一、概述
本节来看一下ASP.NET MVC【View的呈现】的内容,View的呈现是在Action执行之后进行,Action的执行生成一个ActionResult,【View的呈现】的功能就是:通过InvokeActionResult方法对【Action的执行】中生成的ActionResult进行处理。(ActionResult泛指那些继承自抽象类System.Web.Mvc.ActonResult的类的实例)
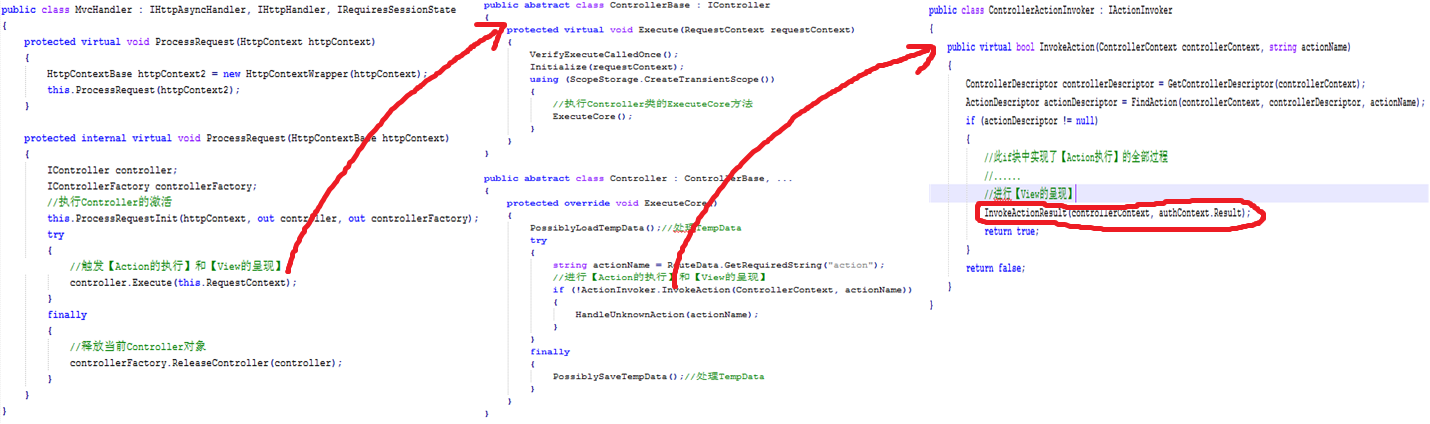
为了会纵观【View的呈现】在全局中的位置,下面我们再来回顾下处理请求的整个流程:在此系列开篇的时候介绍了MVC的生命周期 , 对于ASP.NET和ASP.NET MVC,都是将相应的类的方法注册到HttpApplication事件中,通过事件的依次执行从而完成对请求的处理。而针对MVC,请求是先 经过路由系统,然后由一个MvcHandler来处理的,当请求到来时,执行此MvcHandler的ProcessRequest方法(因为已将 MvcHandler类的ProcessRequest方法注册到HttpApplication的事件中,所以事件的执行就触发了此方法),下图就是一个简要的执行过程!
public class ControllerActionInvoker : IActionInvoker
{
protected virtual void InvokeActionResult(ControllerContext controllerContext, ActionResult actionResult)
{
actionResult.ExecuteResult(controllerContext);
}
}
整个过程大致经过【Controller的激活】-->【Action的执行】-->【View的呈现】,由上图可知,【View的呈现】是由ControllerActionInvoker类中的InvokeActionResult方法来触发的!
二、ActionResult的创建
概述中提到,【View的呈现】的功能就是:通过InvokeActionResult方法对【Action的执行】中生成的ActionResult进行处理。即:ActionResult是在【Action的执行】中创建的,创建方式有:
- 请求没有通过Action的过滤器时,在过滤器的方法中创建一个ActionResult,将其当作最终的ActionResult,进行View的呈现
- 请求通过所有过滤器,将Action方法返回的ActionResult当作最终的ActionResult,进行View的呈现。
注:在Action方法中其实调用Controller类中的方法来进行创建ActionResult实例的,如:return Content("OK");等同于return new ContentResult(){ Content="OK"};
例、自定义个Action过滤器,当没有通过时按照过滤器中定义的ActionResult进行View的呈现,具体执行过程下一部分介绍!

public class MyActionFilter:FilterAttribute,IActionFilter { public void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext filterContext) { } public void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext) { if (filterContext.RouteData.DataTokens["OOK"] != "WuPeiqi") { ContentResult contentResult = new ContentResult(); contentResult.Content = "DataToKens值有误"; filterContext.Result = contentResult; } } } //将此过滤器应用的Action上,那么当请求中DataTokens的值不是不是相应的值时,就会用过滤器中的ContentResult对象来进行View的呈现,否则,就是利用Action方法Index中创建的ActionResult进行View的呈现! public class HomeController : Controller { [MyActionFilter] public ActionResult Index() { return Content("正确"); } }
三、View呈现过程分析
ASP.NET MVC的【View的呈现】其实就是执行ActonResult的ExcuteResult方法!而接下来我们介绍的就是这个ExcuteResult方法触发了那些操作!!!在介绍之前我们先来看看微软提供了那些ActionResult!(ActionResult泛指那些继承自System.Web.Mvc.ActionResult的类)

public abstract class ActionResult { public abstract void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context); }
- EmptyResult
- ContentResult
- FileResult
- JavaScriptResult
- JsonResult
- HttpStatusCodeResult
- RedirectResult
- RedirectToRouteResult
- ViewResult
在ASP.NET MVC 的【Action的执行】中创建以上任意一个ActionResult对象,并执行该对象的ExcuteResult方法,从而进行【View的呈现】。这里的最后一项ViewResult比较特殊,它的处理流程相对复杂,涉及到Razor引擎什么的,之后详细介绍!
下面就来看一些以上ActionResult的源码,了解下【View的呈现】如何实现!
1、EmptyResult
public class EmptyResult : ActionResult
{
private static readonly EmptyResult _singleton = new EmptyResult();
internal static EmptyResult Instance
{
get { return _singleton; }
}
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
}
}
由EmptyResult源码可见,其ExecuteReuslt方法什么都没做,也就是该ActionReuslt的【View的呈现】部分不做任何操作,那么此流程也就执行完毕。再看概述中的图可知,接下来进行【对TempData再一次处理】-->【释放Controller对象】,之后再继续HttpApplication其他的事件,包括对Session的处理、缓存的处理、对请求的返回等。
2、ContentResult
ContentResult用于将字符串响应给客户端!
public class ContentResult : ActionResult
{
public string Content { get; set; }
public Encoding ContentEncoding { get; set; }
public string ContentType { get; set; }
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
HttpResponseBase response = context.HttpContext.Response;
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(ContentType))
{
response.ContentType = ContentType;
}
if (ContentEncoding != null)
{
response.ContentEncoding = ContentEncoding;
}
if (Content != null)
{
response.Write(Content);
}
}
}
上述context.HttpContext.Response得到的是一个HttpResponseWrapper类型的对象response,该对象内有一个HttpResponse类型的私有变量_httpResponse,对于该HttpResponseWrapper对象的属性和方法其实都是执行私有变量_httpResponse对应的属性和方法!
由于HttpResponseWrapper对象属性和方法都是对私有变量_httpResponse的相关操作,而查看HttpResponseWrapper类部分源代码,_httpResponse变量是通过构造函数赋值的,而该构造函数的参数值是怎么来的呢?是在HttpApplication事件之前,通过HttpRuntime类创建请求上下文HttpContext对象时,又触发创建了HttpResponse对象并赋值到请求上下文HttpContext对象的一个私有变量中保存着的!
又由于HttpResponse对象的属性和方法又都是对私有变量_writer的相关操作,再看HttpResponse类的源代码,它的Write的方法其实是执行其TextWriter类型的私有变量_writer的Write方法,而该私有变量_writer是怎么来的呢?是在HttpApplication事件之前,通过HttpRuntime类创建请求上下文HttpContext对象时,触发创建了HttpResponse对象,之后又初始化HttpResponse对象的_writer字段为一个HttpWriter对象。
最终,执行HttpWriter对象的Write方法,根据ContentType定义的媒体类型和ContentEncoding定义的编码方法将字符串发送到 HTTP 输出流。ContentType定义的是MIME类型(默认为”text/html"),ContentEncoding定义的编码方式(默认是操作系统的当前 ANSI 代码页的编码System.Text.Encoding.Default)。

public class HttpResponseWrapper : HttpResponseBase { private HttpResponse _httpResponse; //设置或获取响应内容的编码类型 public override Encoding ContentEncoding { get { return this._httpResponse.ContentEncoding; } set { this._httpResponse.ContentEncoding = value; } } public override string ContentType { get { return this._httpResponse.ContentType; } set { this._httpResponse.ContentType = value; } } public override void Write(string s) { this._httpResponse.Write(s); } }

public sealed class HttpResponse { private TextWriter _writer; private Encoding _encoding; private string _contentType = "text/html"; public Encoding ContentEncoding { get { if (this._encoding == null) { //获取webconfig文件中,globalization节点的值 GlobalizationSection globalization = RuntimeConfig.GetLKGConfig(this._context).Globalization; if (globalization != null) { //设置Http响应的内容编码 this._encoding = globalization.ResponseEncoding; } //没有在globalization节点中配置编码类型 if (this._encoding == null) { //获取操作系统的当前 ANSI 代码页的编码并赋值给Http响应内容的编码 this._encoding = Encoding.Default; } } return this._encoding; } set { if (value == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("value"); } //当没有设置编码类型或者编码类型和原来的不相同时,根据value重新设定编码类型 if (this._encoding == null || !this._encoding.Equals(value)) { this._encoding = value; this._encoder = null; if (this._httpWriter != null) { //将HttpResponse类中与编码相关的属性值赋值到HttpWriter对象中与编码相关的属性 //以便HttpWriter输出响应流时按照此编码进行 this._httpWriter.UpdateResponseEncoding(); } } } } public string ContentType { get { return this._contentType; } set { if (!this._headersWritten) { this._contentTypeSetByManagedCaller = true; this._contentType = value; return; } if (this._contentType == value) { return; } throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Cannot_set_content_type_after_headers_sent")); } } public void Write(string s) { this._writer.Write(s); } }

public sealed class HttpWriter : TextWriter { //根据编码规则将字符串发送到 HTTP 输出流 public override void Write(string s) { if (this._ignoringFurtherWrites) { return; } if (s == null) { return; } if (s.Length != 0) { if (s.Length < this._charBufferFree) { StringUtil.UnsafeStringCopy(s, 0, this._charBuffer, this._charBufferLength - this._charBufferFree, s.Length); this._charBufferFree -= s.Length; } else { int i = s.Length; int num = 0; while (i > 0) { if (this._charBufferFree == 0) { this.FlushCharBuffer(false); } int num2 = (i < this._charBufferFree) ? i : this._charBufferFree; StringUtil.UnsafeStringCopy(s, num, this._charBuffer, this._charBufferLength - this._charBufferFree, num2); this._charBufferFree -= num2; num += num2; i -= num2; } } } if (!this._responseBufferingOn) { //将信息写入 HTTP 响应输出流。 this._response.Flush(); } } //更新编码相关的字段 internal void UpdateResponseEncoding() { if (this._responseEncodingUpdated && this._charBufferLength != this._charBufferFree) { this.FlushCharBuffer(true); } this._responseEncoding = this._response.ContentEncoding; this._responseEncoder = this._response.ContentEncoder; this._responseCodePage = this._responseEncoding.CodePage; this._responseCodePageIsAsciiCompat = CodePageUtils.IsAsciiCompatibleCodePage(this._responseCodePage); this._responseEncodingUpdated = true; } }
在ASP.NET MVC 的Controller类中提供了以下三个创建ContentResult的重载,当然也可以直接在Action中创建ContentReuslt对象并作为方法的返回值。

public abstract class Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncController, IAsyncManagerContainer { //省略其他方法 protected internal ContentResult Content(string content) { return Content(content, null /* contentType */); } protected internal ContentResult Content(string content, string contentType) { return Content(content, contentType, null /* contentEncoding */); } protected internal virtual ContentResult Content(string content, string contentType, Encoding contentEncoding) { return new ContentResult { Content = content, ContentType = contentType, ContentEncoding = contentEncoding }; } }
扩展:请求上下文HttpContext、HttpResponse、HttpRequest创建流程
当请求到达IIS,IIS根据请求的后缀名判断是否加载aspnet_isapi.dll,一旦工作进程加载了aspnet_isapi.dll,就会加载IsapiRuntime,被加载的IsapiRuntime会接管Http请求,之后IsapiRuntime执行其方法ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType),该方法实现从ISAPI扩展控制块(ECB)中获取当前Http请求相关信息并封装到IsapiWorkrRequest对象中。然后将该对象传递给HttpRuntime,通过该类中的ProcessRequestInternal()方法创建HttpContext类实例,进入ProcessRequestInternal方法之后,内部触发一系列的方法,最终创建一个HttpContent实例(可通过HttpContent.Current获取到这个实例),且该实例会在整个生命周期内存活。创建HttpContext对象时,同时也创建了HttpRequest和HttpResponse对象,并赋值到私有字段中,通过公有属性去获取这两个对象。
之后HttpRuntime类会向HttpApplicationFactory类 提出请求,要求返回一个HttpApplication对象,HttpApplicationFactory在收到请求之后会检查是否有已经存在并且空闲的对象,如果有就取出一个HttpApplication对象返回给HttpRuntime类,如果没有,则要创建一个给HttpRuntime。

public sealed class ISAPIRuntime : MarshalByRefObject, IISAPIRuntime, IISAPIRuntime2, IRegisteredObject { public ISAPIRuntime() { //将该ISAPIRuntime对象放在应用程序的已注册对象列表中 HostingEnvironment.RegisterObject(this); } public int ProcessRequest(IntPtr ecb, int iWRType) { IntPtr intPtr = IntPtr.Zero; if (iWRType == 2) { intPtr = ecb; ecb = UnsafeNativeMethods.GetEcb(intPtr); } ISAPIWorkerRequest iSAPIWorkerRequest = null; int result; try { bool useOOP = iWRType == 1; //将ISAPI扩展控制块(ECB)中Http请求相关的信息封装到IsapiWorkerRequest对象中 iSAPIWorkerRequest = ISAPIWorkerRequest.CreateWorkerRequest(ecb, useOOP); iSAPIWorkerRequest.Initialize(); string appPathTranslated = iSAPIWorkerRequest.GetAppPathTranslated(); string appDomainAppPathInternal = HttpRuntime.AppDomainAppPathInternal; if (appDomainAppPathInternal == null || StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(appPathTranslated, appDomainAppPathInternal)) { //ASP.NET运行时开始执行 HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNoDemand(iSAPIWorkerRequest); result = 0; } else { HttpRuntime.ShutdownAppDomain(ApplicationShutdownReason.PhysicalApplicationPathChanged, SR.GetString("Hosting_Phys_Path_Changed", new object[] { appDomainAppPathInternal, appPathTranslated })); result = 1; } } //省略部分代码 return result; } }

public sealed class HttpRuntime { //静态字段 private static HttpRuntime _theRuntime; public HttpRuntime() { } //静态构造函数 static HttpRuntime() { HttpRuntime.s_autogenKeys = new byte[1024]; HttpRuntime.DirectorySeparatorString = new string(Path.DirectorySeparatorChar, 1); HttpRuntime.DoubleDirectorySeparatorString = new string(Path.DirectorySeparatorChar, 2); HttpRuntime.s_InvalidPhysicalPathChars = new char[] { '/', '?', '*', '<', '>', '|', '"' }; HttpRuntime.s_initialized = false; HttpRuntime.s_isEngineLoaded = false; HttpRuntime.s_factoryLock = new object(); HttpRuntime.AddAppDomainTraceMessage("*HttpRuntime::cctor"); HttpRuntime.StaticInit(); HttpRuntime._theRuntime = new HttpRuntime(); HttpRuntime._theRuntime.Init(); HttpRuntime.AddAppDomainTraceMessage("HttpRuntime::cctor*"); } internal static void ProcessRequestNoDemand(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { RequestQueue requestQueue = HttpRuntime._theRuntime._requestQueue; wr.UpdateInitialCounters(); if (requestQueue != null) { wr = requestQueue.GetRequestToExecute(wr); } if (wr != null) { HttpRuntime.CalculateWaitTimeAndUpdatePerfCounter(wr); wr.ResetStartTime(); //继续执行 HttpRuntime.ProcessRequestNow(wr); } } internal static void ProcessRequestNow(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { //继续执行 HttpRuntime._theRuntime.ProcessRequestInternal(wr); } private void ProcessRequestInternal(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { Interlocked.Increment(ref this._activeRequestCount); if (this._disposingHttpRuntime) { try { wr.SendStatus(503, "Server Too Busy"); wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Server Too Busy</body></html>"); wr.SendResponseFromMemory(bytes, bytes.Length); wr.FlushResponse(true); wr.EndOfRequest(); } finally { Interlocked.Decrement(ref this._activeRequestCount); } return; } HttpContext httpContext; try { //创建请求上下文,继续执行 httpContext = new HttpContext(wr, false); } catch { try { wr.SendStatus(400, "Bad Request"); wr.SendKnownResponseHeader(12, "text/html; charset=utf-8"); byte[] bytes2 = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("<html><body>Bad Request</body></html>"); wr.SendResponseFromMemory(bytes2, bytes2.Length); wr.FlushResponse(true); wr.EndOfRequest(); return; } finally { Interlocked.Decrement(ref this._activeRequestCount); } } wr.SetEndOfSendNotification(this._asyncEndOfSendCallback, httpContext); HostingEnvironment.IncrementBusyCount(); try { try { this.EnsureFirstRequestInit(httpContext); } catch { if (!httpContext.Request.IsDebuggingRequest) { throw; } } //初始化HttpResponse的TextWriter httpContext.Response.InitResponseWriter(); //通过 HttpApplicationFactory获取HttpApplication实例 IHttpHandler applicationInstance = HttpApplicationFactory.GetApplicationInstance(httpContext); if (applicationInstance == null) { throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Unable_create_app_object")); } if (EtwTrace.IsTraceEnabled(5, 1)) { EtwTrace.Trace(EtwTraceType.ETW_TYPE_START_HANDLER, httpContext.WorkerRequest, applicationInstance.GetType().FullName, "Start"); } if (applicationInstance is IHttpAsyncHandler) { IHttpAsyncHandler httpAsyncHandler = (IHttpAsyncHandler)applicationInstance; httpContext.AsyncAppHandler = httpAsyncHandler; httpAsyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(httpContext, this._handlerCompletionCallback, httpContext); } else { applicationInstance.ProcessRequest(httpContext); this.FinishRequest(httpContext.WorkerRequest, httpContext, null); } } catch (Exception e) { httpContext.Response.InitResponseWriter(); this.FinishRequest(wr, httpContext, e); } } }

public sealed class HttpContext : IServiceProvider, IPrincipalContainer { //构造函数 public HttpContext(HttpWorkerRequest wr) { this._wr = wr; //初始化HttpContext并创建HttpRequest和HttpResponse this.Init(new HttpRequest(wr, this), new HttpResponse(wr, this)); //初始化HttpResponse的TextWriter this._response.InitResponseWriter(); } private void Init(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) { this._request = request; this._response = response; //省略其他代码 } }
3、FileResult
FileResult用于将某个物理文件的内容响应给客户端!
public abstract class FileResult : ActionResult
{
private string _fileDownloadName;
protected FileResult(string contentType)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(contentType))
{
throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "contentType");
}
ContentType = contentType;
}
public string ContentType { get; private set; }
public string FileDownloadName
{
get { return _fileDownloadName ?? String.Empty; }
set { _fileDownloadName = value; }
}
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
HttpResponseBase response = context.HttpContext.Response;
//response.ContentType默认为“text/html”
response.ContentType = ContentType;
//如果没有指定文件被下载的名称,则按照内联的方法输出文件,否则按照附件的形式。
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(FileDownloadName))
{
//处理文件名 并 构造“Content-Disposition”的报头的值
//例如:文件名中包含Unicode码或包含特殊符号等
string headerValue = ContentDispositionUtil.GetHeaderValue(FileDownloadName);
//采用附件形式,需要为响应创建一个名称为“Content-Disposition”的报头,该报头的值格式为“attachment;filename={文件名}”
context.HttpContext.Response.AddHeader("Content-Disposition", headerValue);
}
WriteFile(response);
}
protected abstract void WriteFile(HttpResponseBase response);
//处理文件名并构造 “Content-Disposition”的报头的值
internal static class ContentDispositionUtil
{
private const string HexDigits = "0123456789ABCDEF";
private static void AddByteToStringBuilder(byte b, StringBuilder builder)
{
builder.Append('%');
int i = b;
AddHexDigitToStringBuilder(i >> 4, builder);
AddHexDigitToStringBuilder(i % 16, builder);
}
private static void AddHexDigitToStringBuilder(int digit, StringBuilder builder)
{
builder.Append(HexDigits[digit]);
}
private static string CreateRfc2231HeaderValue(string filename)
{
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("attachment; filename*=UTF-8''");
byte[] filenameBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(filename);
foreach (byte b in filenameBytes)
{
if (IsByteValidHeaderValueCharacter(b))
{
builder.Append((char)b);
}
else
{
AddByteToStringBuilder(b, builder);
}
}
return builder.ToString();
}
public static string GetHeaderValue(string fileName)
{
// If fileName contains any Unicode characters, encode according
// to RFC 2231 (with clarifications from RFC 5987)
foreach (char c in fileName)
{
if ((int)c > 127)
{
return CreateRfc2231HeaderValue(fileName);
}
}
// Knowing there are no Unicode characters in this fileName, rely on
// ContentDisposition.ToString() to encode properly.
// In .Net 4.0, ContentDisposition.ToString() throws FormatException if
// the file name contains Unicode characters.
// In .Net 4.5, ContentDisposition.ToString() no longer throws FormatException
// if it contains Unicode, and it will not encode Unicode as we require here.
// The Unicode test above is identical to the 4.0 FormatException test,
// allowing this helper to give the same results in 4.0 and 4.5.
ContentDisposition disposition = new ContentDisposition() { FileName = fileName };
return disposition.ToString();
}
// Application of RFC 2231 Encoding to Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Header Fields, sec. 3.2
// http://greenbytes.de/tech/webdav/draft-reschke-rfc2231-in-http-latest.html
private static bool IsByteValidHeaderValueCharacter(byte b)
{
if ((byte)'0' <= b && b <= (byte)'9')
{
return true; // is digit
}
if ((byte)'a' <= b && b <= (byte)'z')
{
return true; // lowercase letter
}
if ((byte)'A' <= b && b <= (byte)'Z')
{
return true; // uppercase letter
}
switch (b)
{
case (byte)'-':
case (byte)'.':
case (byte)'_':
case (byte)'~':
case (byte)':':
case (byte)'!':
case (byte)'$':
case (byte)'&':
case (byte)'+':
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
对于FileResult,具有一个表示媒体类型的只读属性ContentType,该属性在构造函数中被初始化。当我们基于某个物理文件创建相应的FileReuslt对象的时候应该根据文件的类型指定该媒体类型属性,例如:目标文件是.jpg图片,那么对应的媒体类型应该是“image/jpeg”;对于一个.pdf文件,则采用“application/pdf”。
对于FileResult,还具有一个表示下载文件名的属性FileDownloadName,如果该属性没有指定或者设置的值为null,则会按照内联的方式利用浏览器直接打开响应的文件,否则会以附件的形式被下载并且文件名为属性FileDownloadName的值。(查看FileResult源码可知,内联和附件的区别是响应是否包含“Content-Disposition”报头)
FileReult仅仅是一个抽象类,对于文件内容的输出实现在抽象方法WriteFile方法中。FileResult有三个派生类实现了WriterFile方法分别是:

public class FileContentResult : FileResult { //参数为字节数组、响应的媒体类型 public FileContentResult(byte[] fileContents, string contentType) : base(contentType) { if (fileContents == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("fileContents"); } FileContents = fileContents; } public byte[] FileContents { get; private set; } protected override void WriteFile(HttpResponseBase response) { //将字节数组输出 response.OutputStream.Write(FileContents, 0, FileContents.Length); } }

public class FileStreamResult : FileResult { // default buffer size as defined in BufferedStream type private const int BufferSize = 0x1000; //参数为:文件流、媒体类型 public FileStreamResult(Stream fileStream, string contentType) : base(contentType) { if (fileStream == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("fileStream"); } FileStream = fileStream; } public Stream FileStream { get; private set; } protected override void WriteFile(HttpResponseBase response) { // grab chunks of data and write to the output stream Stream outputStream = response.OutputStream; using (FileStream) { byte[] buffer = new byte[BufferSize]; while (true) { int bytesRead = FileStream.Read(buffer, 0, BufferSize); if (bytesRead == 0) { // no more data break; } outputStream.Write(buffer, 0, bytesRead); } } } }

public class FilePathResult : FileResult { //参数为:文件路径、媒体类型 public FilePathResult(string fileName, string contentType) : base(contentType) { if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(fileName)) { throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "fileName"); } FileName = fileName; } public string FileName { get; private set; } protected override void WriteFile(HttpResponseBase response) { response.TransmitFile(FileName); } }
以上的三个继承自FileResult的类,最终都是通过 文件的字节数组 的形式发送到Http输出流,不同的是作为开发者其起始点不一,FileContentResult传入字节数组然后将内容写入当前Http响应的输出流,FileStreamReuslt传入数据流,之后内部存入字节数组再将内容写入当前Http响应的输出流,FilePathResult传入文件地址,之后内部读取文件并存入字节数组再将内容写入当前Http响应的输出流。
在ASP.NET MVC 的Controller类中提供了创建以上三个FileResult派生类的对象的重载,当然也可以直接在Action中创建相应的FileReuslt对象并作为方法的返回值。

public abstract class Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncController, IAsyncManagerContainer { protected internal FileContentResult File(byte[] fileContents, string contentType) { return File(fileContents, contentType, null /* fileDownloadName */); } protected internal virtual FileContentResult File(byte[] fileContents, string contentType, string fileDownloadName) { return new FileContentResult(fileContents, contentType) { FileDownloadName = fileDownloadName }; } protected internal FileStreamResult File(Stream fileStream, string contentType) { return File(fileStream, contentType, null /* fileDownloadName */); } protected internal virtual FileStreamResult File(Stream fileStream, string contentType, string fileDownloadName) { return new FileStreamResult(fileStream, contentType) { FileDownloadName = fileDownloadName }; } protected internal FilePathResult File(string fileName, string contentType) { return File(fileName, contentType, null /* fileDownloadName */); } protected internal virtual FilePathResult File(string fileName, string contentType, string fileDownloadName) { return new FilePathResult(fileName, contentType) { FileDownloadName = fileDownloadName }; } }
4、JavaScriptResult
在后台动态的以字符串形式传入一段JavaScript脚本,并作为请求的响应使得脚本在客户端被执行!
public class JavaScriptResult : ActionResult
{
public string Script { get; set; }
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
HttpResponseBase response = context.HttpContext.Response;
//指定响应的媒体类型
response.ContentType = "application/x-javascript";
if (Script != null)
{
response.Write(Script);
}
}
}
通过JavaScriptResult源码可以看出,其输出方式和ContentResult相同,不同的只是在JavaScriptResult中内部指定了输出的媒体类型为“application/x-javascript”(也可以是“text/javascript”),而我们也可以通过设置ContentResult的输出媒体类型来实现与JavaScriptResult相同的功能!
在ASP.NET MVC 的Controller类中提供了创建JavaScriptResult对象的方法,当然也可以直接在Action中创建JavaScriptResult对象并作为方法的返回值。

public abstract class Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncController, IAsyncManagerContainer { //省略其他代码 protected internal virtual JavaScriptResult JavaScript(string script) { return new JavaScriptResult { Script = script }; } }
5、JsonResult
JsonResutl用于以Json的格式返回响应的数据!
public class JsonResult : ActionResult
{
public JsonResult()
{
//定义枚举类型,默认拒绝Get请求的响应
JsonRequestBehavior = JsonRequestBehavior.DenyGet;
}
public Encoding ContentEncoding { get; set; }
public string ContentType { get; set; }
public object Data { get; set; }
//是否决绝Http Get请求(默认拒绝---构造函数中定义)
public JsonRequestBehavior JsonRequestBehavior { get; set; }
/// <summary>
///指定 JSON 字符串的最大长度(UTF-8 字符的最大数量)。 默认长度为 102400。
/// </summary>
public int? MaxJsonLength { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 指定要序列化类型的最大深度。 默认的递归限制为 100。
/// </summary>
public int? RecursionLimit { get; set; }
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
//如果拒绝Get请求&&发送来的请求也是Get方式
if (JsonRequestBehavior == JsonRequestBehavior.DenyGet &&
String.Equals(context.HttpContext.Request.HttpMethod, "GET", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(MvcResources.JsonRequest_GetNotAllowed);
}
HttpResponseBase response = context.HttpContext.Response;
//默认媒体类型为"application/json"
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(ContentType))
{
response.ContentType = ContentType;
}
else
{
response.ContentType = "application/json";
}
//编码类型的选取还是和ContentResult中一样,优先级:显示设定>WebConfig中节点>Encoding.Default
if (ContentEncoding != null)
{
response.ContentEncoding = ContentEncoding;
}
if (Data != null)
{
//通过JavaScriptSerializer来将CLR对象序列化成Json格式字符串
JavaScriptSerializer serializer = new JavaScriptSerializer();
if (MaxJsonLength.HasValue)
{
//serializer.MaxJsonLength是JSON 字符串的最大长度(UTF-8 字符的最大数量)。 默认长度为 102400
serializer.MaxJsonLength = MaxJsonLength.Value;
}
if (RecursionLimit.HasValue)
{
//serializer.RecursionLimit是指要序列化类型的最大深度。 默认的递归限制为 100
serializer.RecursionLimit = RecursionLimit.Value;
}
//将Json格式的字符串写入当前Http响应的输出流
response.Write(serializer.Serialize(Data));
}
}
}
public enum JsonRequestBehavior
{
AllowGet,
DenyGet,
}
对于JsonResult,其构造函数中为属性JsonRequestBehavior设置了一个枚举值DenyGet,该枚举值的作用就是拒绝对GET请求进行响应,也就是默认情况下,对于Json格式的数据响应,Get请求是不予支持的。如果想要支持Get请求,可以显示的设置JsonRequestBehavior属性的枚举值为AllowGet。
对于JsonResult,其默认的媒体类型为“application/json”。
JsonResult就是将CLR对象到Json格式字符串的序列化过程,而上述源码中的object类型的Data属性就是用来获取或设置原始的CLR对象,原始的CLR对象通过JavaScriptSerializer类的Serialize方法的序列化,将CLR对象转换成Json格式的字符串。在JavaScriptSerializer类在对CLR对象进行序列化时还可以对过程进行一些设置,即:MaxJsonLength(Json字符串的最大长度)、RecursionLimit(序列化类时递归的最大深度)。可以在JsonResult对应的属性中设置,也可以在WebConfig中设置。更多设置
<configuration>
<system.web.extensions>
<scripting>
<webServices>
<jsonSerialization maxJsonLength="5000"/>
</webServices>
</scripting>
</system.web.extensions>
</configuration>
在ASP.NET MVC 的Controller类中提供了一下创建JsonResult对象的方法,当然也可以直接在Action中创建JsonResult对象并作为方法的返回值。

public abstract class Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncController, IAsyncManagerContainer { //省略其他代码 protected internal JsonResult Json(object data) { return Json(data, null /* contentType */, null /* contentEncoding */, JsonRequestBehavior.DenyGet); } protected internal JsonResult Json(object data, string contentType) { return Json(data, contentType, null /* contentEncoding */, JsonRequestBehavior.DenyGet); } protected internal virtual JsonResult Json(object data, string contentType, Encoding contentEncoding) { return Json(data, contentType, contentEncoding, JsonRequestBehavior.DenyGet); } protected internal JsonResult Json(object data, JsonRequestBehavior behavior) { return Json(data, null /* contentType */, null /* contentEncoding */, behavior); } protected internal JsonResult Json(object data, string contentType, JsonRequestBehavior behavior) { return Json(data, contentType, null /* contentEncoding */, behavior); } protected internal virtual JsonResult Json(object data, string contentType, Encoding contentEncoding, JsonRequestBehavior behavior) { return new JsonResult { Data = data, ContentType = contentType, ContentEncoding = contentEncoding, JsonRequestBehavior = behavior }; } }
6、HttpStatusCodeResult
HttpStatusCodeResult用于返回对Http请求响应状态的代码和一个可选的状态描述!
public class HttpStatusCodeResult : ActionResult
{
public HttpStatusCodeResult(int statusCode)
: this(statusCode, null)
{
}
//HttStatusCode是个枚举类型,用于定义状态代码
public HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode statusCode)
: this(statusCode, null)
{
}
public HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode statusCode, string statusDescription)
: this((int)statusCode, statusDescription)
{
}
public HttpStatusCodeResult(int statusCode, string statusDescription)
{
StatusCode = statusCode;
StatusDescription = statusDescription;
}
//响应状态代码
public int StatusCode { get; private set; }
//响应状态描述
public string StatusDescription { get; private set; }
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
//默认状态代码为:200
context.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode = StatusCode;
if (StatusDescription != null)
{
context.HttpContext.Response.StatusDescription = StatusDescription;
}
}
}
HttpStatusCodeResult为Http的响应头设置状态代码和状态描述,设置时,可以通过构造函数传入值也可以通过给属性赋值来操作。对于HttpStatustCodeResult的构造函数中HttpStatusCode类型的参数,它是一个枚举类型,其中包含了众多Http响应头状态。
值得一说的是,如果我们采用Visual StudioDvelopment Server作为Web应用的宿主,通过HttpStatusCodeResult的StatusDescription属性设置的状态描述信息不会反映在Http响应中,只有采用IIS作为宿主才会真正将此信息写入响应消息。

public enum HttpStatusCode { Continue = 100, SwitchingProtocols, OK = 200, Created, Accepted, NonAuthoritativeInformation, NoContent, ResetContent, PartialContent, MultipleChoices = 300, Ambiguous = 300, MovedPermanently, Moved = 301, Found, Redirect = 302, SeeOther, RedirectMethod = 303, NotModified, UseProxy, Unused, TemporaryRedirect, RedirectKeepVerb = 307, BadRequest = 400, Unauthorized, PaymentRequired, Forbidden, NotFound, MethodNotAllowed, NotAcceptable, ProxyAuthenticationRequired, RequestTimeout, Conflict, Gone, LengthRequired, PreconditionFailed, RequestEntityTooLarge, RequestUriTooLong, UnsupportedMediaType, RequestedRangeNotSatisfiable, ExpectationFailed, UpgradeRequired = 426, InternalServerError = 500, NotImplemented, BadGateway, ServiceUnavailable, GatewayTimeout, HttpVersionNotSupported }
ASP.NET MVC中有两个继承自HttpStatusCodeResult的类,即:HttpNotFoundResult和AuthorizeAttribute,用于指定特定相应状态和状态描述,本质上还是执行HttpStatusCodeResult来完成,只不过在内部为HttpStatuCodeResult指定了响应状态,分别是404、401。

public class HttpNotFoundResult : HttpStatusCodeResult { public HttpNotFoundResult() : this(null) { } // NotFound is equivalent to HTTP status 404. public HttpNotFoundResult(string statusDescription) : base(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, statusDescription) { } }

public class HttpUnauthorizedResult : HttpStatusCodeResult { public HttpUnauthorizedResult() : this(null) { } // Unauthorized is equivalent to HTTP status 401, the status code for unauthorized // access. Other code might intercept this and perform some special logic. For // example, the FormsAuthenticationModule looks for 401 responses and instead // redirects the user to the login page. public HttpUnauthorizedResult(string statusDescription) : base(HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized, statusDescription) { } }
7、RedirecteResult
RedirectResult用于实现针对某个地址的重定向!
public class RedirectResult : ActionResult
{
public RedirectResult(string url)
: this(url, permanent: false)
{
}
public RedirectResult(string url, bool permanent)
{
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(url))
{
throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "url");
}
Permanent = permanent;
Url = url;
}
//是否永久重定向,默认为否。(永久重定向的Http状态码为301,否则是暂时重定向Http状态码为302)
public bool Permanent { get; private set; }
//要跳转的地址(相对地址或绝对地址)
public string Url { get; private set; }
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
if (context.IsChildAction)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(MvcResources.RedirectAction_CannotRedirectInChildAction);
}
//处理Url地址,相对地址的处理。
string destinationUrl = UrlHelper.GenerateContentUrl(Url, context.HttpContext);
context.Controller.TempData.Keep();
//是否永久重定向
if (Permanent)
{
context.HttpContext.Response.RedirectPermanent(destinationUrl, endResponse: false);
}
else
{
context.HttpContext.Response.Redirect(destinationUrl, endResponse: false);
}
}
}
对于RedirectResult,可以定义暂时重定向(302重定向)和永久重定向(301重定向),两种重定向的不同作用主要体现在SEO上,搜索引擎会使用永久重定向目标地址更新自己的索引,而暂时重定向则不会。另外,永久重定向是在ASP.NET 4之后引进的,在之前如果想要实现永久重定向的话,需要自己来设置Http响应状态码为301。
对于UrlHelper.GenerateCotentUrl方法,用来处理Url。当定义的Url为相对地址时,如:~/xxx/xxx,该方法会利用请求上下文来补全地址。
public static string GenerateContentUrl(string contentPath, HttpContextBase httpContext)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(contentPath))
{
throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "contentPath");
}
if (httpContext == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("httpContext");
}
if (contentPath[0] == '~')
{
return PathHelpers.GenerateClientUrl(httpContext, contentPath);
}
return contentPath;
}
对于ASP.NET MVC的Controller类中定义了一下几个方法来创建RedirectResult,然也可以直接在Action中创建RedirectResult对象并作为方法的返回值。

public abstract class Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncController, IAsyncManagerContainer { //省略其他代码 protected internal virtual RedirectResult Redirect(string url) { if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(url)) { throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "url"); } return new RedirectResult(url); } protected internal virtual RedirectResult RedirectPermanent(string url) { if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(url)) { throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "url"); } return new RedirectResult(url, permanent: true); } }
8、RedirectToRoutResult
RedirectToRouteResult用于将路由信息中的Controller和Action拼接成Url,再进行跳转!
public class RedirectToRouteResult : ActionResult
{
private RouteCollection _routes;
public RedirectToRouteResult(RouteValueDictionary routeValues)
:
this(null, routeValues)
{
}
public RedirectToRouteResult(string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues)
: this(routeName, routeValues, permanent: false)
{
}
public RedirectToRouteResult(string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, bool permanent)
{
Permanent = permanent;
RouteName = routeName ?? String.Empty;
RouteValues = routeValues ?? new RouteValueDictionary();
}
public bool Permanent { get; private set; }
public string RouteName { get; private set; }
public RouteValueDictionary RouteValues { get; private set; }
internal RouteCollection Routes
{
get
{
if (_routes == null)
{
_routes = RouteTable.Routes;
}
return _routes;
}
set { _routes = value; }
}
public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context)
{
if (context == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("context");
}
if (context.IsChildAction)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(MvcResources.RedirectAction_CannotRedirectInChildAction);
}
string destinationUrl = UrlHelper.GenerateUrl(RouteName, null /* actionName */, null /* controllerName */, RouteValues, Routes, context.RequestContext, false /* includeImplicitMvcValues */);
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(destinationUrl))
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(MvcResources.Common_NoRouteMatched);
}
context.Controller.TempData.Keep();
if (Permanent)
{
context.HttpContext.Response.RedirectPermanent(destinationUrl, endResponse: false);
}
else
{
context.HttpContext.Response.Redirect(destinationUrl, endResponse: false);
}
}
}
RedirectToRouteResult和RedirectResult都是实现重定向,只不过RedirectToRouteResult的跳转地址是通过路由信息中的Controller和Action的拼接来完成的,其他均和RedirectResult相同!
ASP.NET MVC在Controller类中定义了几个方法用于创建RedirectToRouteResult对象,当然也可以直接在Action中创建RedirectToRouteResult对象并作为方法的返回值。

public abstract class Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncController, IAsyncManagerContainer { //省略其他代码 protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToAction(string actionName) { return RedirectToAction(actionName, (RouteValueDictionary)null); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToAction(string actionName, object routeValues) { return RedirectToAction(actionName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToAction(string actionName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { return RedirectToAction(actionName, null /* controllerName */, routeValues); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToAction(string actionName, string controllerName) { return RedirectToAction(actionName, controllerName, (RouteValueDictionary)null); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToAction(string actionName, string controllerName, object routeValues) { return RedirectToAction(actionName, controllerName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal virtual RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToAction(string actionName, string controllerName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { RouteValueDictionary mergedRouteValues; if (RouteData == null) { mergedRouteValues = RouteValuesHelpers.MergeRouteValues(actionName, controllerName, null, routeValues, includeImplicitMvcValues: true); } else { mergedRouteValues = RouteValuesHelpers.MergeRouteValues(actionName, controllerName, RouteData.Values, routeValues, includeImplicitMvcValues: true); } return new RedirectToRouteResult(mergedRouteValues); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToActionPermanent(string actionName) { return RedirectToActionPermanent(actionName, (RouteValueDictionary)null); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToActionPermanent(string actionName, object routeValues) { return RedirectToActionPermanent(actionName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToActionPermanent(string actionName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { return RedirectToActionPermanent(actionName, null /* controllerName */, routeValues); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToActionPermanent(string actionName, string controllerName) { return RedirectToActionPermanent(actionName, controllerName, (RouteValueDictionary)null); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToActionPermanent(string actionName, string controllerName, object routeValues) { return RedirectToActionPermanent(actionName, controllerName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal virtual RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToActionPermanent(string actionName, string controllerName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { RouteValueDictionary implicitRouteValues = (RouteData != null) ? RouteData.Values : null; RouteValueDictionary mergedRouteValues = RouteValuesHelpers.MergeRouteValues(actionName, controllerName, implicitRouteValues, routeValues, includeImplicitMvcValues: true); return new RedirectToRouteResult(null, mergedRouteValues, permanent: true); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoute(object routeValues) { return RedirectToRoute(new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoute(RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { return RedirectToRoute(null /* routeName */, routeValues); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoute(string routeName) { return RedirectToRoute(routeName, (RouteValueDictionary)null); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoute(string routeName, object routeValues) { return RedirectToRoute(routeName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal virtual RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoute(string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { return new RedirectToRouteResult(routeName, RouteValuesHelpers.GetRouteValues(routeValues)); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoutePermanent(object routeValues) { return RedirectToRoutePermanent(new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoutePermanent(RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { return RedirectToRoutePermanent(null /* routeName */, routeValues); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoutePermanent(string routeName) { return RedirectToRoutePermanent(routeName, (RouteValueDictionary)null); } protected internal RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoutePermanent(string routeName, object routeValues) { return RedirectToRoutePermanent(routeName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues)); } protected internal virtual RedirectToRouteResult RedirectToRoutePermanent(string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) { return new RedirectToRouteResult(routeName, RouteValuesHelpers.GetRouteValues(routeValues), permanent: true); } }
9、ViewResult
ViewResult内容包含了:PartialViewResult和ViewResult。ViewResult将视图页的内容响应给客户端,而PartialViewResult称分部视图,其响应请求时不输出那写html、head、body等标签,只是将分部视图中内容返回!由于ViewResult和PartialViewResult在进行【View呈现】的过程大致相同,所以此处就只针对ViewResult进行详细解读,而PartialViewRsult详细过程将不再敖述。(分部视图的更多信息:关于如何PartialViewResult的使用)

public abstract class ViewResultBase : ActionResult { private DynamicViewDataDictionary _dynamicViewData; private TempDataDictionary _tempData; private ViewDataDictionary _viewData; private ViewEngineCollection _viewEngineCollection; private string _viewName; public object Model { get { return ViewData.Model; } } public TempDataDictionary TempData { get { if (_tempData == null) { _tempData = new TempDataDictionary(); } return _tempData; } set { _tempData = value; } } public IView View { get; set; } public dynamic ViewBag { get { if (_dynamicViewData == null) { _dynamicViewData = new DynamicViewDataDictionary(() => ViewData); } return _dynamicViewData; } } public ViewDataDictionary ViewData { get { if (_viewData == null) { _viewData = new ViewDataDictionary(); } return _viewData; } set { _viewData = value; } } //获取或设置视图引擎,ASP.NET有两个视图引擎,分别是:WebFormViewEngine、RazorViewEngine。 public ViewEngineCollection ViewEngineCollection { get { return _viewEngineCollection ?? ViewEngines.Engines; } set { _viewEngineCollection = value; } } public string ViewName { get { return _viewName ?? String.Empty; } set { _viewName = value; } } public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context) { if (context == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("context"); } //如果没有设置ViewName就将当前Action作为ViewName if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(ViewName)) { ViewName = context.RouteData.GetRequiredString("action"); } ViewEngineResult result = null; if (View == null) { //通过视图引擎去寻找视图 result = FindView(context); View = result.View; } TextWriter writer = context.HttpContext.Response.Output; ViewContext viewContext = new ViewContext(context, View, ViewData, TempData, writer); //使用指定的编写器对象来呈现指定的视图上下文 View.Render(viewContext, writer); if (result != null) { result.ViewEngine.ReleaseView(context, View); } } protected abstract ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext context); }

public class ViewResult : ViewResultBase { private string _masterName; public string MasterName { get { return _masterName ?? String.Empty; } set { _masterName = value; } } protected override ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext context) { //根据View引擎去寻找View //此处ViewEngineCollection是ViewResultBase类中的一个属性,表示视图引擎集合。 ViewEngineResult result = ViewEngineCollection.FindView(context, ViewName, MasterName); //如果找到了指定的VIew,则返回。 if (result.View != null) { return result; } //没有找到指定的View,那么就将查找路径给通过异常返回。 StringBuilder locationsText = new StringBuilder(); foreach (string location in result.SearchedLocations) { locationsText.AppendLine(); locationsText.Append(location); } throw new InvalidOperationException(String.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, MvcResources.Common_ViewNotFound, ViewName, locationsText)); } }

public class PartialViewResult : ViewResultBase { /// <summary>Returns the <see cref="T:System.Web.Mvc.ViewEngineResult" /> object that is used to render the view.</summary> /// <returns>The view engine result.</returns> /// <param name="context">The controller context.</param> /// <exception cref="T:System.InvalidOperationException">An error occurred while the method was attempting to find the view.</exception> protected override ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext context) { ViewEngineResult viewEngineResult = base.ViewEngineCollection.FindPartialView(context, base.ViewName); if (viewEngineResult.View != null) { return viewEngineResult; } StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); foreach (string current in viewEngineResult.SearchedLocations) { stringBuilder.AppendLine(); stringBuilder.Append(current); } throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, MvcResources.Common_PartialViewNotFound, new object[] { base.ViewName, stringBuilder })); } }
Controller类中定义的创建ViewResult和PartialViewResult对象的方法:

public abstract class Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter, IAsyncController, IController, IAsyncManagerContainer { //省略其他代码... //PartialViewResult protected internal PartialViewResult PartialView() { return this.PartialView(null, null); } protected internal PartialViewResult PartialView(object model) { return this.PartialView(null, model); } protected internal PartialViewResult PartialView(string viewName) { return this.PartialView(viewName, null); } protected internal virtual PartialViewResult PartialView(string viewName, object model) { if (model != null) { base.ViewData.Model = model; } return new PartialViewResult { ViewName = viewName, ViewData = base.ViewData, TempData = base.TempData, ViewEngineCollection = this.ViewEngineCollection }; } //ViewResult protected internal ViewResult View() { string viewName = null; string masterName = null; object model = null; return this.View(viewName, masterName, model); } protected internal ViewResult View(object model) { return this.View(null, null, model); } protected internal ViewResult View(string viewName) { string masterName = null; object model = null; return this.View(viewName, masterName, model); } protected internal ViewResult View(string viewName, string masterName) { return this.View(viewName, masterName, null); } protected internal ViewResult View(string viewName, object model) { return this.View(viewName, null, model); } protected internal virtual ViewResult View(string viewName, string masterName, object model) { if (model != null) { base.ViewData.Model = model; } return new ViewResult { ViewName = viewName, MasterName = masterName, ViewData = base.ViewData, TempData = base.TempData, ViewEngineCollection = this.ViewEngineCollection }; } protected internal ViewResult View(IView view) { return this.View(view, null); } protected internal virtual ViewResult View(IView view, object model) { if (model != null) { base.ViewData.Model = model; } return new ViewResult { View = view, ViewData = base.ViewData, TempData = base.TempData }; } }
ViewResult进行呈现的大致流程为:
- 获取视图引擎,默认有两个:ASPX引擎、Razor引擎。
- 根据视图页名称,通过视图引擎去检查是否存在对应的视图页,如果存在,则创建视图对象。如果不存在,则将所有视图引擎寻找过的路径作为异常返回。
- 创建视图对象之后,处理视图页中的内容(先处理_ViewStart.cshtml,之后再处理相应的试图页)。例如:TempData、Html.XXX等。
- 视图页内容处理完毕之后,就将视图内容作为响应返回给客户端。
对于上述流程中的第三步中,创建视图对象之后,通过它来对视图页进行处理。在对处理视图页时,首先要处理_ViewStart.cshtml文件(相当与asp.net中的Page_Load方法),之后再去处理请求的试图页。例如:如果在~/View/HomeController目录下创建一个_ViewStart.cshtml文件,那么之后当请求HomeController目录下的任意视图页时,都会先执行_ViewStart.cshtml,如果再在~/View目录下创建一个_ViewStart.cshtml的话,那么在请求HomeController目录下的任意视图页时,那么两个_ViewStart.cshtml都会先执行,且顺序为:先~/View目录下后~/View/HomeController目录下的_ViewStart.cshtml。
由于ViewResult的详细过程涉及内容较多,所以将另写一篇博文来对其进行详细分析:《白话学习MVC(十)View的呈现二》
