Non-local Neural Networks
一. 论文简介
图像上(扩大感受野),视频序列(临近几帧像素不同的问题联合),从局部信息到全局信息
主要做的贡献如下(可能之前有人已提出):
- 解决局部感受野,设计一个Block
二. 模块详解
2.1 Local和Non-Local
Local和Non-Local都是针对感受野来说的,3*3卷积就代表当前像素的感受野范围为9(8也可以,就是那个意思)
插曲:
- 看到这篇论文,真的有种相见恨晚的感觉,之前看到shuffleNet,通道之间打乱(按一定规则排序)可以增加信息量,获得更好的结果。那么为什么不能把feature打乱呢?((B、C、W、H)),咱们一一分析:
- B在采样的时候已经打乱了,而且多少也可以设定。理论上,制药模型足够鲁棒,B越大越好。
- C的操作有很多,直接卷积就是对C的扩展,打乱是ShuffleNet的做法,不同权重是Attention的做法,大部分论文都是对C的操作,比如ResNet就是对不同通道相加.....
- W、H的操作很少,最直接FC操作,这个操作效果很好,但是计算量太大。现在回归都不使用FC,使用1*1卷积+Reshape操作进行代替,比如人脸关键点(小网络)。
- 我本来的想法是将feature按block进行重新组合,然后卷积操作就可以获得不同区域的信息。
注释:
- 使用多个卷积串联可以增大感受野,但是在计算的过程中会丢失信息,所以串联得到的全局信息是不足的(做什么都会丢失,多少而已)。
- 使用SE模块可以获得全局信息,但是完全没有FC强大。
- 有没有比FC计算量小,而且信息量获得和FC差不多的?
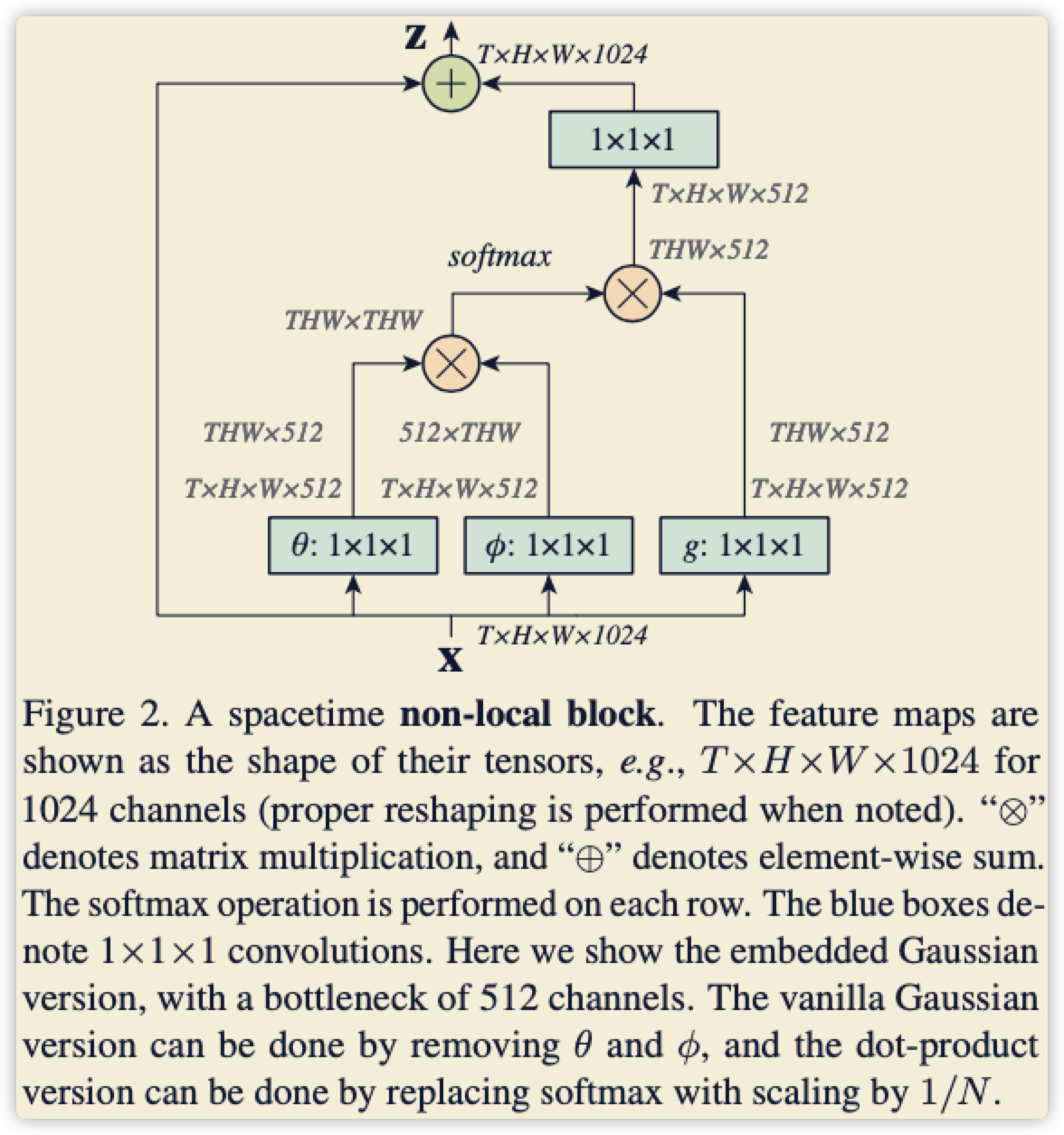
下面这幅图是论文的核心,某一个点的预测,需要获得不同位置的辅助,同时辅助的强度需要一个W权重控制。

2.2 具体实现
2.2.1 理论部分
看下面公式 ((1)),(x) 表示输入特征,(x_j) 当前特征,(x_i) 周围特征,(f) 表示相关函数(变换函数、(x_i 、 x_j) 关系函数) (C) 表示归一化值(一般softmax即可), (g) 表示当前特征变换函数。
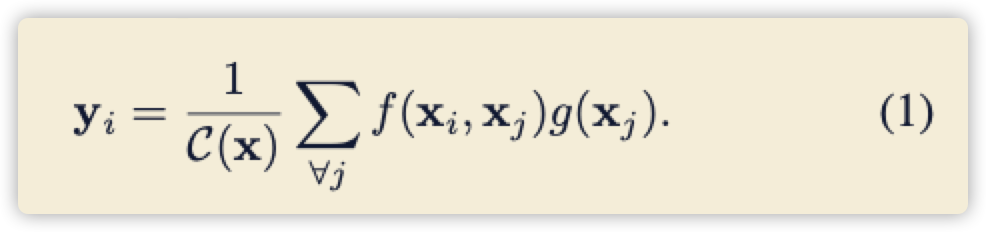
其实很简单的一个函数,(f) 当做相关性函数(具体实现后面说),(g) 直接当做一个卷积,那么两者相乘就可以得到全局信息的 (x)。
整片文章都在介绍 (f) 这个二元函数的生成方式,有Gaussian、Embedded Gaussian、.....具体不用细看,因为实现比较麻烦,能用卷积的肯定不用其他的。
下面公式((4)) 代表高斯函数,公式((5)) 代表 (g) 函数:
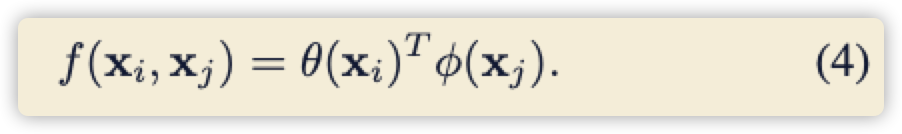
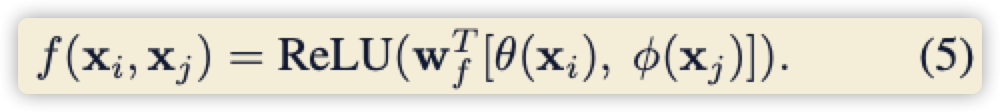
如果还不懂上面的公式,直接看代码就恍然大悟
2.2.2 具体实现
代码的实现完全是按照论文叙述,整体结构如下图所示,其中下采样直接在 (phi、g) 后面加maxpooling即可。
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class _NonLocalBlockND(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, dimension=3, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True):
super(_NonLocalBlockND, self).__init__()
assert dimension in [1, 2, 3]
self.dimension = dimension
self.sub_sample = sub_sample
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.inter_channels = inter_channels
if self.inter_channels is None:
self.inter_channels = in_channels // 2
if self.inter_channels == 0:
self.inter_channels = 1
if dimension == 3:
conv_nd = nn.Conv3d
max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=(1, 2, 2))
bn = nn.BatchNorm3d
elif dimension == 2:
conv_nd = nn.Conv2d
max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2))
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d
else:
conv_nd = nn.Conv1d
max_pool_layer = nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=(2))
bn = nn.BatchNorm1d
self.g = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
if bn_layer:
self.W = nn.Sequential(
conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
bn(self.in_channels)
)
nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].weight, 0)
nn.init.constant_(self.W[1].bias, 0)
else:
self.W = conv_nd(in_channels=self.inter_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
nn.init.constant_(self.W.weight, 0)
nn.init.constant_(self.W.bias, 0)
self.theta = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.phi = conv_nd(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.inter_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
if sub_sample:
self.g = nn.Sequential(self.g, max_pool_layer)
self.phi = nn.Sequential(self.phi, max_pool_layer)
def forward(self, x):
'''
:param x: (b, c, t, h, w)
:return:
'''
batch_size = x.size(0)
g_x = self.g(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1)
g_x = g_x.permute(0, 2, 1)
theta_x = self.theta(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1)
theta_x = theta_x.permute(0, 2, 1)
phi_x = self.phi(x).view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, -1)
f = torch.matmul(theta_x, phi_x)
f_div_C = F.softmax(f, dim=-1)
y = torch.matmul(f_div_C, g_x)
y = y.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
y = y.view(batch_size, self.inter_channels, *x.size()[2:])
W_y = self.W(y)
z = W_y + x
return z
class NONLocalBlock1D(_NonLocalBlockND):
def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True):
super(NONLocalBlock1D, self).__init__(in_channels,
inter_channels=inter_channels,
dimension=1, sub_sample=sub_sample,
bn_layer=bn_layer)
class NONLocalBlock2D(_NonLocalBlockND):
def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True):
super(NONLocalBlock2D, self).__init__(in_channels,
inter_channels=inter_channels,
dimension=2, sub_sample=sub_sample,
bn_layer=bn_layer)
class NONLocalBlock3D(_NonLocalBlockND):
def __init__(self, in_channels, inter_channels=None, sub_sample=True, bn_layer=True):
super(NONLocalBlock3D, self).__init__(in_channels,
inter_channels=inter_channels,
dimension=3, sub_sample=sub_sample,
bn_layer=bn_layer)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import torch
for (sub_sample, bn_layer) in [(True, True), (False, False), (True, False), (False, True)]:
'''
img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20)
net = NONLocalBlock1D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample, bn_layer=bn_layer)
out = net(img)
print(out.size())
'''
img = torch.zeros(2, 3, 20, 20)
net = NONLocalBlock2D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample, bn_layer=bn_layer)
out = net(img)
print(out.size())
img = torch.randn(2, 3, 8, 20, 20)
net = NONLocalBlock3D(3, sub_sample=sub_sample, bn_layer=bn_layer)
out = net(img)
print(out.size())