摘要
之前学习过c#中定时器Timer的基本用法,在使用过程中,有一个问题,一直困扰着自己,就是在初始化定时器的时候,如果设置的interval过小,或者每次执行的业务非常耗时的时候,这时候该怎么处理?第一次还没执行结束,下一次已经触发了。
基础
之前学习时的一个例子:http://www.cnblogs.com/wolf-sun/p/5849229.html
一个例子
如果设置的interval比较大,而业务执行过程耗时很小,如下所示:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Timers; namespace TimerTest { class Program { static Timer timer = new Timer(); static void Main(string[] args) { timer.Interval = 1000; timer.AutoReset = true; timer.Enabled = true; timer.Elapsed += timer_Elapsed; Console.Read(); } static int count = 1; static void timer_Elapsed(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("第{0}次触发", count.ToString()); if (count == 10) { timer.Enabled = false; } Console.WriteLine("当前线程:" + System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); Console.WriteLine("第{0}次处理完成", count.ToString()); count++; } } }
执行过程
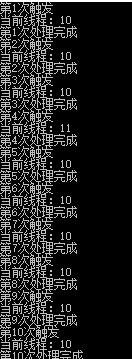
但实际中由于业务非常复杂,执行很耗时
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(2000);

可以看到这是,已经开始乱了,线程id已经变了,如果在里面涉及到引用的类型,必然引起多个线程修改同一个变量的问题,造成并不是我们想要的结果。
当然,这个时候有很多处理方法,加锁,或者设置标致量,等本次运行结束时,再运行下一次的。但这种方式,会造成timer的空转。
加锁
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Timers; namespace TimerTest { class Program { static readonly object obj = new object(); static Timer timer = new Timer(); static void Main(string[] args) { timer.Interval = 1000; timer.AutoReset = true; timer.Enabled = true; timer.Elapsed += timer_Elapsed; Console.Read(); } static int count = 1; static void timer_Elapsed(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e) { lock (obj) { Console.WriteLine("第{0}次触发", count.ToString()); if (count == 10) { timer.Enabled = false; } Console.WriteLine("当前线程:" + System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("第{0}次处理完成", count.ToString()); count++; } } } }
执行

标志量
static void timer_Elapsed(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e) { if (isRunning) { isRunning = false; Console.WriteLine("第{0}次触发", count.ToString()); if (count == 10) { timer.Enabled = false; } Console.WriteLine("当前线程:" + System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("第{0}次处理完成", count.ToString()); count++; isRunning = true; } }
运行结果

但仍有另外一种方式,可以在当前处理业务的时候,将当前的timer先停止,执行完毕之后开启。
static void timer_Elapsed(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e) { timer.Enabled = false; if (count == 10) { timer.Enabled = false; return; } Console.WriteLine("第{0}次触发", count.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("当前线程:" + System.Threading.Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("第{0}次处理完成", count.ToString()); timer.Enabled = true; count++; }
执行结果

总结
可以尝试测试开启100个定时器甚至更多的进行测试比较,推荐使用处理业务之前关闭,处理结束之后开启的方式。