Description
You are in charge of data in a company, so you are called "Data Handler". Different from the data in computer, the data you have are really in huge volume, and each data contains only one integer. All the data are placed in a line from left to right. There are two "hand" to handle the data, call hand "L" and hand "R". Every hand is between two adjacent data or at the end of the data line.
In one day, the company gives you many commands to handle these data, so you should finish them one by one. At the beginning, there are N data, and hand "L" and "R" are in some positions. Each command is one the following formats:
(1)MoveLeft L/R: it means that you should move the hand "L"/"R" left one data unit;
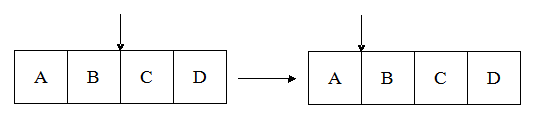
(2)MoveRight L/R: it means that you should move the hand "L"/"R" right one data unit;
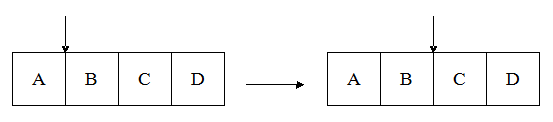
(3)Insert L X: it means that you should insert the data that contains X at the right of the hand "L";
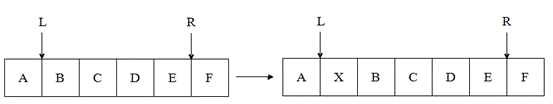
(4)Insert R X: it means that you should insert the data that contains X at the left of the hand "R";
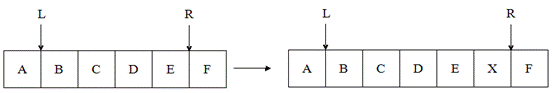
(5)Delete L: it means that you should delete the one data at the right of the hand "L";
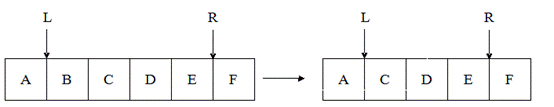
(6)Delete R: it means that you should delete the one data at the left of the hand "R";
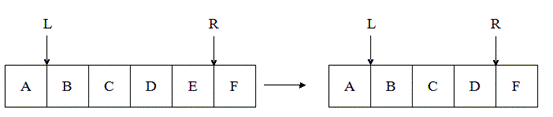
(7)Reverse: it means that you should reverse all the data between hand "L" and hand "R".

After finish all the commands, you should record all the data from left to right. So please do it.
In one day, the company gives you many commands to handle these data, so you should finish them one by one. At the beginning, there are N data, and hand "L" and "R" are in some positions. Each command is one the following formats:
(1)MoveLeft L/R: it means that you should move the hand "L"/"R" left one data unit;

(2)MoveRight L/R: it means that you should move the hand "L"/"R" right one data unit;

(3)Insert L X: it means that you should insert the data that contains X at the right of the hand "L";

(4)Insert R X: it means that you should insert the data that contains X at the left of the hand "R";

(5)Delete L: it means that you should delete the one data at the right of the hand "L";

(6)Delete R: it means that you should delete the one data at the left of the hand "R";

(7)Reverse: it means that you should reverse all the data between hand "L" and hand "R".

After finish all the commands, you should record all the data from left to right. So please do it.
Input
The first line contains an integer T(1<=T<=10), the number of test cases.
Then T test cases follow. For each test case, the first line contains an integer N(1<=N<=500000), the number of data at the beginning. The second line contains N integers, means the integer in each data, from left to right. The third line contains two integers L and R (1<=L<=R<=N), the positions of hand "L" and hand "R". It means that hand "L" is at the left of the L-th data and hand "R" is at the right of the R-th data. The fourth line contains one integer M(1<=M<=500000), the number of commands. Then M lines follow, each line contains a command in the above format. All the integers in the data will in range [-10000,10000].
It is guaranteed that there are always some data between hand "L" and "R", and if the hand is at the left/right end of the data line, it will not receive the command MoveLeft/MoveRight.
Because of large input, please use scanf instead of cin.
Then T test cases follow. For each test case, the first line contains an integer N(1<=N<=500000), the number of data at the beginning. The second line contains N integers, means the integer in each data, from left to right. The third line contains two integers L and R (1<=L<=R<=N), the positions of hand "L" and hand "R". It means that hand "L" is at the left of the L-th data and hand "R" is at the right of the R-th data. The fourth line contains one integer M(1<=M<=500000), the number of commands. Then M lines follow, each line contains a command in the above format. All the integers in the data will in range [-10000,10000].
It is guaranteed that there are always some data between hand "L" and "R", and if the hand is at the left/right end of the data line, it will not receive the command MoveLeft/MoveRight.
Because of large input, please use scanf instead of cin.
Output
For each test case, output the integers in the data from left to right in one line, separated in a single space.
Because of large output, please use printf instead of cout.
Because of large output, please use printf instead of cout.
Sample Input
2
5
1 2 3 4 5
1 5
5
MoveLeft R
Insert R 6
Reverse
Delete R
Insert L 7
5
6536 5207 2609 6604 -4046
1 3
5
Delete L
Insert R -9221
Reverse
Delete L
MoveRight L
Sample Output
7 6 4 3 2 5
2609 5207 6604 -4046
题意: 给出一串数字,左端L 指向左边某个数字下标,右端R 指向右边某个数字下标,
现在给出一些可行操作 MoveLeft Insert Reverse Delete (详见题意配图)
要求在L和R中间对这串数据进行操作 最后输出完成操作的这串数字
分析:
建立一个双端链表 将每个数字连接起来 每次进行操作只需重新连接某个数字的端点
插入和移动操作 单向链表就可以进行 然而双向链表最大的优势在于 翻转
给出的数据最大为500000
考虑纯暴力(每一次都将L与R间数据全部翻转)的最坏情况 500000*500000 很明显超时
这里的暴力需要一点技巧
比如 一串数字为
1 2 3 4 5
L指向1 的下标 R指向 5的下标
现在我们把这串数字分为三段 L及其左边一段 L与R中间一段 R及其右边一段
数字之间 左端接左数字下标 右端接右数字下标 中间段就只需标记读取方向 而不改变端点的连接方式
那么
如果 L与R中间的数 是从左到右读取 那么MoveLeft Insert操作只需按照题意进行
如果 是从右向左读取 MoveLeft L 就相当于是 将1 连到 4 与 5 之间 再将L指向 虚拟下标 0 这样做是为了保证L与R之间的读取方向不变
其他操作同理
来分析一下第一组数据吧
0 | 1 2 3 4 5 | 6
L = 0 R = 6
MoveLeft R
0 | 1 2 3 4 5 | 6
L R L与R间读取方向 :左→右
Insert R 6
0 | 1 2 3 4 6 5 | 6
L R L与R间读取方向 :左→右
L R L与R间读取方向 :左→右
Reverse
0 | 1 2 3 4 6 5 | 6
L R L与R间读取方向 :右→左
L R L与R间读取方向 :右→左
Delete R
0 | 2 3 4 6 5 | 6
L R L与R间读取方向 :右→左
L R L与R间读取方向 :右→左
Insert L 7
0 | 2 3 4 6 7 5 | 6
L R L与R间读取方向 :右→左
L R L与R间读取方向 :右→左
那么此时输出为 7 6 4 3 2 5 L与R间数据就按照了从右向左输出 而连接顺序不变
附上AC代码
1 #include<cstring> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<cmath> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 #define AA struct ss 10 11 AA 12 { 13 int r,l; 14 int num; 15 int ans; 16 }T[1500006]; 17 18 int L,R; 19 int vis; 20 int flag; 21 int sum; 22 int n; 23 24 bool MoveLeft(char *s) 25 { 26 if(strcmp(s,"MoveLeft")!=0) return false; 27 28 char ss[5]; 29 scanf("%s",ss); 30 31 if(ss[0]=='R') 32 { 33 int p=T[R].l; 34 if(!flag) R=T[p].num; 35 else 36 { 37 int q=T[L].r; 38 int q1=T[q].r; 39 T[R].l=T[q].num; 40 T[p].r=T[q].num; 41 42 T[q].l=T[p].num; 43 T[q].r=T[R].num; 44 45 T[q1].l=T[L].num; 46 T[L].r=T[q1].num; 47 48 R= T[q].num; 49 } 50 sum--; 51 } 52 else 53 { 54 int p=T[L].l; 55 if(!flag) L=T[p].num; 56 else 57 { 58 int q=T[L].r; 59 int q1=T[R].l; 60 T[p].r=T[q].num; 61 T[q].l=T[p].num; 62 63 T[q1].r=T[L].num; 64 T[L].r=T[R].num; 65 66 T[R].l=T[L].num; 67 T[L].l=T[q1].num; 68 69 L = T[p].num; 70 } 71 sum++; 72 } 73 return true; 74 } 75 76 bool MoveRight(char *s) 77 { 78 if(strcmp(s,"MoveRight")!=0) return false; 79 80 char ss[5]; 81 scanf("%s",ss); 82 83 if(ss[0]=='R') 84 { 85 int p=T[R].r; 86 if(!flag) R=T[p].num; 87 else 88 { 89 int q=T[L].r; 90 int q1=T[R].l; 91 T[L].r= T[R].num; 92 T[R].r= T[q].num; 93 94 T[q].l= T[R].num; 95 T[R].l= T[L].num; 96 97 T[q1].r= T[p].num; 98 T[p].l= T[q1].num; 99 100 R= T[p].num; 101 } 102 sum++; 103 } 104 else 105 { 106 int p=T[L].r; 107 if(!flag) L=T[p].num; 108 else 109 { 110 int q= T[R].l; 111 int q1= T[q].l; 112 113 T[L].r= T[q].num; 114 T[q].l= T[L].num; 115 116 T[q].r= T[p].num; 117 T[p].l= T[q].num; 118 119 T[q1].r=T[R].num; 120 T[R].l=T[q1].num; 121 122 L= T[q].num; 123 } 124 sum--; 125 } 126 return true; 127 } 128 129 bool Insert(char *s) 130 { 131 if(strcmp(s,"Insert")!=0 ) return false; 132 133 char p[6]; 134 scanf("%s",p); 135 scanf("%d",&T[vis].ans); 136 T[vis].num=vis; 137 138 if(p[0]=='R') 139 { 140 int q = T[R].l; 141 142 if(!flag) 143 { 144 T[q].r=T[vis].num; 145 T[vis].l=T[q].num; 146 T[vis].r=T[R].num; 147 T[R].l=T[vis].num; 148 } 149 else 150 { 151 q=T[L].r; 152 T[L].r=T[vis].num; 153 T[vis].l=T[L].num; 154 T[vis].r=T[q].num; 155 T[q].l=T[vis].num; 156 } 157 } 158 else 159 { 160 int q = T[L].r; 161 162 if(!flag) 163 { 164 T[L].r=T[vis].num; 165 T[vis].l=T[L].num; 166 T[vis].r=T[q].num; 167 T[q].l=T[vis].num; 168 } 169 else 170 { 171 q = T[R].l; 172 T[q].r=T[vis].num; 173 T[vis].l=T[q].num; 174 T[vis].r=T[R].num; 175 T[R].l=T[vis].num; 176 } 177 178 } 179 vis++; 180 sum++; 181 182 return true; 183 } 184 185 bool Delete(char *s) 186 { 187 if(strcmp(s,"Delete")!=0 ) return false; 188 189 char p[5]; 190 scanf("%s",p); 191 192 if(sum==0) return true; 193 if(p[0]=='R') 194 { 195 if(flag){ 196 int q1 = T[L].r; 197 int q2 = T[q1].r; 198 199 T[L].r=T[q2].num; 200 T[q2].l=T[L].num; 201 202 T[q1].r=q1; 203 T[q1].l=q1; 204 } 205 else 206 { 207 int q1=T[R].l; 208 int q2=T[q1].l; 209 210 T[q2].r=T[R].num; 211 T[R].l=T[q2].num; 212 213 T[q1].r=q1; 214 T[q1].l=q1; 215 } 216 } 217 else 218 { 219 if(!flag){ 220 int q1 = T[L].r; 221 int q2 = T[q1].r; 222 223 T[q2].l=T[L].num; 224 T[L].r=q2; 225 226 T[q1].l=q1; 227 T[q1].r=q1; 228 } 229 else 230 { 231 int q1=T[R].l; 232 int q2=T[q1].l; 233 234 T[q2].r=T[R].num; 235 T[R].l=T[q2].num; 236 237 T[q1].r=q1; 238 T[q1].l=q1; 239 } 240 } 241 sum--; 242 return true; 243 } 244 245 bool Reverse(char *s) 246 { 247 if(strcmp(s,"Reverse")!=0) return false; 248 249 if(!flag) flag=1; 250 else flag=0; 251 return true; 252 } 253 254 void change() 255 {
//这里是将L 与 R 端点 链表节点重新连接一下 方便输出 256 if(!sum) return ; 257 int q1=T[R].l,q2=T[L].r; 258 259 T[L].r = T[q1].num; 260 T[q1].r = T[L].num; 261 T[q2].l = T[R].num; 262 T[R].l = T[q2].num; 263 } 264 265 void pr() 266 { 267 if(flag) change(); 268 269 int q=0; 270 for(int i=T[0].r ; T[i].num!=n+1 ; ) 271 { 272 printf("%d",T[i].ans); 273 int s=i; 274 275 if(T[i].l==q) i=T[i].r; 276 else if(T[i].r==q) i=T[i].l; //这里的输出用了一点小技巧 :判断当前数据在上一数据的位置l 或者 r 然后改变输出 i 的方向 277 278 q=T[s].num; 279 if(T[i].num!=n+1) printf(" "); 280 } 281 } 282 283 int main() 284 { 285 int t; 286 scanf("%d",&t); 287 while(t--) 288 { 289 scanf("%d",&n); 290 291 T[0].l=0; 292 T[0].r=1; 293 T[0].num=0; 294 T[0].ans=0; 295 296 T[n+1].l=n; 297 T[n+1].r=n+1; 298 T[n+1].num=n+1; 299 T[n+1].ans=0; 300 vis = n+2; 301 flag = 0; 302 303 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 304 { 305 scanf("%d",&T[i].ans); 306 T[i].num=i; 307 T[i].r=i+1; 308 T[i].l=i-1; 309 } 310 311 scanf("%d%d",&L,&R); 312 L--,R++; 313 sum = R-L-1; 314 315 int time; 316 scanf("%d",&time); 317 318 while(time--) 319 { 320 char s[50]; 321 scanf("%s",s); 322 if( MoveLeft(s) ) ; 323 else if( MoveRight(s) ) ; 324 else if( Insert(s) ) ; 325 else if( Delete(s) ) ; 326 else if( Reverse(s) ) ; 327 if(sum<=1) flag=0; 328 } 329 330 pr(); 331 puts(""); 332 333 } 334 return 0; 335 }
还有一种是 双端队列做法 利用已有的函数简化了链表操作