题目链接:HDU 5572
Problem Description
On an infinite smooth table, there's a big round fixed cylinder and a little ball whose volume can be ignored.
Currently the ball stands still at point (A), then we'll give it an initial speed and a direction. If the ball hits the cylinder, it will bounce back with no energy losses.
We're just curious about whether the ball will pass point (B) after some time.
Input
First line contains an integer (T), which indicates the number of test cases.
Every test case contains three lines.
The first line contains three integers (O_x), (O_y) and (r), indicating the center of cylinder is ((O_x, O_y)) and its radius is (r).
The second line contains four integers (A_x), (A_y), (V_x) and (V_y), indicating the coordinate of (A) is ((A_x, A_y)) and the initial direction vector is ((V_x, V_y)).
The last line contains two integers (B_x) and (B_y), indicating the coordinate of point (B) is ((B_x,B_y)).
⋅ (1 ≤ T ≤ 100.)
⋅ (|O_x|,|O_y|≤ 1000.)
⋅ (1 ≤ r ≤ 100.)
⋅ (|A_x|,|A_y|,|B_x|,|B_y|≤ 1000.)
⋅ (|V_x|,|V_y|≤ 1000.)
⋅ (V_x≠0 or V_y≠0.)
⋅ both (A) and (B) are outside of the cylinder and they are not at same position.
Output
For every test case, you should output " Case #x: y", where (x) indicates the case number and counts from (1). (y) is " (Yes)" if the ball will pass point (B) after some time, otherwise (y) is " (No)".
Sample Input
2
0 0 1
2 2 0 1
-1 -1
0 0 1
-1 2 1 -1
1 2
Sample Output
Case #1: No
Case #2: Yes
Source
Solution
题意
在光滑平面上有一个圆,圆外有两点 (a),(b),给定 (a) 的方向向量,求 (a) 运动一段时间后能否到达 (b)((a) 碰到圆后没有反弹没有能量损失)。
思路
分类讨论一下。
点 (a) 的运动在圆外或者与圆相切时直接判断。
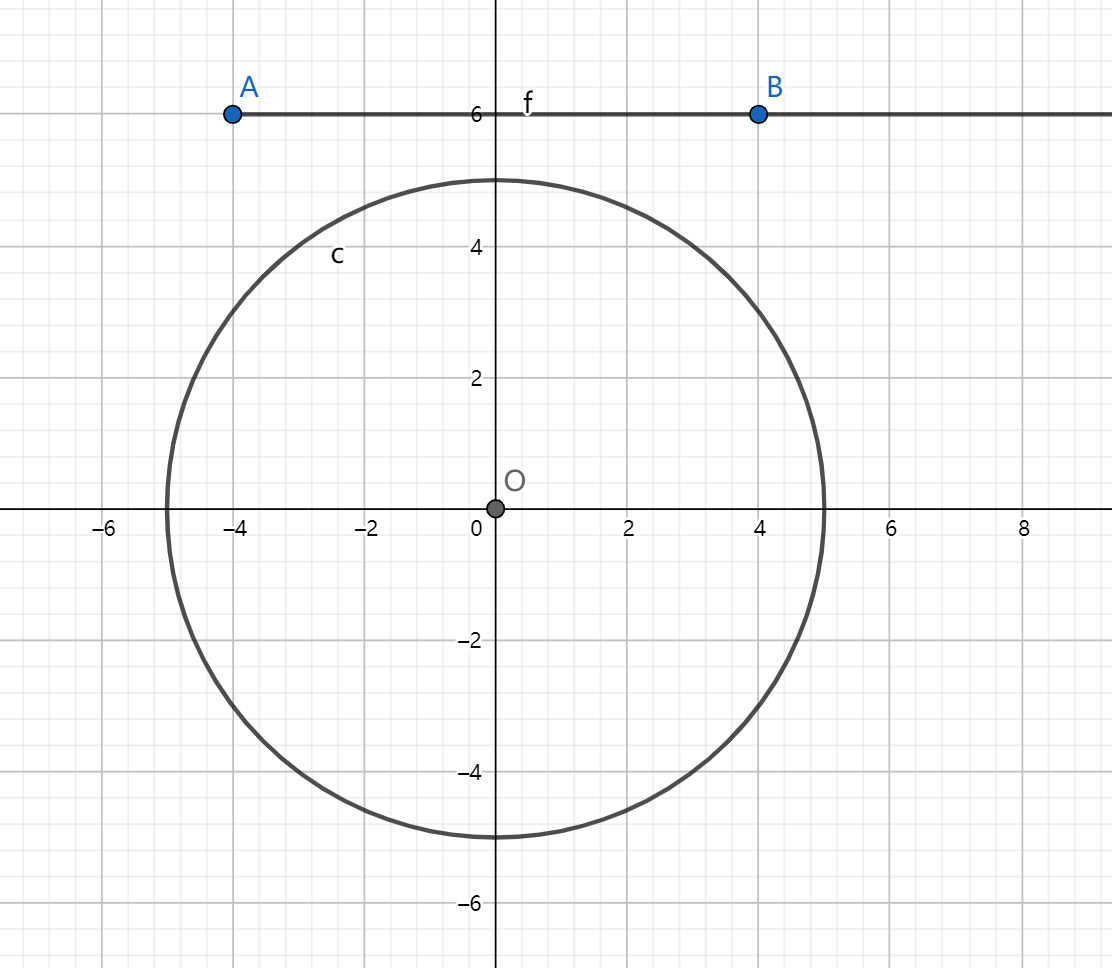
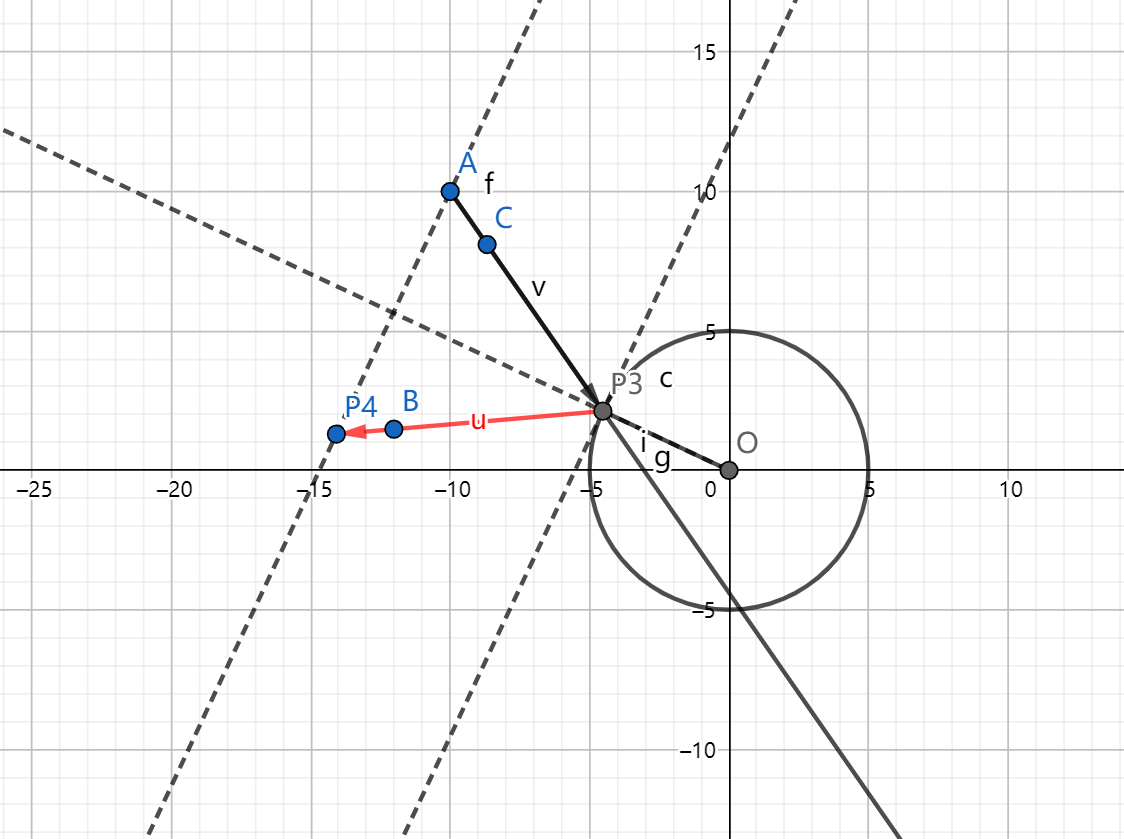
注意是射线,下图的情况是不行的。
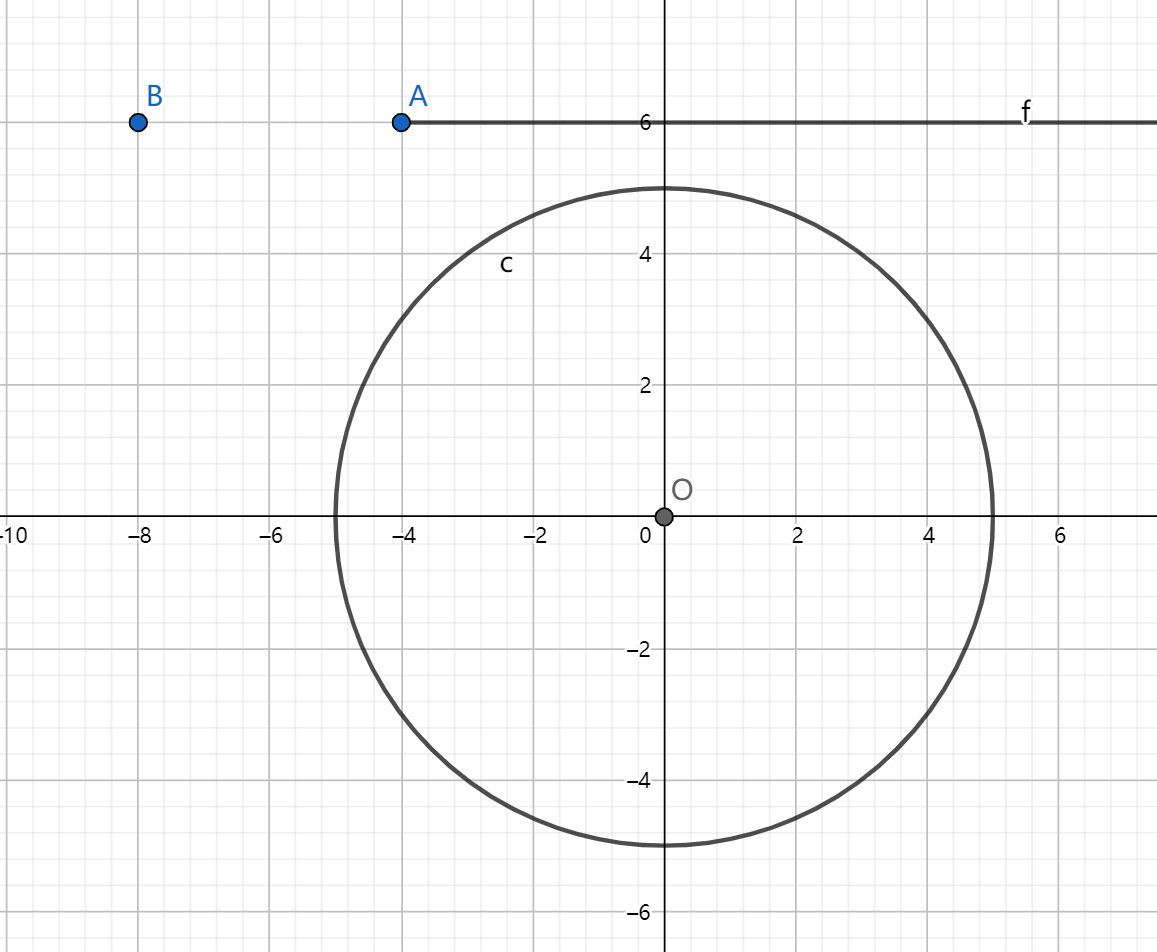
相交时如果点 (b) 在圆的另一边也是不行的。
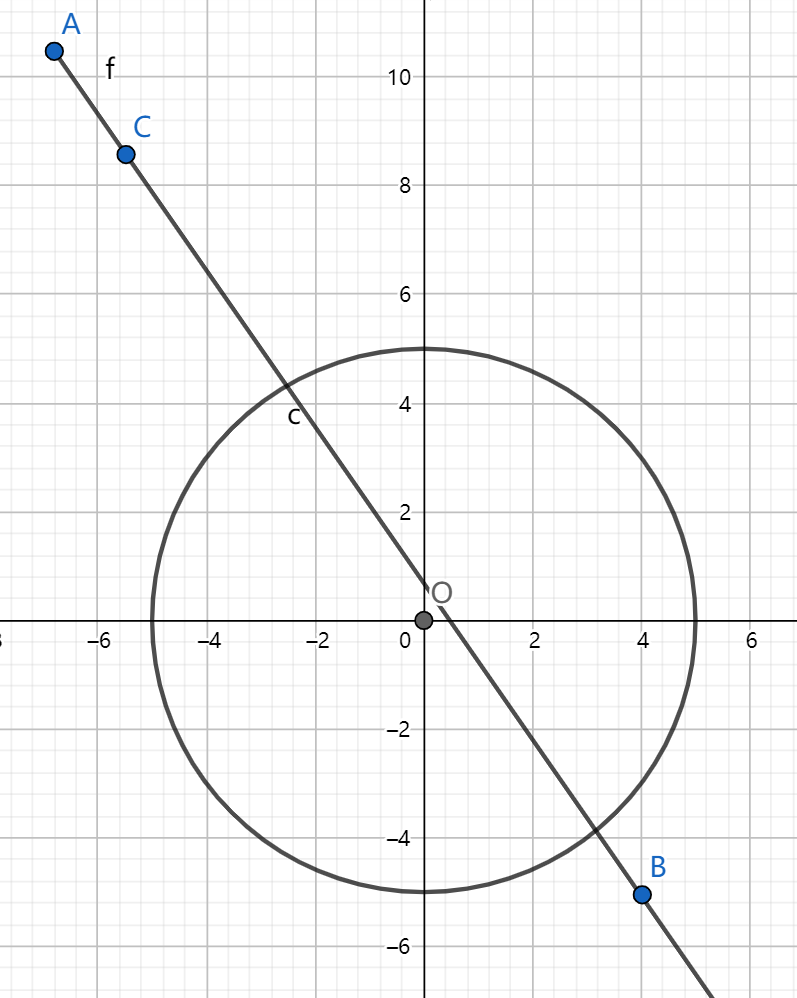
相交时有两种情况,一种是不经过反射就到达点 (b),另一种是经过反射才到达点 (b)。
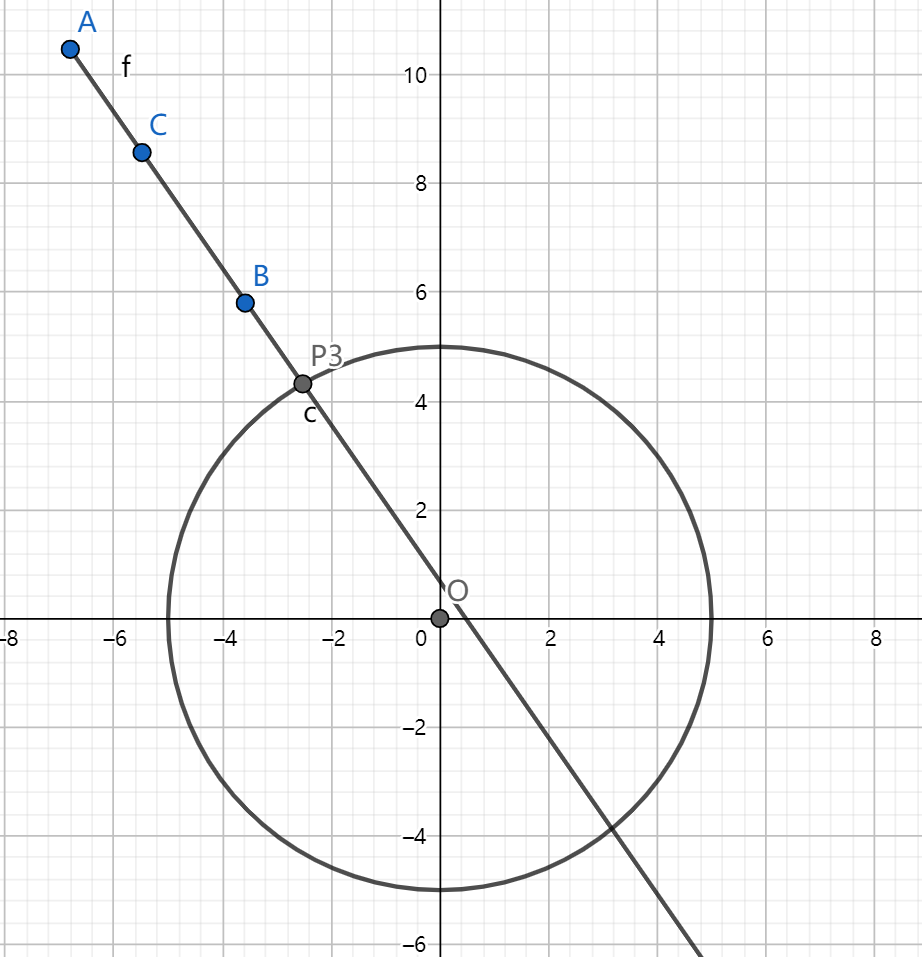
反射后的射线求一下对称点即可。(代码中的 P3 和 P4 点就是下图中的两点)
模板来自kuangbin的计算几何模板。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const db eps = 1e-8;
const db inf = 1e18;
const db pi = acos(-1.0);
inline int dcmp(db x) {
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x > 0? 1: -1;
}
struct Point{
double x,y;
Point(){}
Point(double _x,double _y){
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
void input(){
scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y);
}
bool operator == (Point b)const{
return dcmp(x-b.x) == 0 && dcmp(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (Point b)const{
return dcmp(x-b.x)== 0?dcmp(y-b.y)<0:x<b.x;
}
Point operator -(const Point &b)const{
return Point(x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
double operator ^(const Point &b)const{
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
double operator *(const Point &b)const{
return x*b.x + y*b.y;
}
double len(){
return hypot(x,y);
}
double len2(){
return x*x + y*y;
}
double distance(Point p){
return hypot(x-p.x,y-p.y);
}
db dis2(const Point a) {
return pow(x - a.x, 2) + pow(y - a.y, 2);
}
db dis(const Point a) {
return sqrt(dis2(a));
}
Point operator +(const Point &b)const{
return Point(x+b.x,y+b.y);
}
Point operator *(const double &k)const{
return Point(x*k,y*k);
}
Point operator /(const double &k)const{
return Point(x/k,y/k);
}
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point p = *this;
return fabs(atan2( fabs((a-p)^(b-p)),(a-p)*(b-p) ));
}
Point trunc(double r){
double l = len();
if(!dcmp(l))return *this;
r /= l;
return Point(x*r,y*r);
}
};
struct Line{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line(Point _s,Point _e){
s = _s;
e = _e;
}
void input(){
s.input();
e.input();
}
void adjust(){
if(e < s)swap(s,e);
}
double length(){
return s.distance(e);
}
double angle(){
double k = atan2(e.y-s.y,e.x-s.x);
if(dcmp(k) < 0)k += pi;
if(dcmp(k-pi) == 0)k -= pi;
return k;
}
int relation(Point p){
int c = dcmp((p-s)^(e-s));
if(c < 0)return 1;
else if(c > 0)return 2;
else return 3;
}
double dispointtoline(Point p){
return fabs((p-s)^(e-s))/length();
}
// 点 p 在直线上的投影
Point lineprog(Point p){
return s + ( ((e-s)*((e-s)*(p-s)))/((e-s).len2()) );
}
// 点 p 关于直线的对称点
Point symmetrypoint(Point p){
Point q = lineprog(p);
return Point(2*q.x-p.x,2*q.y-p.y);
}
};
struct Circle{
Point p;
double r;
Circle(){}
Circle(Point _p,double _r){
p = _p;
r = _r;
}
void input(){
p.input();
scanf("%lf",&r);
}
int relationline(Line v){
double dst = v.dispointtoline(p);
if(dcmp(dst-r) < 0)return 2;
else if(dcmp(dst-r) == 0)return 1;
return 0;
}
// 直线和圆的交点
int pointcrossline(Line v,Point &p1,Point &p2){
if(!(*this).relationline(v))return 0;
Point a = v.lineprog(p);
double d = v.dispointtoline(p);
d = sqrt(r*r-d*d);
if(dcmp(d) == 0){
p1 = a;
p2 = a;
return 1;
}
p1 = a + (v.e-v.s).trunc(d);
p2 = a - (v.e-v.s).trunc(d);
return 2;
}
};
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
int kase = 0;
while(T--) {
Circle o;
o.input();
Point a, b, c;
a.input();
Point v;
v.input(); // 方向向量
b.input();
c = a + v;
Line l = Line(a, c); // 射线ac代表a运动的方向
Point p1, p2, p3;
int cnt = o.pointcrossline(l, p1, p2); // 求直线ac与圆的交点
if(cnt == 2) { // 判断交点在线段外还是线段内
if((p1 - a)*(c - a) < 0) {
cnt = 0;
}
}
if(cnt == 0 || cnt == 1) { // 没有交点或者直线ac与圆相切
// 判断射线ac是否经过点b
if(dcmp((b - a)^(c - a)) == 0 && dcmp((b - a)*(c - a)) > 0) {
printf("Case #%d: Yes
", ++kase);
continue;
} else {
printf("Case #%d: No
", ++kase);
continue;
}
} else {
// 找从圆外进入圆内的一个交点 p3
if(p1.dis2(a) < p2.dis2(a)) {
p3 = p1;
} else {
p3 = p2;
}
// 判断点b是否在线段ap3上
if(dcmp((b - a)^(c - a)) == 0 && dcmp((b - a)*(c - a)) > 0) {
if((p3 - a)*(p3 - b) < 0) {
printf("Case #%d: No
", ++kase);
continue;
} else {
printf("Case #%d: Yes
", ++kase);
continue;
}
}
// 反弹的情况
Line tmp = Line(o.p, p3);
Point p4 = tmp.symmetrypoint(a); // 反射后的一个点 点a关于圆心到交点p3所在直线的对称点
// 判断反射后能否到达点b
if(dcmp((b - p3)^(p4 - p3)) == 0 && dcmp((b - p3)*(p4 - p3)) > 0) {
printf("Case #%d: Yes
", ++kase);
continue;
} else {
printf("Case #%d: No
", ++kase);
continue;
}
}
}
return 0;
}