一、原子变量操作类以AtomicLong为例
AtomicLong是原子性递增或者递减类,基本上所有的方法都是对unsafe实例的方法的封装使用,用户不能对unsafe直接使用,原子操作类封装后可直接供用户使用。
1.初始化及变量
// setup to use Unsafe.compareAndSwapLong for updates private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();//引用unsafe单例 private static final long valueOffset; /** * Records whether the underlying JVM supports lockless * compareAndSwap for longs. While the Unsafe.compareAndSwapLong * method works in either case, some constructions should be * handled at Java level to avoid locking user-visible locks. */ static final boolean VM_SUPPORTS_LONG_CAS = VMSupportsCS8();//判断JVM是否支持Long类型无锁CAS /** * Returns whether underlying JVM supports lockless CompareAndSet * for longs. Called only once and cached in VM_SUPPORTS_LONG_CAS. */ private static native boolean VMSupportsCS8(); static { try { valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset (AtomicLong.class.getDeclaredField("value"));//获取AtomicLong中变量value的偏移量,以便unsafe操作 } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); } } private volatile long value;//实际变量值 /** * Creates a new AtomicLong with the given initial value. * * @param initialValue the initial value */ public AtomicLong(long initialValue) { value = initialValue; } /** * Creates a new AtomicLong with initial value {@code 0}. */ public AtomicLong() { }
2.部分方法:基本上所有的方法都是对unsafe的方法的封装使用
/** * Atomically increments by one the current value. * unsafe 自增返回自增值 * @return the updated value */ public final long incrementAndGet() { return unsafe.getAndAddLong(this, valueOffset, 1L) + 1L; } /** * Atomically decrements by one the current value. * unsafe 自减返回自减值 * @return the updated value */ public final long decrementAndGet() { return unsafe.getAndAddLong(this, valueOffset, -1L) - 1L; } /** * Atomically increments by one the current value. * unsafe 获取当前值,后自增 * @return the previous value */ public final long getAndIncrement() { return unsafe.getAndAddLong(this, valueOffset, 1L); } /** * Atomically decrements by one the current value. * unsafe 获取当前值,后自减 * @return the previous value */ public final long getAndDecrement() { return unsafe.getAndAddLong(this, valueOffset, -1L); } /** * Atomically sets the value to the given updated value * if the current value {@code ==} the expected value. * 赋值的原子操作 * @param expect the expected value * @param update the new value * @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that * the actual value was not equal to the expected value. */ public final boolean compareAndSet(long expect, long update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, expect, update); }
3、实现
public class AtomicTest { private static AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(); private static Integer[] arrayOne = new Integer[]{0,1,2,3,0,5,6,0,56,0}; private static Integer[] arrayTwo = new Integer[]{10,1,2,3,0,5,6,0,56,0}; private static void zeroCount(Integer[] array){ if (array == null || array.length == 0){ return; } int size = array.length; for (int i = 0; i< size; ++i){ if (array[i].intValue() == 0){ atomicLong.incrementAndGet();//计算0的个数 } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread threadOne = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { zeroCount(arrayOne); } }); Thread threadTwo = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { zeroCount(arrayTwo); } }); threadOne.start(); threadTwo.start(); threadOne.join(); threadTwo.join(); System.out.println("zero count :" + atomicLong.get()); } }
在没有原子类的情况下,实现计数器需要使用一定的同步措施,比如使用synchronized关键字等,属于阻塞同步,线程切换会导致核心态与用户态切换,对性能有一定的损耗,
而AtromicLong使用的是CAS非阻塞算法,一直运行在用户态,性能更好。
但在高并发情况下使用AtomicLong,会导致大量线程竞争更新同一个原子变量,其中只有一个线程CAS操作会成功,其他大量线程竞争失败后,会不断地循环进行自旋尝试,白白浪费CPU资源。
于是JDK8新增一个LongAdder来克服AtomicLong的缺点。把一个value分解成多个变量Cell,让同样多的线程去竞争多个Cell资源(多对一关系转变为多对多关系),提升性能;
代码中的多个变量实际是一个Cells数组,由于数组内存连续,容易产生伪共享,需要@sun.misc.Contended注解修饰Cell避免伪共享。
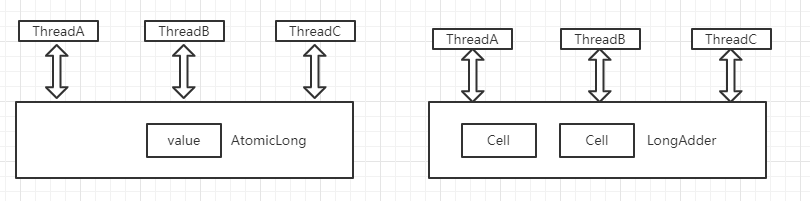
二、LongAdder类

1. LongAdder的父类Striped64
1)声明了三个变量:一个延迟初始化的原子性更新数组Cells、一个基值变量base和一个用来实现自旋锁的变量cellsBusy。
/** * Table of cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.Cell数组,不为空是,大小是2的n次方 */ transient volatile Cell[] cells; /** * Base value, used mainly when there is no contention, but also as * a fallback during table initialization races. Updated via CAS. */ transient volatile long base;//一个保险措施:相当于AtomicLong的value,在单线程时使用;或者多线程并发时cells数组初始化失败,作为value用回原AtomicLong逻辑 /** * Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating Cells.调整Cells大小或者创建Cells时自旋锁 */ transient volatile int cellsBusy;
2)初始化了unsafe实例引用(单例),注意这里多获取了Thread类threadLocalRandomProbe的偏移量
// Unsafe mechanics private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; private static final long BASE; private static final long CELLSBUSY; private static final long PROBE; static { try { UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class<?> sk = Striped64.class; BASE = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (sk.getDeclaredField("base")); CELLSBUSY = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (sk.getDeclaredField("cellsBusy")); Class<?> tk = Thread.class; PROBE = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (tk.getDeclaredField("threadLocalRandomProbe")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } }
3)定义了Cell静态内部类,Cell初始化了unsafe引用,提供CAS操作保证了Cell中value值的原子性,另外@sun.misc.Contended修饰避免了伪共享。
/** * Padded variant of AtomicLong supporting only raw accesses plus CAS. * * JVM intrinsics note: It would be possible to use a release-only * form of CAS here, if it were provided. */ @sun.misc.Contended static final class Cell { volatile long value; Cell(long x) { value = x; } final boolean cas(long cmp, long val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, cmp, val); } // Unsafe mechanics private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; private static final long valueOffset; static { try { UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class<?> ak = Cell.class; valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (ak.getDeclaredField("value")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } } }
2.LongAdder的方法
long sum():返回计算器的值,内部操作是累加所有Cell的value,但是求和时未加锁,返回结果不是一个原子快照;不并发时结果准确,并发时结果可能不准确了
void reset():重置操作,base置0,cells数组中元素置0;
long sumThenReset:返回sun后将cells,base重置为0;
T TValue():返回对应基本类型强定义装换(T)sum();
void add(long x):
/** * Adds the given value. * * @param x the value to add */ public void add(long x) { Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a; if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {//cells不为空或者base累加CAS操作失败 boolean uncontended = true;// if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 || (a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null || !(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x)))//cells为空 或 cells大小为0 或 映射的cell为空 或 cell存在但cas操作失败时 longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended);//包含cells数组被初始化和扩容的逻辑代码 } }
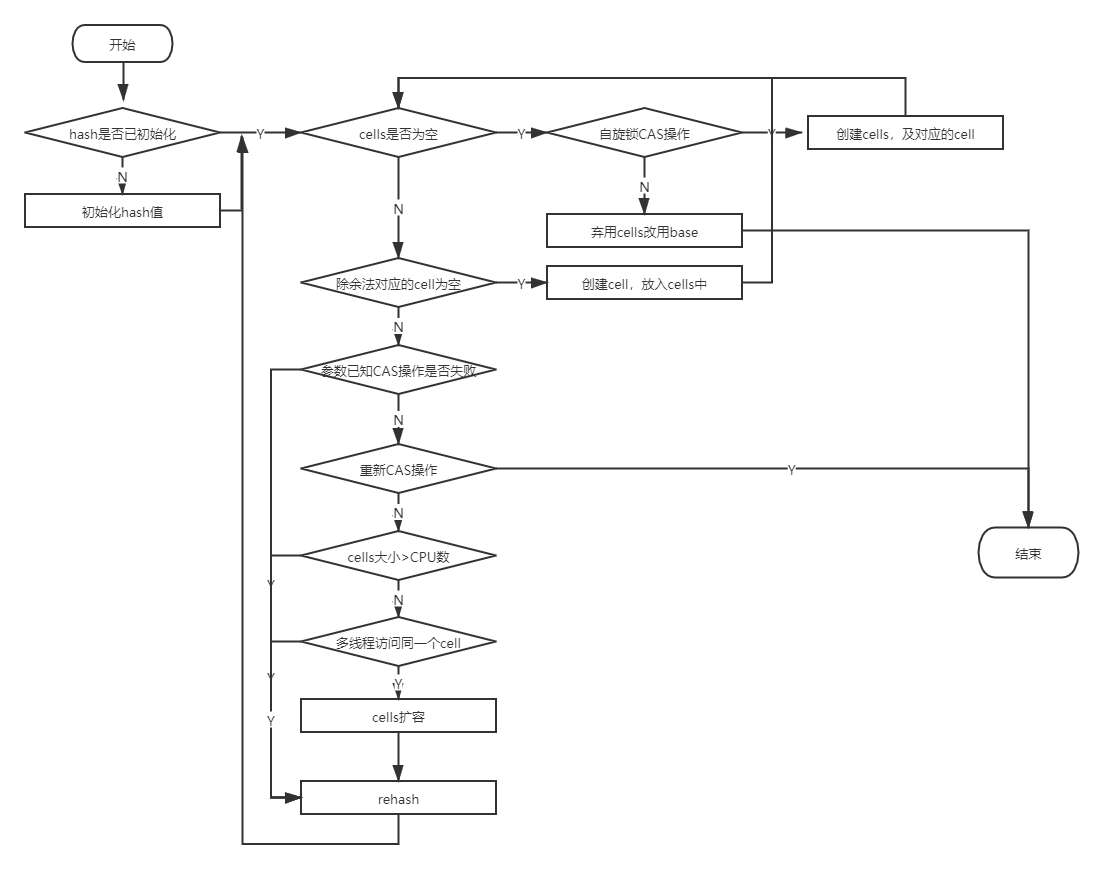
void longAccumulate(long x,LongBinaryOperator fn,boolean wasUncontended):是父类Striped64的方法,LongAdder继承了此方法并没有重写。它主要处理cells数组初始化、创建、扩容及多线程争用同一cell的问题
/** * Handles cases of updates involving initialization, resizing, * creating new Cells, and/or contention. See above for * explanation. This method suffers the usual non-modularity * problems of optimistic retry code, relying on rechecked sets of * reads. * 处理涉及cells初始化,扩容,创建及争用的情况,该方法会遇到乐观重试代码的模块性问题,依赖与重新检查的读取 * @param x the value * @param fn the update function, or null for add (this convention * avoids the need for an extra field or function in LongAdder). * @param wasUncontended false if CAS failed before call */ final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn, boolean wasUncontended) { int h; //初始化当前线程threadLocalRandomProbe的值 if ((h = getProbe()) == 0) { ThreadLocalRandom.current(); // force initialization h = getProbe(); wasUncontended = true; } boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty for (;;) { Cell[] as; Cell a; int n; long v; //cells不为空时扩容 if ((as = cells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) { //哈希函数除余法:probe%(length-1)得到当前线程对应cells数组中的Cell //cell为空 if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) { if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell Cell r = new Cell(x); // Optimistically create //cellsBusy的CAS配合上面for循环实现自旋锁,乐观重试 if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) { boolean created = false; try { // Recheck under lock Cell[] rs; int m, j; //再次校验cell为空,后赋值,重新检查 if ((rs = cells) != null && (m = rs.length) > 0 && rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) { rs[j] = r; created = true; } } finally { cellsBusy = 0; } if (created) break; continue; // Slot is now non-empty } } collide = false; } //CAS操作失败时 下面方法advanceProbe(probe) rehash probe的值后重新循环一遍 else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash //当前Cell存在,则执行CAS设置add后终止 else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; //当前Cell数组元素个数大于CPU个数,多线程访问了同一个cell导致cells != as else if (n >= NCPU || cells != as) collide = false; // At max size or stale //是否有冲突 else if (!collide) collide = true; //如果当前元素个数没有达到CPU个数并且多线程访问同一个cell则扩容 else if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) { try { if (cells == as) { // Expand table unless stale //扩容策略*2 Cell[] rs = new Cell[n << 1]; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) rs[i] = as[i]; cells = rs; } } finally { cellsBusy = 0; } collide = false; continue; // Retry with expanded table } //为了能够找到一个空闲的Cell,重新计算h的值(rehash),xorshift算法生成随机数 h = advanceProbe(h); } //cells为空,创建cells else if (cellsBusy == 0 && cells == as && casCellsBusy()) { boolean init = false; try { // Initialize table if (cells == as) { Cell[] rs = new Cell[2]; rs[h & 1] = new Cell(x); cells = rs; init = true; } } finally { cellsBusy = 0; } if (init) break; } else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; // Fall back on using base } }
同一个类所以简单画一个流程图
总结:
1.采用cells数组代替一个原子变量,使得多线程操作一个变量变化为多线程操作操作多个原子变量,提高了性能,
2.数组的连续存储,更容易导致伪共享,需要字节填充——@sun.misc.Contended注解,避免了伪共享
3.cells的创建、扩容及cell的创建利用了cellsBusy实现自旋锁保证了原子性
4.用当前线程的threadLocalRandomProbe作为hash值,以除余法为哈希函数求得当前线程访问Cell数组里的哪一个元素,需要注意的是扩容时并没有改变cells中cell的位置,即扩容后线程和cell的映射关系可能会改变
5.当多个线程访问了数组cells中同一个cell元素时,cells数组小于CPU个数时,并且发生扩容;cells数组达到最大值(CPU个数)时,只能rehash重新循环。
6.保险策略:当cells数组初始化失败时,用基值变量base作为单一原子变量执行,即回到原来的ActomicLong的单一原子变量value的逻辑。
另外:
final void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn, boolean wasUncontended) { ... else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; ... else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; }
LongAdder中调用父类Striped64的longAccumulate(long x,LongBinaryOperator fn,boolean wasUncontended)方法时第二个参数fn传入null
LongAccumulator与LongAdder结构相同但可以传入自定义的fn,功能更加强大。
三、LongAccumulator类
LongAccumulator与LongAdder的结构相同。
1.初始化与变量
private final LongBinaryOperator function;//双目运算器接口,输入两个参数返回一个计算值 private final long identity;// /** * Creates a new instance using the given accumulator function * and identity element. * @param accumulatorFunction a side-effect-free function of two arguments * @param identity identity (initial value) for the accumulator function */ public LongAccumulator(LongBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction, long identity) { this.function = accumulatorFunction; base = this.identity = identity; }
2.方法
public void add(long x) { Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a; if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) { boolean uncontended = true; if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 || (a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null || !(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x))) longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended); } } public void accumulate(long x) { Cell[] as; long b, v, r; int m; Cell a; if ((as = cells) != null || (r = function.applyAsLong(b = base, x)) != b && !casBase(b, r)) { boolean uncontended = true; if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 || (a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null || !(uncontended = (r = function.applyAsLong(v = a.value, x)) == v || a.cas(v, r))) longAccumulate(x, function, uncontended); } }
1.LongAdder.add()与LongAccumulator.accumulate()逻辑基本一模一样,仅仅运算器不一样
2.LongAccumulator的双目运算器function不能为空,可动态指定运算器规则,所以LongAdder其实是LongAccumulator的一个特例,LongAccumulator功能更加强大
LongAdder adder = new LongAdder(); //accumulator相当于上面adder LongAccmulator accumulator = new Long Accumulator(new LongBinaryOperator(){ @Override public long applyAsLong(long left, long right){ return left + right;//LongAccumulator功能更加强大表现在这里,还可以是left * right等自定义逻辑 } });
参考自《Java并发编程之美》