1.网络编程的基本概念
1.1 网络的概念
- 网络:一组相互连接的计算机,多台计算机组成,使用物理线路进行连接

1.2 网络连接的功能
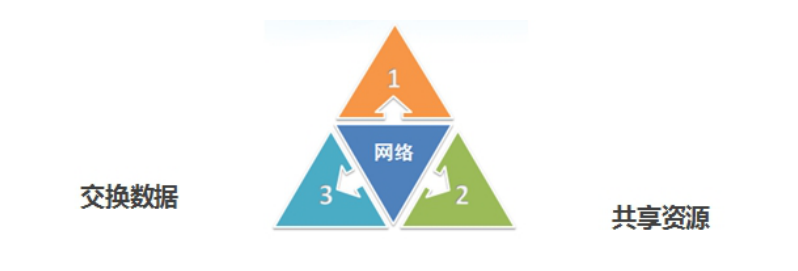
1.3 网络编程的三要素
- 1) IP 地址:唯一标识网络上的每一台计算机,两台计算机之间通信的必备有素 。相当于一个人的住址。
- 2) 端口号:计算机中应用的标号(代表一个应用程序),0-1024 系统使用或保留端口 ,端号口占 2 个字节,所以有效端口 0-65535。 这个相当于门牌号。
- 有效端口 0-65535
- 3)通信协议:通信的规则TCP,UDP。相当于生活中的交通规则。
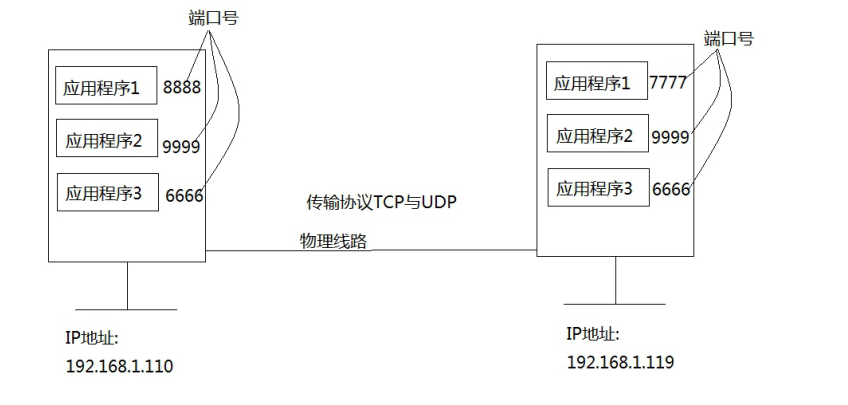
2.IP_端口_Socket 含义
2.1IP 地址
- IP 地址用于标识网络上的唯一一台计算机,共 32 位,4 个 8位二进制数组成
- IP 地址分为:IPv4 和 IPv6
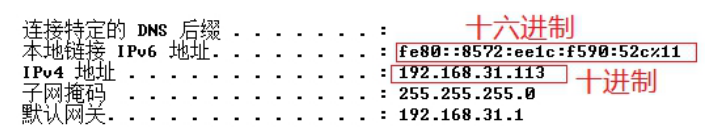
- IPv4:“点分十进制表示法” 129.254.26.110 一个由8位二进制数组成,所以是32位。
- IPv6:“十六进制表示法”
- IP 地址=网络 ID+主机 ID
- 网络 ID:标识计算机或网络设备所有的网段
- 主机 ID:标识特定的主机或网络设备

特殊 IP 地址:
- 1) 127.0.0.1:本机回环地址,用于本机测试
- 2) 255.255.255.255:当前子网,一般用于当前子网广播信息
c类:255.255.255.0
b类:255.255.0.0
a类:255.0.0.0
2.2 端口号
- 端口号:虚拟的概念,使用 0-65535 之间的整数,用于标识不同的应用程序
- 每个网络程序都会至少有一个端口号
2.3Socket 含义
Socket 称为“套接字”,是计算机之间通信的一种约定或一种方式,通过 Socket 这种约定,一台计算机可以接收其他计算机的数据,也可以向其他计算机发送数据。
每一个客户端都使用一个 Socket 对象表示,服务器端使用 ServerSocket 等待客户端的连接。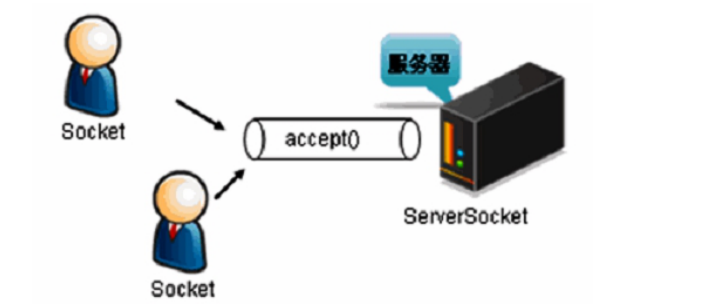
生活案例:
如果你想写封邮件发给远方的朋友,如何写信、将信打包,
属于应用层。信怎么写,怎么打包完全由我们做主;
而当我们将信投入邮筒时,邮筒的那个口就是套接字,在
进入套接字之后,就是传输层、网络层等(邮局、公路交管
或者航线等)其它层次的工作了。我们从来不会去关心信是
如何从西安发往北京的,我们只知道写好了投入邮筒就 OK
了

3.TCP 和 UDP 协议的区别
3.1 数据的传输
网络参考模式
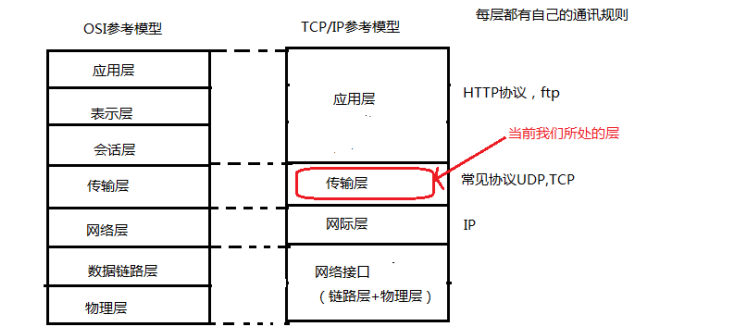
- (1) OSI 参考模式:开放系统互连参考模型(Open System Interconnect)
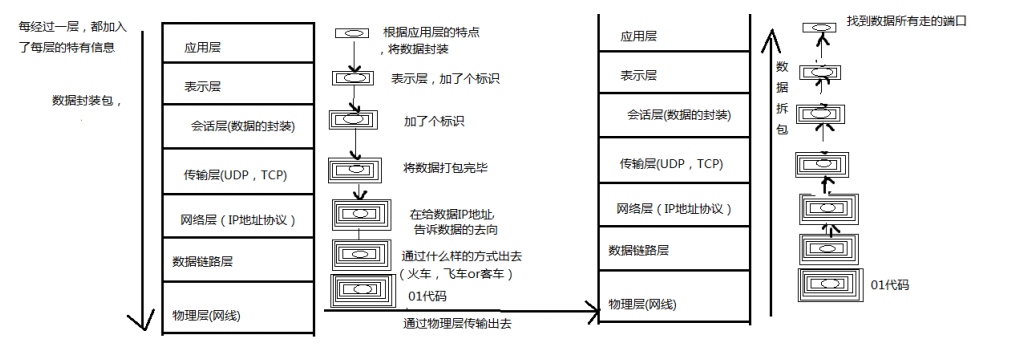
- (2) TCP/IP 参考模型:传输控制/网际协议 Transfer ControlnProtocol/Internet Protocol
3.2TCP 和 UDP 协议的区别
Tcp(transfer control protocol)传输控制协议
一种面向连接(连接导向)的、可靠的、基于字节流的运输层(Transport layer)通信协议。

特色
- (1)面向连接
- (2)点到点的通信
- (3)高可靠性:三次握手
- (4)占用系统资源多、效率低
生活案例
打电话
UDP(User DatagramProtocol)
一种无连接的传输层协议,提供面向事务的简单不可靠信息传送服务。
特点
(1)非面向连接,传输不可靠,可能丢失
(2)发送不管对方是否准备好,接收方收到也不确认
(3)数据报的大小限制在64k内
(4)非常简单的协议,开销小
生活案例
(1)发送短信 发电报

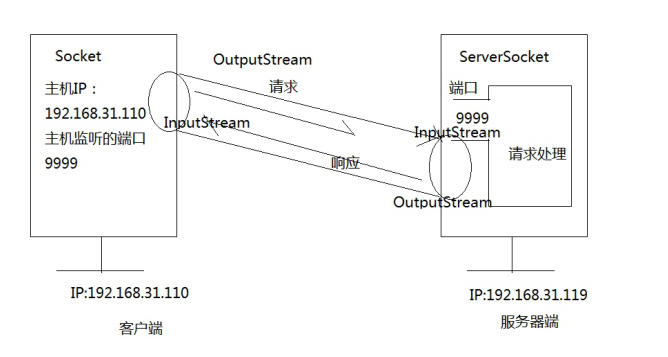
4.TCP 协议数据传递细节
4.1TCP 通信原理
- 服务器创建 ServerSocket,在指定端口监听并处理请求
- 客户端创建 Socket,向服务器发送请求

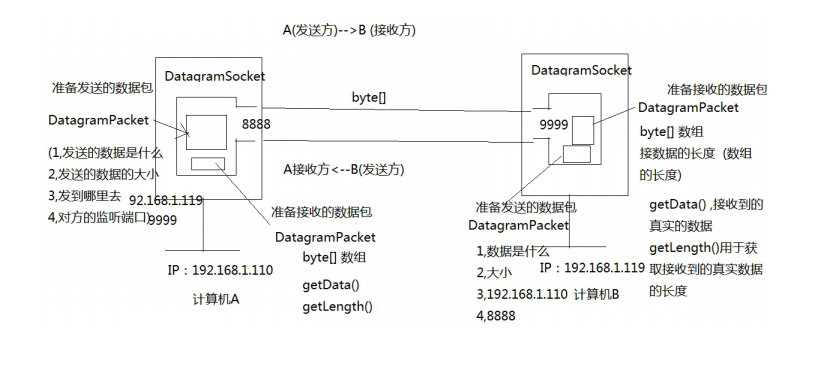
5.UDP 协议数据传递细节
5.1UDP 协议数据传递细节
- 1) 不需要利用 IO 流实现数据的传输
- 2) 每个数据发送单元被统一封装成数据包的方式,发送方将
- 数据包发送到网络中,数据包在网络中去寻找他的目的地。
- 3) DatagramSocket:用于发送或接收数据包
- 4) DatagramPacket:数据包

6.InetAddress 类_InetSocketAddress 类
6.1InetAddress 类
封装计算机的 IP 地址,不包含端口号
6.2InetAddress 类常用的方法


package net; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.UnknownHostException; public class TestInetAddress { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException { //(1)获取InetAddress的方式 InetAddress ia=InetAddress.getLocalHost(); System.out.println("获取主机ip地址:"+ia.getHostAddress()); System.out.println("获取主机名称:"+ia.getHostName()); //根据域名得到InetAddress InetAddress ia2=InetAddress.getByName("www.jd.com"); System.out.println("京东服务器的ip地址:"+ia2.getHostAddress()); System.out.println("主机名称:"+ia2.getHostName()); //()根据ip地址获取一个inetAddress对象 InetAddress ia3=InetAddress.getByName("61.135.253.15"); System.out.println("服务器主机ip"+ia3.getHostAddress()); System.out.println("主机名称:"+ia3.getHostName()); //如果61.135.253.15ip地址不存在或者DNS(域名解析系统)不允许进行IP地址和我们域名的映射 } }

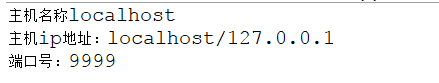
6.3InetSocketAddress 类
- 此类用于实现 IP 套接字地址 (IP 地址+端口号),用于socket 通信

package net; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.UnknownHostException; public class TestSocketAddress { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException { //创建对象 InetSocketAddress tsa = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",9999); InetSocketAddress tsa2 = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9999); InetSocketAddress tsa3 = new InetSocketAddress("192.168.31.113",9999); InetAddress ia=InetAddress.getByName("localhost"); InetSocketAddress tsa4 = new InetSocketAddress(ia,9999); System.out.println("主机名称"+tsa4.getHostName()); System.out.println("主机ip地址:"+tsa4.getAddress()); System.out.println("端口号:"+tsa4.getPort()); } }
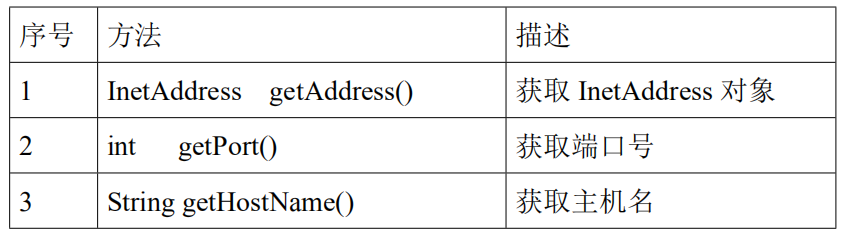
6.4InetSocketAddress 类常用的方法
8.URL
8.1URL 类
URL(Uniform Resource Locator)
- 统一资源定位符,由 4 部分组成:协议 、存放资源的主机域名、端口号和资源文件名。
- https://www.baidu.com:80/index.html#aa?username=bjsxt&pwd=bjsxt
URL 是指向互联网“资源”的指针
- 资源可以是简单的文件或目录,也可以是对更为复杂的对象的引用,例如对数据库或搜索引擎的查询。
8.2URL 类常用方法
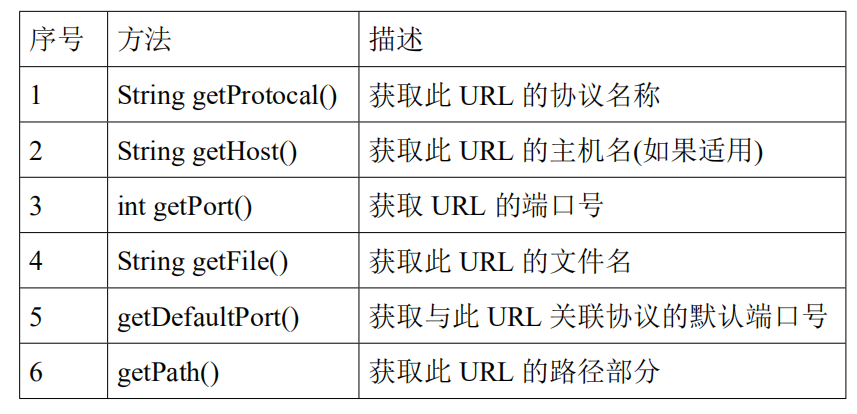
8.3openStream()方法
打开到此 URL 的连接并返回一个用于从该连接读入的InputStream

package net; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; public class TestURL { public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException { URL url=new URL("https://www.baidu.com:80/index.html#aa?username=bjsxt&pwd=bjsxt"); System.out.println("协议名称:"+url.getProtocol()); System.out.println("主机名称:"+url.getHost()); System.out.println("端口号:"+url.getPort()); System.out.println("获取资源路径:"+url.getFile()); System.out.println("获取资源路径:"+url.getPath()); System.out.println("获取默认端口:"+url.getDefaultPort()); } }

package net; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.net.URL; public class TestURL2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /**网络爬虫 * (1)从网络上获取资源 www.baidu.com * (2)存储到本地 * */ //(1)创建URL对象 URL url=new URL("https://www.baidu.com");//主页资源 //(2)获取字节输入流 InputStream is=url.openStream(); //(3)缓冲流 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, "utf-8")); //(4)存储到本地 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("index.html"),"utf-8")); //(5)边读边写 String line=null; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ bw.write(line); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } //(6)关闭流 bw.close(); br.close(); } }
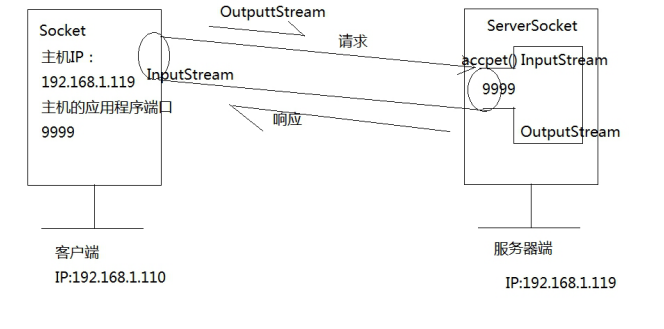
8.基于 TCP 协议的 Socket 编程_双向通信_实现单次请求与响应
8.1 传输示意图
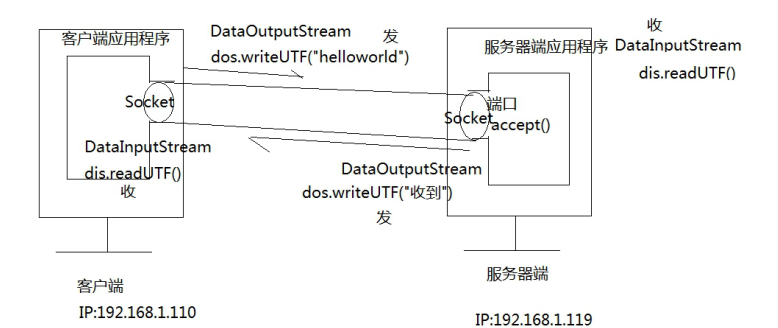
8.2 客户端


package com.bjsxt.entity; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.Scanner; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //(1)创建Socket对象,用于连接服务器 Socket client=new Socket("localhost", 8888); //(2)获取输出流 (对象流) ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); //(3)创建User对象 //调用获取用户对象的方法 User u=getUser();//new User("bjsxt", "bjsxt"); //(4)User对象发送到服务器 oos.writeObject(u); //(5)获取输入流(数据流) DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); System.out.println(dis.readUTF()); //(6)关闭流 if(dis!=null){ dis.close(); } if(oos!=null){ oos.close(); } if(client!=null){ client.close(); } } //获取用户对象的方法 public static User getUser(){ Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String userName=input.next(); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String password=input.next(); //封装成User对象 return new User(userName,password); } }

package socket.entity; import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable{//用于封装用户名和密码 /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = -1024620476475735473L; //用于封装用户名和密码 private String username; private String password; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public User(String username, String password) { super(); this.username = username; this.password = password; } public User() { super(); } }
8.3 服务器端
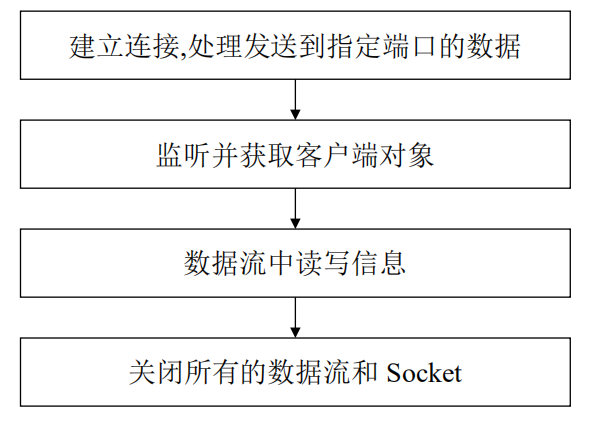

package com.bjsxt.server; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import com.bjsxt.entity.User; import com.bjsxt.thread.ServerThread; public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { System.out.println("----------------------服务器端已启动---------------------"); //(1)创建ServerSocket对象 ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(8888); while(true){ Socket socket=server.accept(); //创建线程类的对象,并启动线程 ServerThread st=new ServerThread(socket); //启动线程 new Thread(st).start(); } } }

package com.bjsxt.thread; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.net.Socket; import com.bjsxt.entity.User; public class ServerThread implements Runnable{ private Socket socket;//成员变量 public ServerThread(Socket socket){ this.socket=socket; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"请求登录"); //(2)获取输入流--(对象流) ObjectInputStream ois=null; //(4)获取输出流(数据流) DataOutputStream dos=null; try { ois = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); User user=(User) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()+"请求登录:用户名"+user.getUserName()+" 密码:"+user.getPassword()); String str=""; //(3)对用户名和密码进行验证 if("bjsxt".equals(user.getUserName())&&"bjsxt".equals(user.getPassword())){ str="登录成功"; }else{ str="对不起,账号号密码不正确"; } dos = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); dos.writeUTF(str); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //(5)关闭流 if(dos!=null){ try { dos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(ois!=null){ try { ois.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(socket!=null){ try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
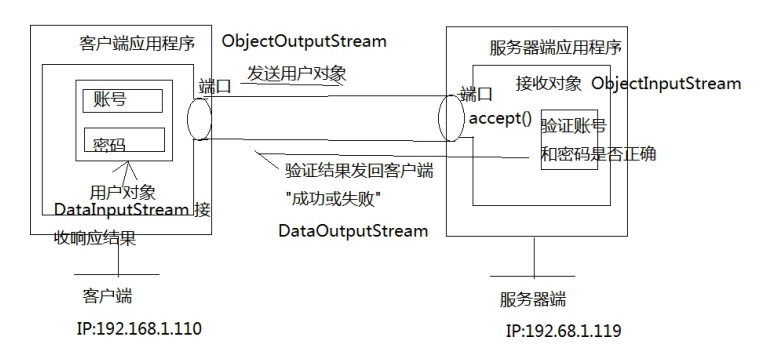
9.基于 TCP 协议的 Socket 编程_双向通信_实现模拟用户登录
9.1 双向通信_用户登录示意图
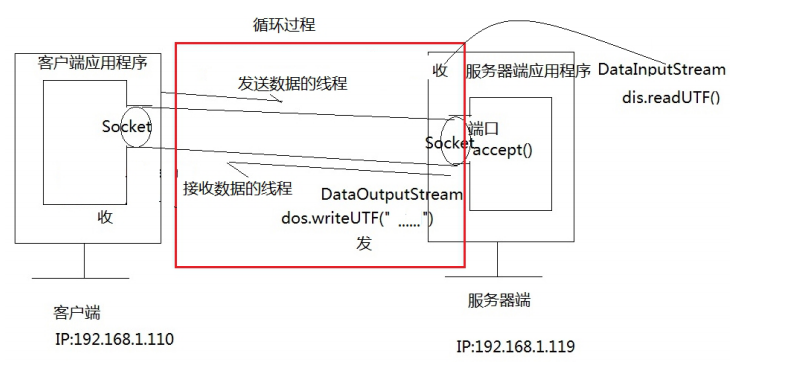
10.基于 TCP 协议的 Socket 编程_聊天室_客户端多线程
10.1 单次聊天的缺点
只能客户端先发送数据,然后才能接收数据,如果不发就收不到,(接收和发送是在一个线程中实现的)不符合实际情况。
10.2 解决方案
- (1)多次聊天可以使用循环来解决
- (2)先发后收的问题可以使用线程来解决,一个接收数据的线程,一个发送数据的线程
10.3 最终实现
- 单个客户端与服务器端多次通信

package com.bjsxt.chat.client; import java.io.Closeable; import java.io.IOException; public class CloseUtil { public static void closeAll(Closeable... able){ for (Closeable c : able) { if (c!=null) { try { c.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }

package com.bjsxt.chat.client; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //(1)创建Socket对象 Socket client=new Socket("localhost",9999); //(2)从键盘获取数据 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //(3)获取输出流 DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); //(4)获取输入流 DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); //从键盘获取数据 String str=br.readLine(); dos.writeUTF(str);//向服务器端发送数据 System.out.println(dis.readUTF());//接收服务器端的数据 } }

package com.bjsxt.chat.server; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("----------------服务器端已开启---------------------"); //(1)创建ServerSocket对象 ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(9999); //(2)监听客户端是否有客户端连接 Socket socket=server.accept(); //获取输入流 DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); //获取输出流 DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); String str=dis.readUTF(); System.out.println("客户端发送了:"+str); dos.writeUTF("服务器端收到了:"+str); //(5)关闭流 CloseUtil.closeAll(dos,dis,socket); } }
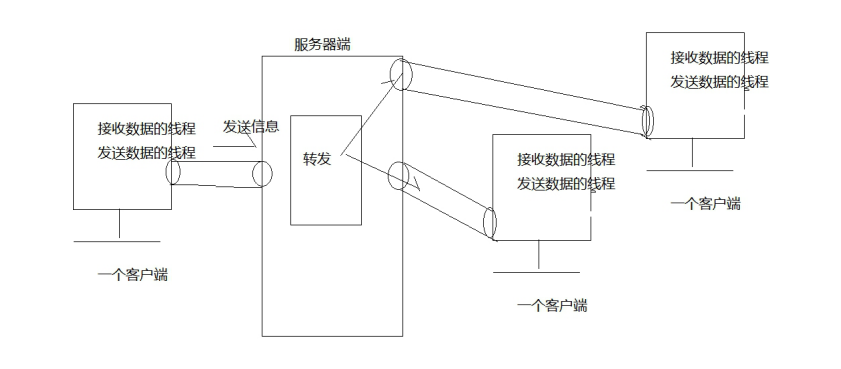
11.基于 TCP 协议的 Socket 编程_聊天室_群聊

package com.bjsxt.chat.client; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //(1)创建Socket对象 Socket client=new Socket("localhost",9999); //创建发送的线程类对象 Send send=new Send(client); //创建接收的线程类对象 Receive receive=new Receive(client); //创建Thread类对象并启动线程 new Thread(send).start(); new Thread(receive).start(); } }

package com.bjsxt.chat.client; import java.io.Closeable; import java.io.IOException; public class CloseUtil { public static void closeAll(Closeable... able){ for (Closeable c : able) { if (c!=null) { try { c.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }

1 package com.bjsxt.chat.client; 2 3 import java.io.DataInputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.net.Socket; 6 7 public class Receive implements Runnable { 8 //用于接收数据的数据流 9 private DataInputStream dis; 10 private boolean flag=true; 11 public Receive(Socket client){ 12 try { 13 dis=new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); 14 } catch (IOException e) { 15 flag=false; 16 CloseUtil.closeAll(dis,client); 17 } 18 } 19 private String getMessage(){ 20 String str=""; 21 try { 22 str = dis.readUTF(); 23 } catch (IOException e) { 24 flag=false; 25 CloseUtil.closeAll(dis); 26 } 27 return str; 28 } 29 @Override 30 public void run() { 31 while(flag){ 32 System.out.println(this.getMessage()); 33 } 34 } 35 36 }

package com.bjsxt.chat.client; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.Socket; public class Send implements Runnable { //(2)从键盘获取数据 private BufferedReader br; //发送数据的数据流 private DataOutputStream dos; private boolean flag=true;//默认为true public Send(){ br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); } public Send(Socket client){ this();//调用本类的无参构造方法 try { dos=new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); } catch (IOException e) { flag=false; CloseUtil.closeAll(dos,client); } } private String getMessage(){ String str=""; try { str = br.readLine(); } catch (IOException e) { flag=false; CloseUtil.closeAll(br); } return str; } private void send(String str){ try { dos.writeUTF(str); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { flag=false; CloseUtil.closeAll(dos); } } @Override public void run() { while(flag){ //调用发送信息的方法 this.send(getMessage()); } } }

package com.bjsxt.chat.server; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.List; /* * 每一个客户端都是条道路 * 1.输入流 * 2.输出流 * 3.接收数据 *4.发送数据 */ public class MyChannel implements Runnable{ private DataInputStream dis; private DataOutputStream dos; private boolean flag=true; public MyChannel(Socket client){ try { dis=new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream()); dos=new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); } catch (IOException e) { flag=false; CloseUtil.closeAll(dis,dos); } } //接收数据的方法 private String receive(){ String str=""; try { str=dis.readUTF(); } catch (IOException e) { flag=false; CloseUtil.closeAll(dis,dos); Server.list.remove(this); } return str; } //发送数据的方法 private void send(String str){ if (str!=null&&str.length()!=0) { try { dos.writeUTF(str); dos.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { flag=false; CloseUtil.closeAll(dos,dis); Server.list.remove(this); } } } //转发的方法 private void sendOther(){ String str=this.receive(); List<MyChannel> list=Server.list; for (MyChannel other : list) { if (other==this) { continue;//不发给自己 } other.send(str);//发送数组 } } @Override public void run() { while(flag){ //调用发送数据的方法 //this.send(receive()); sendOther(); } } }

package com.bjsxt.chat.server; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Server { //创建集合对象,存储每一个连接进来的客户端 public static List<MyChannel> list=new ArrayList<MyChannel>(); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("----------------服务器端已开启---------------------"); // (1)创建ServerSocket对象 ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(9999); // (2)监听客户端是否有客户端连接 while(true){ Socket socket = server.accept(); //创建线程类的对象 MyChannel channel=new MyChannel(socket); //添加到集合中 list.add(channel); //启动线程 new Thread(channel).start();; } // (5)关闭流 //CloseUtil.closeAll(dos, dis, socket); } }
12.UDP 通信_DatagramSocket 实现_客户咨询
- 1) 不需要利用 IO 流实现数据的传输
- 2) 每个数据发送单元被统一封装成数据包的方式,发送方将数据包发送到网络中,数据包在网络中去寻找他的目的地。
- 3) DatagramSocket:用于发送或接收数据包
- 4) DatagramPacket:数据包

package com.bjsxt.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; public class Test1 { //一次双向通信 /**一发 * 一收 * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("咨询者"); //创建DatagramSocket对象 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(8888);//本应用程序的端口 //准备要发送的数据 byte[] buf="helloworld".getBytes(); //创建数据报对象 //发送的数据, 发多少,发到哪台主机,主机程序使用的端口 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999); //发送 ds.send(dp); /**接收数据*/ byte [] buf2=new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket dp2=new DatagramPacket(buf2, buf2.length); // 借助String的构造方法查看 ds.receive(dp2); String str=new String(dp2.getData(),0,dp2.getLength()); System.out.println("客服说:"+str); ds.close(); } }

package com.bjsxt.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test2 { //一次双向通信 /**一发 * 一收 * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("咨询者"); Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); //创建DatagramSocket对象 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(8888);//本应用程序的端口 while(true){ //准备要发送的数据 String s=input.next(); byte[] buf=s.getBytes(); //创建数据报对象 //发送的数据, 发多少,发到哪台主机,主机程序使用的端口 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999); //发送 ds.send(dp); /**接收数据*/ byte [] buf2=new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket dp2=new DatagramPacket(buf2, buf2.length); // 借助String的构造方法查看 ds.receive(dp2); String str=new String(dp2.getData(),0,dp2.getLength()); System.out.println("客服说:"+str); if("bye".equals(s)){ break; } } ds.close(); } }

package com.bjsxt.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; public class Test1 { //接收方 /** 一收, * 一发 * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { System.out.println("客服人员"); DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(9999); //准 备接收数据 byte [] buf=new byte[1024]; //准 备数据报接收 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); //接收 ds.receive(dp); //查看接收到的数据 String str=new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength()); System.out.println("客户说:"+str); /**回复数据*/ byte [] buf2="welcome to beijing".getBytes(); DatagramPacket dp2=new DatagramPacket(buf2, buf2.length, dp.getAddress(), dp.getPort()); ds.send(dp2); //关闭 ds.close(); } }

package com.bjsxt.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test2 { //接收方 /** 一收, * 一发 * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("客服人员"); DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(9999); while(true){ //准 备接收数据 byte [] buf=new byte[1024]; //准 备数据报接收 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); //接收 ds.receive(dp); //查看接收到的数据 String str=new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength()); System.out.println("客户说:"+str); String s=input.next(); /**回复数据*/ byte [] buf2=s.getBytes(); DatagramPacket dp2=new DatagramPacket(buf2, buf2.length, dp.getAddress(), dp.getPort()); ds.send(dp2); if("bye".equals(s)){ break; } } //关闭 ds.close(); } }
