Overview
- Use HBase when u need random, realtime read/write access to ur Big Data.
- HBase is an open-source, distributed, versioned, non-relational database modeled after Google's Bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data
- Bigtable是一个疏松的、分布式的、持久的多维排序的map。这个map被行键,列键,和时间戳索引.每一个值都是非解释的byte数组.【引自BigTable论文:A Bigtable is a sparse, distributed, persistent multidimensional sorted map. The map is indexed by a row key, column key, and a timestamp; each value in the map is an uninterpreted array of bytes.】
Features
- Linear and modular scalability; 可扩展性
- Strictly consistent reads and writes; 强读写一致性
- Automatic and configurable sharding of tables; 自动、可配置的表分区
- Automatic failover support between RegionServers; RegionServers间自动的失效备援
- Convenient base classes for backing Hadoop MapReduce jobs with Apach HBase tables;
- Easy to use Java API for client access;
- Block cache and Bloom filters for real-time queries; 块缓存 & bloom filter for实时查询 [for high volume query optimization]
- Thrift gateway and a REST-ful Web service that supports XML, Protobuf, and binary data encoding options;
- Extensible jruby-based(JIRB) shell;
- Support for exporting metrics via the Hadoop metrics subsystem to files or Ganglia; or via JMX
Data Model
- 在HBase中,数据存储在表(包含有行和列)中。
- HBase术语:
- Tables:一个HBase table由多行组成;
- Row: Hbase中的一行由 a row key + one or more columns with values associated with them组成。 行是按row key字母顺序存储的。因此,row key的设计是十分重要的。
- column:A column in HBase consists of a column family and a column qualifier, which are delimited by a
:(colon) character. 【列由列族 + 列修饰符组成。】 - column family: Column families physically colocate a set of columns and their values, often for performance reasons. 列族一般是处于性能考虑,每个列族都有一系列的存储特性:比如值是否cache到内存,数据如何压缩,row key如何编码等等。一个表中的每一行都有相同的列族,尽管一个给定的行在给定列族上不存储任何东西。
- column qualifier: A column qualifier is added to a column family to provide the index for a given piece of data. [列修饰符用于给给定的一块数据提供索引。]
- Cell: cell是行、列族和列修饰符的组成,并且包含值和时间戳(用以表示值的版本)。
- timestamp: 时间戳是与每个值一起写入的,用做值的版本修饰符。缺省情况下,timestamp表示数据写入regionServer时的时间,你也可以指定。
Conceptual View
- Eg:
- TableName: webtable
- contains two rows--> com.cnn.www & com.example.www [rowkey]
- three column families--> contents & anchor & people
- anchor contains two columns--> anchor:cssnsi.com & anchor:my.look.ca [列anchor:cssnsi.com由列族anchor和cssnsi.com修饰符组成]
- contains 5 versions of the row with rowkey com.cnn.www
Physical View
- 尽管在概念层面上,表可以被看成行的稀疏集合。但在物理上它们是通过列族存储的。一个新的列修饰符(column_family:column_qualifier)可以随时被添加到已有的列族中。
-
Table 5. ColumnFamily anchorRow Key Time Stamp Column Family anchor"com.cnn.www"
t9
anchor:cnnsi.com = "CNN""com.cnn.www"
t8
anchor:my.look.ca = "CNN.com"Table 6. ColumnFamily contentsRow Key Time Stamp ColumnFamily contents:"com.cnn.www"
t6
contents:html = "<html>…"
"com.cnn.www"
t5
contents:html = "<html>…"
"com.cnn.www"
t3
contents:html = "<html>…"
Architecture
Overview
NoSQL?
- "NoSQL" is a general term meaning that the database isn’t an RDBMS which supports SQL as its primary access language.
- There are many types of NoSQL databases: BerkeleyDB is an example of a local NoSQL database, whereas HBase is very much a distributed database. Technically speaking, HBase is really more a "Data Store" than "Data Base" because it lacks many of the features you find in an RDBMS, such as typed columns, secondary indexes, triggers, and advanced query languages, etc.【HBase是分布式数据库。它缺少RDBMS中的很多特性,比如二级索引、触发器和高级查询语言等等。】
When should I use HBase?
- HBase并不适合所有场景。
- 首先,确保你有足够的数据。否则你的数据可能在一个单一机器上,其他的node会sitting idle。
- 第二,确保u can like without all the extra featrues that an RDBMS provides(e.g., typed columns, secondary indexes, transactions, advanced query languages, etc.)
- 第三,确保你有足够多硬件设备。
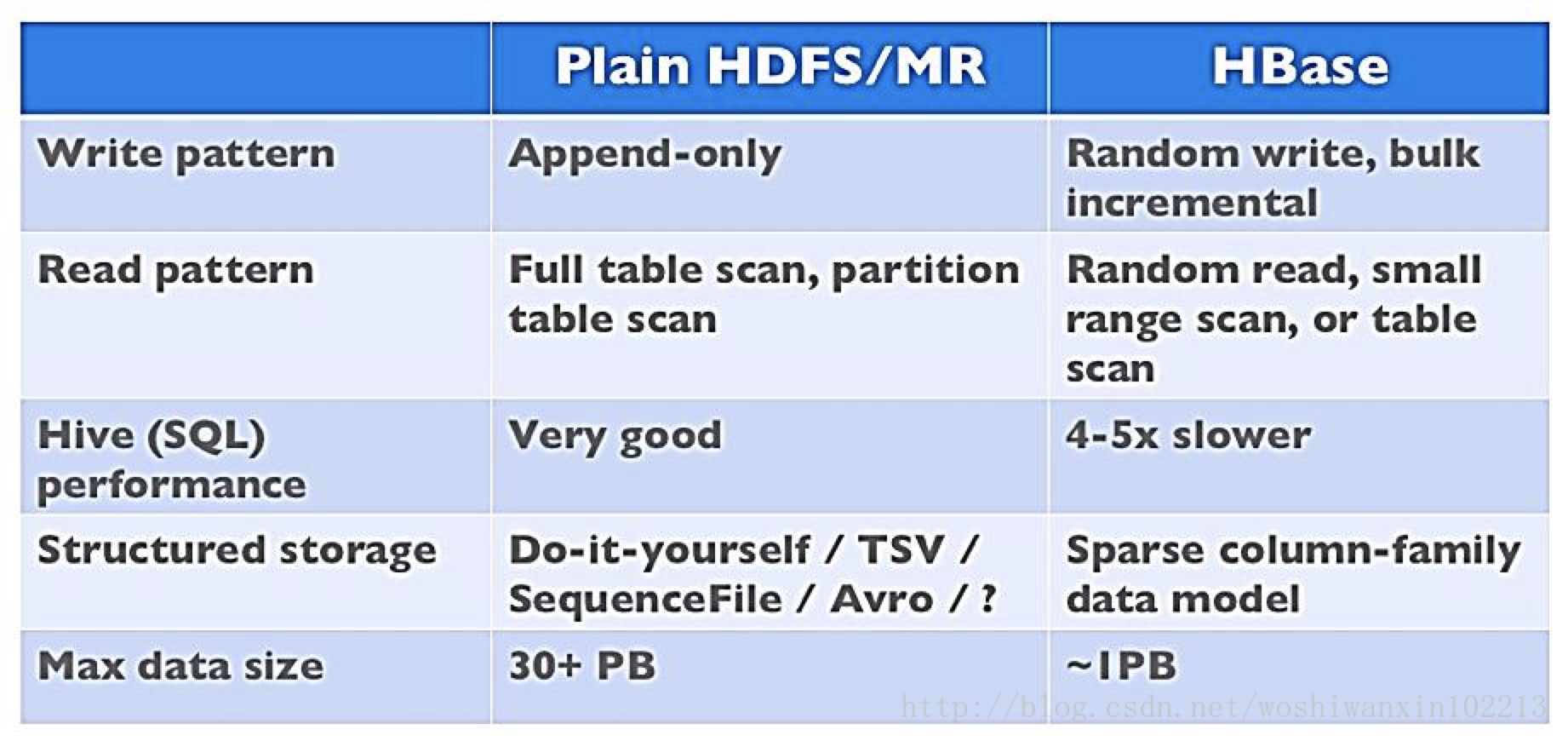
What Is the Difference Between HBase and Hadoop/HDFS?
- HDFS很适合于存储大文件。但是它不提供快速的、单一记录的查询。
- 而HBase is built on top of HDFS, 并且提供对large tables的快速记录查询和更新。
- 关于这一点,你可能会有点困惑。实际上,HBase是通过将数据放在索引的存放在HDFS上的"StoreFiles"来提供高速查询的。关于更详细的解释,可以看下本篇介绍的Data Model部分。
HBase架构及基本组件
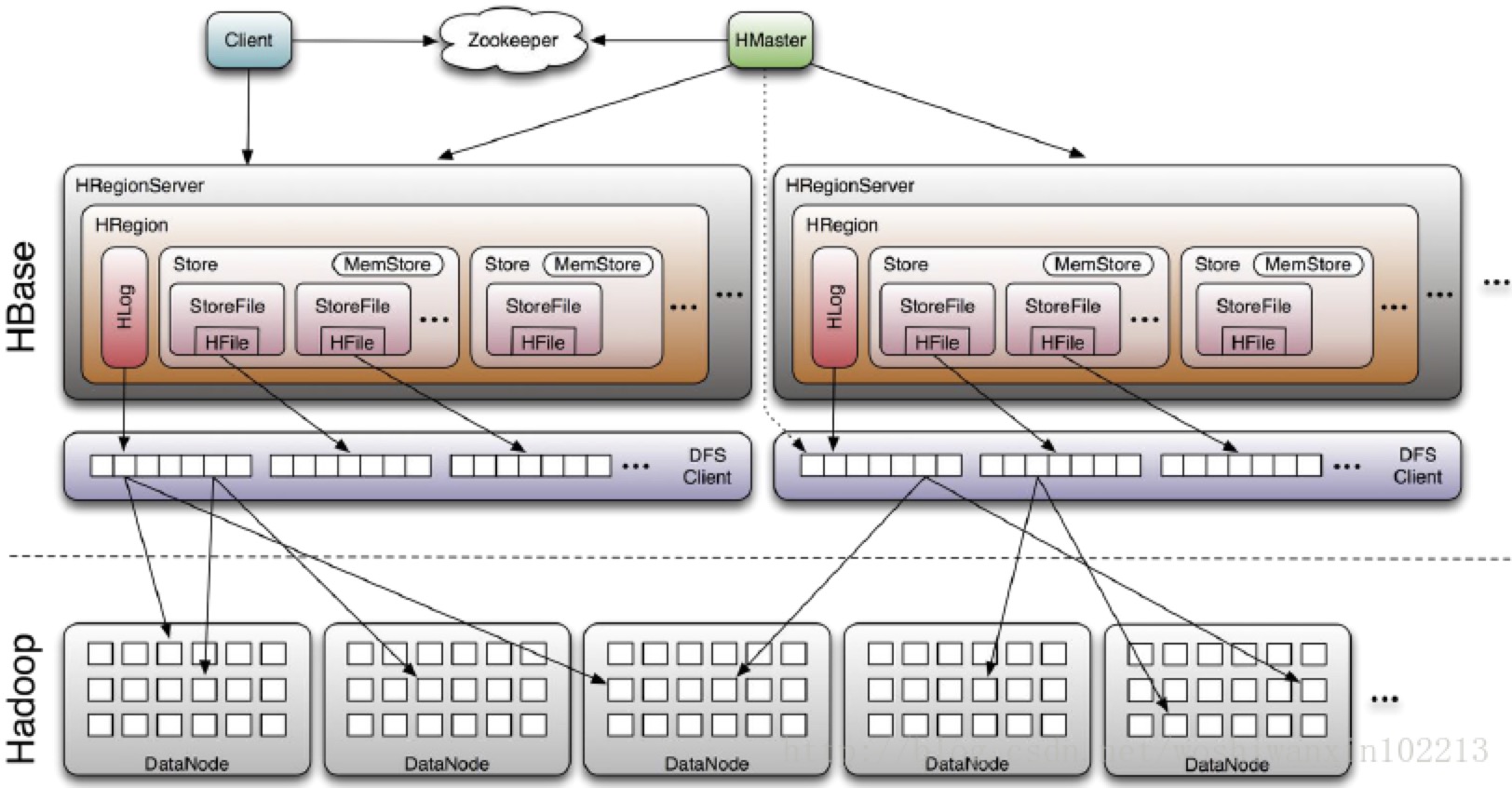
- Client:包含访问HBase的接口,并维护cache来加快对HBase的访问,比如region的位置信息;
- Master:为Region server分配region;负责region server的负载均衡;发现失效的region server并重新分配其上的region;管理用户对table的增删改查操作;【两方面职责:1)协调RegionServer;2)创建、删除、修改Table的定义】
- Region server:维护region,处理对这些region的IO请求;负责切分在运行过程中变得过大的region;
- Zookepper:通过选举,保证任何时候集群只有只有一个master;master和region servers启动时会向zookeeper注册存贮所有region的寻址的入口;实时监测region server的上线和下线信息,并通知给master;存储HBase的schema和table的元数据;zookeeper的引入使得master不再是单点故障。【实现Master主从节点的failover】
- HBase的容错性:
- Master容错:Zookeeper重新选择一个新的Master;无master过程中,数据读取仍照常进行,但region切分、负载均衡等无法进行(master的职责)。【可以启动多个HMaster,通过Zookeeper的Master Election机制保证同时只有一个master处于Active状态,其他HMaster处于热备份状态。一般情况下会启动两个HMaster,非Active的HMaster会定期的和Active HMaster通信以获取其最新状态,从而保证它是实时更新的,因而如果启动了多个HMaster反而增加了Active HMaster的负担。】
- regionServer容错:定时向zookeeper汇报心跳,若一定时间内未出现心跳,Master将该RegionServer上的Region重新分配到其他RegionServer上,失效服务器上“预写”日志由主服务器进行分割并派送给新的RegionServer
- zookeeper容错:zookeeper是一个可靠的服务,一般配置3or5个zookeeper实例。
Summary
- HBase是一个构建在HDFS上的分布式列存储系统;
- Hbase是基于Google BigTable模型开发的,典型的key/value系统;
- for海量结构化数据存储;
- 面向列族的存储和控制权限,列族独立检索;
- 空列并不占用存储空间,表可以设计得非常稀疏;
- 数据多版本:每个单元中的数据可有多个版本,默认情况下版本号自动分配,是单元格插入时的时间戳;
- 数据类型单一:Hbase中数据都是字符串,无类型。
- HBase逻辑视图:
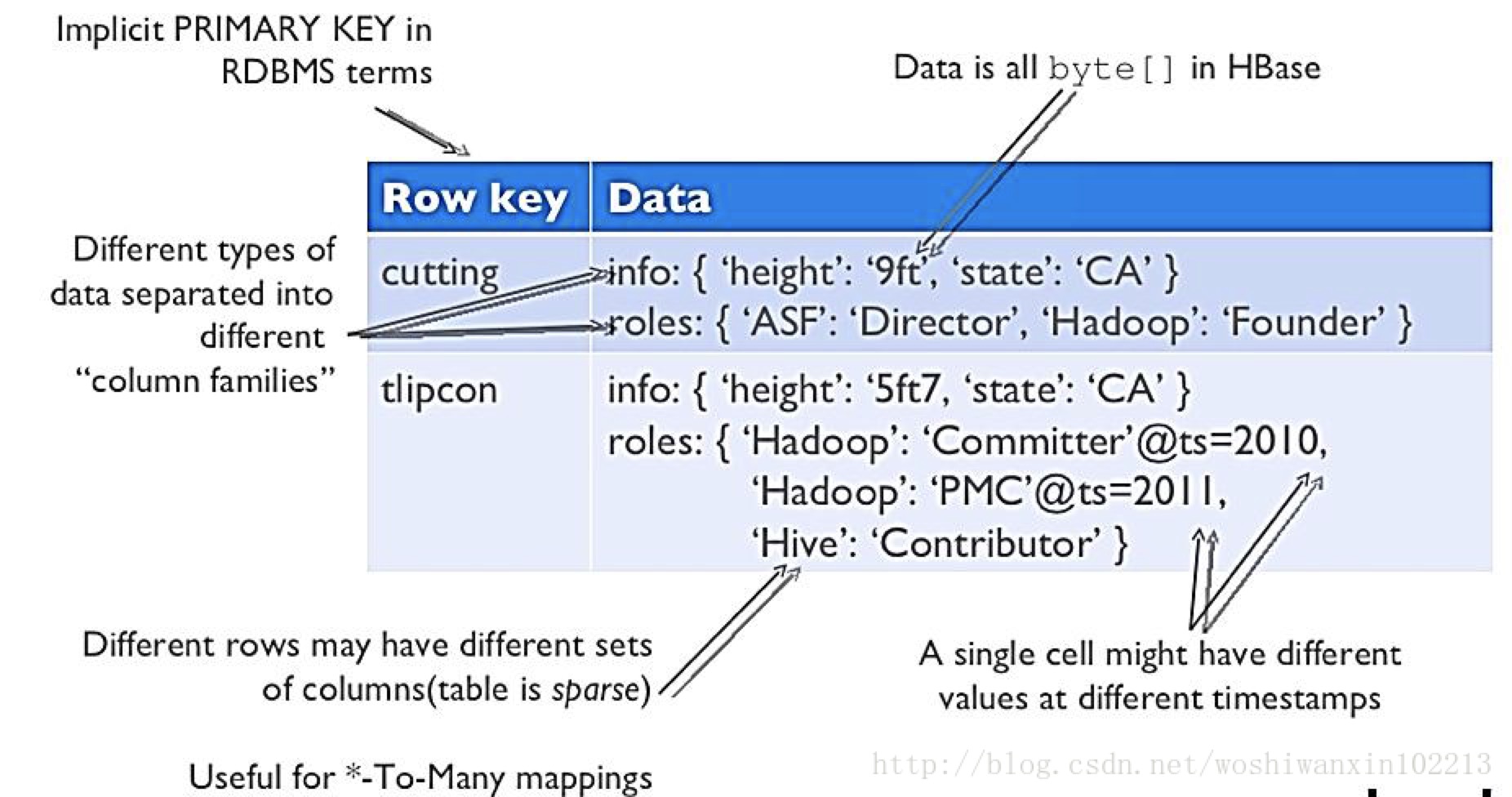
- rowkey是表中每条记录的"主键",方便快速查找,rowkey的设计非常重要。
- 列族内可以随意添加类
- HBase物理模型:
- 每个列族存储在HDFS上的一个单独文件中,空值不会被保存;
- key和version number在每个列族中均有一份;
- HBase为每个值维护了多级索引,即<key, column family, column name, timestamp>
- 物理存储:
- table中所有行都按row key字典序排列;
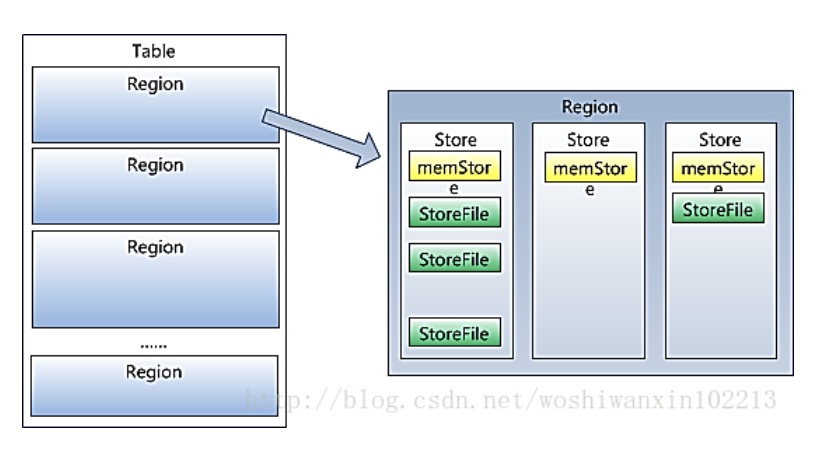
- table在行方向上分隔为多个region;

- region是HBase中分布式存储和负载均衡的最小单元,不同region分布到不同RegionServer上;[分布式是按行划分,而实际存储是按列。Parquet也是酱紫的。]
- 但region不是HBase存储的最小单元。Region由一个或多个store组成,每个store保存一个列族,每个store又由一个memStore和多个storeFile组成。memStore存储子啊内存中,storeFile存储在HDFS上。
- HBase VS HDFS
- 虽然Hbase中有多个RegionServer的概念,RegionServer是调度者,管理Regions,但是数据是持久化在HDFS上的。