:

实现代码如下:
# _*_coding:utf-8_*_
import queue
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.master_queue = queue.Queue()
self.minor_queue = queue.Queue()
def push(self, value):
'''
入栈
:param value:
:return:
'''
self.master_queue.put(value)
def pop(self):
'''
出栈
:return:
'''
if self.master_queue.qsize() == 0:
return None
while True:
if self.master_queue.qsize() == 1:
value = self.master_queue.get()
break
self.minor_queue.put(self.master_queue.get())
self.master_queue, self.minor_queue = self.minor_queue, self.master_queue
return value
obj = Stack()
obj.push("A")
obj.push("B")
obj.push("C")
print(obj.pop()) # C
2,两个栈生成一个队列,如何做?
经典问题再现哈,那反过来怎么做呢?
其实思路差不多,这里就不画图了。简单说一下,这里利用了栈的先进后出的特点,将数据先加入第一个栈,然后通过在第二个栈中添加第一个栈删除的数据,就实现了数据的先进先出。
代码如下:
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.master_stack = []
self.minior_stack = []
def push(self, value):
'''
入队
:return:
'''
self.master_stack.append(value)
def pop(self):
'''
出队:先判断栈B是否为空,为空则将栈A中元素pop出来并push到B,在栈B出栈
如果不为空,则B直接出栈
:return:
'''
if self.minior_stack:
return self.minior_stack.pop()
else:
if self.master_stack != []:
while self.master_stack:
self.minior_stack.append(self.master_stack.pop())
return self.minior_stack.pop()
else:
return None
obj = Queue()
obj.push("A")
obj.push("B")
obj.push("C")
print(obj.pop()) # A
print(obj.pop())
print(obj.pop())
3,什么是https
https是基于http和SSL/TLS实现的一个协议,它可以保证在网络上传输的数据都是加密的,从而保证数据安全。
接下来我们从http协议开始,提出想法并逐步进行分析,最终实现https。
3.1 http协议是不安全的
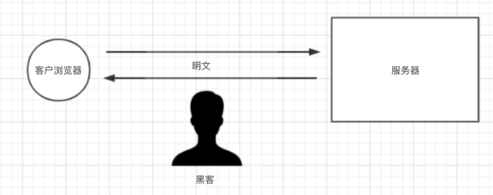
在https诞生之前,所有网站都使用http协议,而http协议在数据传输的过程中都是明文,所以可能存在数据泄露和篡改。
3.2 使用对称密钥进行数据加密
为了防止数据泄露和篡改,我们队数据进行加密,如:生成一个对称密码【DKUFHNAF897123F】,将对称秘钥分别交给浏览器和服务器端,他们之间传输的数据都使用对称秘钥进行加密和解密。

请求和响应流程如下:
- 1,客户端使用对称密钥对请求进行加密,并发送给服务端。
- 2,服务端接受密文之后,使用对称密钥对密文进行解密,然后处理请求。最后再使用对称密钥把要返回的内容再次加密,返回给客户端。
- 3,客户端接受到密文之后,使用对称密钥进行解密,并获取最终的响应内容。
如此一来,数据传输都是密文,解决了明文传输数据的问题,但是,这么干有bug。
- 浏览器如何获取对称密钥?
- 每个客户端的对称密钥相同,浏览器能拿到对称密钥,那么黑客也能拿到,所以,数据加密也就没有意义了。
3.3 动态对称密钥和非对称密钥
为了解决对称密钥动态性以及让客户端和服务端安全的获取对称密钥,可以引入非对称密钥机制。

如此一来,解决了动态对称密钥和数据加密的问题,因为每个用户的对称密钥都是随机生成且传输的过程中都使用了公钥加密(公钥加密的数据只有私钥能解密),所有黑客无法截获对称密钥。而数据传输是通过对称密钥加密过的,所以黑客即使能获取数据也无法去解密看到真实的内容。看似无懈可击,但是,还是有bug。
如果黑客按照上图步骤2劫持,黑客吧自己的公钥返回给客户端,那么客户端会使用黑客的公钥来加密对称密钥,黑客在步骤6,截获请求,使用自己的私钥获取对称密钥,那么后面过程全都完蛋,,
3.4 CA证书的应用
使用CA证书可以解决黑客劫持的问题:
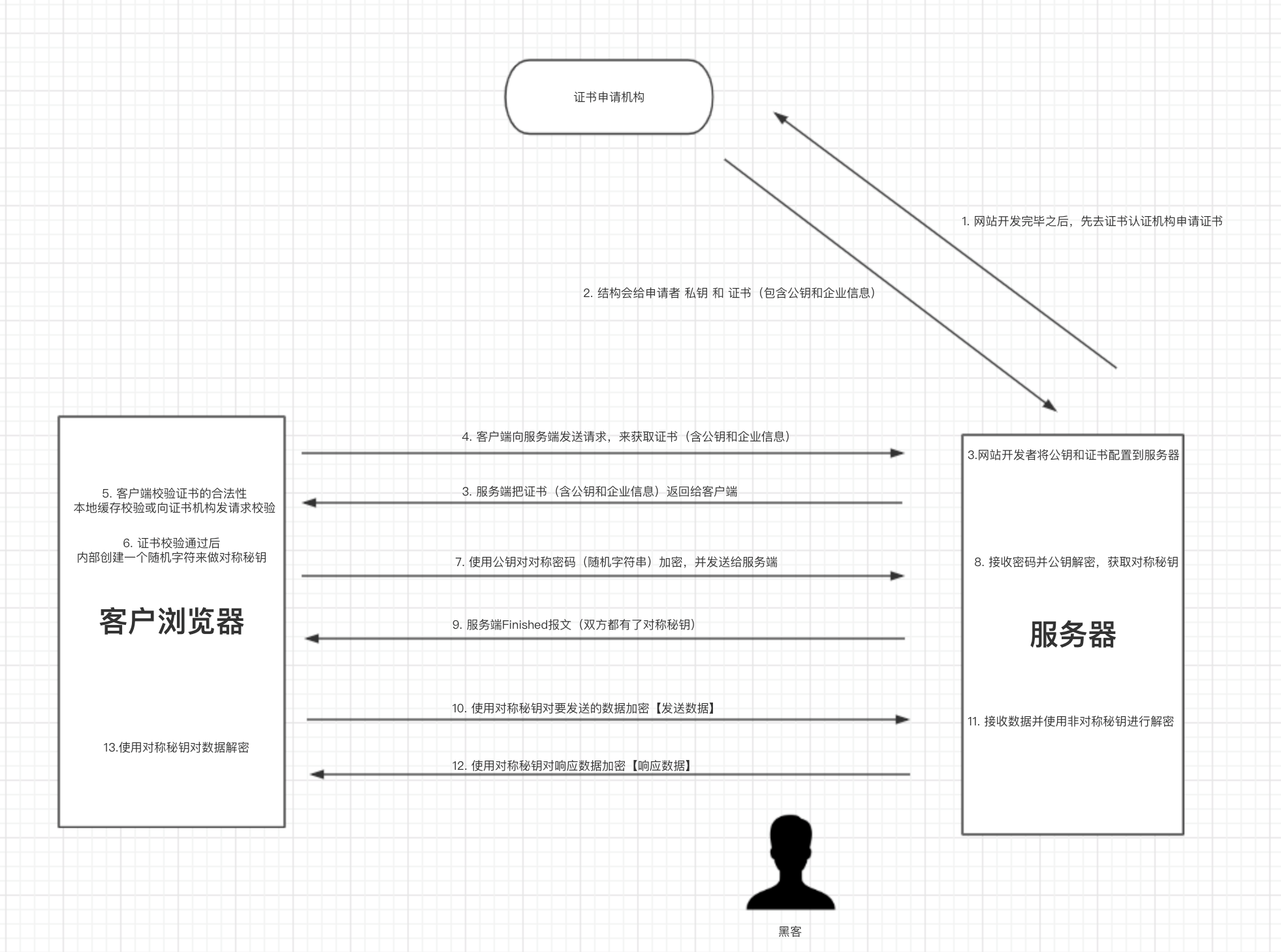
如此一来,就解决了黑客劫持的问题,因为即使黑客劫持后的给浏览器即使返回了证书也无法通过校验,同时浏览器也会提示错误信息。
注意:https是基于http和SSL/TLS实现的一个协议,其中前9个步骤称为是SSL/TLS过程,之后的传输数据利用的就是http协议(收发数据)。
3.5 总结
以上就是Https的实现原理,https可以保证数据安全,但是由于其过程需要反复加密解密所有访问速度会有所下降。
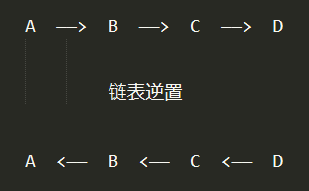
4,链表是一个特殊的数据结构,其中每个节点包含自己的数据以及下一个值的引用(指针),链表的逆置就是指将链表下一个值的引用(指针)调换,如下图所示:
第一步,构建链表
class Node:
def __init__(self, value, next):
self.value = value
self.next = next
head = Node('head', None)
last = head
for i in range(5):
node = Node('v%s' % i, None)
last.next = node
last = node
# 查看链表关系
print("原始链表信息为: ")
print(head.value)
print(head.next.value)
print(head.next.next.value)
print(head.next.next.next.value)
print(head.next.next.next.next.value)
print(head.next.next.next.next.next.value)
'''
原始链表信息为:
head
v0
v1
v2
v3
v4
'''
第二步,链表逆置
实现思路:
1,设置三个遍历分别指向如下三个值
2,将current.next设置为prev
3,整体向右移动一个节点,继续指向第一,第二步

代码如下:
def reverse_linked_list(head):
'''
链表逆置
:param head:
:return:
'''
if not head or not head.next:
return head
prev_node = None
current_node = head
next_node = head.next
while True:
current_node.next = prev_node
if not next_node:
break
prev_node = current_node
current_node = next_node
next_node = current_node.next
return current_node
new_head = reverse_linked_list(head)
print('逆置之后的链表')
print(new_head.value)
print(new_head.next.value)
print(new_head.next.next.value)
print(new_head.next.next.next.value)
print(new_head.next.next.next.next.value)
print(new_head.next.next.next.next.next.value)
'''
逆置之后的链表
v4
v3
v2
v1
v0
head
'''
5,做为Apple Store App独立开发者,你要搞限时促销,为你的应用生成激活码(或者优惠券),使用Python如何生成200个激活码(或者优惠券)?
简介:通用唯一识别码(英语:Universally Unique Identifier,简称UUID)是一种软件建构的标准,亦为开放软件基金会组织在分散式计算环境领域的一部份。
分析:这里参考(http://www.blogjava.net/BearRui/archive/2010/10/19/unique_random_code.html)
主键+随机码的方式.
这种方法优点:使用也比较简单,不用直接去查询数据库,而最大的优点是查询的时候,可以根据邀请码直接得到主键id, 然后根据id去数据库查询(速度很快),再比较查询出来的邀请码和用户提交的邀请码是否一致。
- 生成:id(数据库primary key )->16进制 + "L(标识符)" +随机码
- 获取id:获取16进制的id再转回10进制
import random import string def activation_code(id,length = 10): ''' id+L+随机码 string模块中的三个函数为:string.letters,string.printable.string.printable ''' prefix = hex(int(id))[2:]+'L' #prefix为前缀 length =length -len(prefix) chars = string.ascii_letters+string.digits return prefix + ''.join([random.choice(chars) for i in range(length)]) def get_id(code): '''hex to dec''' return str(int(code.upper(),16)) if __name__ =="__mian__": for i in range(10,500,35): code = activation_code(i) id_hex = code.split('L')[0] id = get_id(id_hex) print (code,id) if __name__=="__main__": for i in range(10,200,35): code = activation_code(i) id_hex = code.split('L')[0] id = get_id(id_hex) print (code,id) #print(code)
6,任一个英文的纯文本文件,统计其中的单词出现的个数
1.strip()没有参数时,删除空白符,包括、n 空格,strip()函数只能用于str类型,list类型等不可用。
2.split()用于分割,分隔符可以自己制定
def world_count(inputfile): if os.path.isfile(inputfile) !=True: print("inputfile not exits") sys.exit() word_count = 0 words = open(inputfile , "r").readlines() for word in words: print("word: %s" %word) temp = word.strip().split('') word_count += len(temp) print("word count:%s" %word_count) return word_count
7,用 Python 写一个爬图片的程序
这个就是一个简单的爬虫,只要模拟浏览器即可
import urllib.request import re url = 'http://tieba.baidu.com/p/2166231880' headers = ("User-Agent","Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/62.0.3202.94 Safari/537.36") opener = urllib.request.build_opener() opener.assheaders = [headers] urllib.request.install_opener(opener) data = urllib.request.urlopen(url).read() data2 = data.decode("utf-8","ignore") pattern = '<img pic_type="0" class="BDE_Image" src="(.*?)" bdwater="杉本有美吧,.*?" width=".*?" height=".*?" changedsize="true">' allurl = re.compile(pattern).findall(data2) #print(allurl) for i in range(0,len(allurl)): #print(allurl[i]) thisimg = allurl[i] file = "D:/pycode/"+str(i)+".jpg" urllib.request.urlretrieve(thisimg,filename = file) print("第" + str(i) + "次爬去成功")
8,一个HTML文件,找出里面的正文
9,有个目录,里面是你自己写过的程序,统计一下你写过多少行代码。包括空行和注释,但是要分别列出来。
import os import string import re os.chdir('C:/workspace') fh=open('test_test.py') read_fh=fh.readlines() fh.close() number_code=0 number_empty=0 number_note=0 pattern='.*#' #正则匹配模式 for x in read_fh: if '#' in x: #计算注释数目 if re.findall(pattern,x)[0][:-1].isspace() or re.findall(pattern,x)[0][:-1]=='': number_note+=1 else: number_code+=1 elif x.isspace(): number_empty+=1 else: number_code+=1 print('code number is %d'%(number_code+number_empty+number_note)) print('empty number is %d'%number_empty) print('note number is %d'%number_note)
10,有1、2、3、4个数字,能组成多少个互不相同且无重复数字的三位数?都是多少?
d = [1,2,3,4] def threenums(): print(None) count = 0 nums = [] for index1 in range(1,5): for index2 in range(1,5): for index3 in range(1,5): if index1 != index2 and index2 != index3 and index3 !=index1: num = 100*index1 +10*index2 +index3 if num not in nums: nums.append(num) count +=1 print(count) print(nums)
11,
企业发放的奖金根据利润提成。
利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%;
利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分,可可提成7.5%;
20万到40万之间时,高于20万元的部分,可提成5%;
40万到60万之间时高于40万元的部分,可提成3%;
60万到100万之间时,高于60万元的部分,可提成1.5%,
高于100万元时,超过100万元的部分按1%提成,
从键盘输入当月利润I,求应发放奖金总数?
def reward(profit): reward = 0.0 if profit <=100000: return profit*0.1 elif profit <=20 and profit >10: return (profit-10000)*0.075+100000*0.1 elif profit <=40 and profit >20: return (profit-10000)*0.05+100000*0.1+10000*0.075 elif profit <=60 and profit >40: return (profit-10000)*0.03+100000*0.1+10000*0.075+100000*0.05 elif profit <=100 and profit >60: return (profit-10000)*0.015+100000*0.1+10000*0.075+100000*0.05+100000*0.03 else: return (profit-10000)*0.01+100000*0.1+10000*0.075+100000*0.05+100000*0.03+100000*0.015 if __name__ == "__mian__": profit = int(input("请输入当月利润:")) print(reward(profit))
12,一个整数,
它加上100后是一个完全平方数,再加上168又是一个完全平方数,
请问该数是多少?
import math for i in range(10000): x = int(math.sqrt(i+100)) y = int(math.sqrt(i+168)) if (x*x == i+100) and (y*y == i+168): print(i)
(未完待续,有时间会继续上传,http://www.cnblogs.com/bakoom/p/5251293.html)