定义:
Object.assign()用于对象的合并,将源对象(source)的所有可枚举属性,复制到目标对象(target),并将目标对象返回出来。
const target = { a: 1 }
const source1 = { b: 2 }
const source2 = { c: 3 }
const result = Object.assign(target, source1, source2)
console.log(target) // {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}
console.log(result) // {a: 1, b: 2, c: 3}
如果目标对象和源对象有同名属性,后面的属性会覆盖前面的属性
const target = { a: 1 }
const source1 = { b: 2, a: 100 }
const source2 = { c: 3, b: 200 }
const result = Object.assign(target, source1, source2)
console.log(target) // {a: 100, b: 200, c: 3}
console.log(result) // {a: 100, b: 200, c: 3}
以上两点特征使用对象的【解构赋值】效果一样
const target = { a: 1 }
const source1 = { b: 2, a: 100 }
const source2 = { c: 3, b: 200 }
const result = Object.assign(target, source1, source2)
const result1 = { ...target, ...source1, ...source2 }
console.log(target) // {a: 100, b: 200, c: 3}
console.log(result) // {a: 100, b: 200, c: 3}
console.log(result1) // {a: 100, b: 200, c: 3}
Object.assign()如果只有一个参数,会直接返回这个参数
const obj = { a: 1 }
console.log(Object.assign(obj) === obj) // true
如果该参数不是对象,则会先转成对象,然后返回
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.assign(2))) // [object Number] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.assign(NaN))) // [object Number] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.assign(true))) // [object Boolean] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.assign('abc'))) // [object String] console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.assign(new Date()))) // [object Date]
undefined和null无法转成对象,如果用它们作为参数,就会报错
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.assign(undefined))) // Uncaught TypeError: Cannot convert undefined or null to object console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Object.assign(null))) // Uncaught TypeError: Cannot convert undefined or null to object
如果源对象(source)不是一个对象,处理规则有所不同。这些参数都会转成对象,如果不能转就会跳过。这意味着,undefined和null不在首位就不会报错
const obj = { a: 1 }
console.log(Object.assign(obj) === obj) // true
console.log(Object.assign(obj, undefined) === obj) // true
console.log(Object.assign(obj, null) === obj) // true
其他数据类型的值,不在首位(target)也不会报错,但是,除了字符串会以数组形式,拷贝入目标对象,其他值都不会产生效果
const s1 = 'abc' const s2 = true const s3 = 100 const s4 = NaN const s5 = new Date() const obj = {} Object.assign(obj, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5) console.log(obj) // {0: 'a', 1: 'b', 2: 'c'}
因为只有字符串的包装对象,会产生可枚举属性
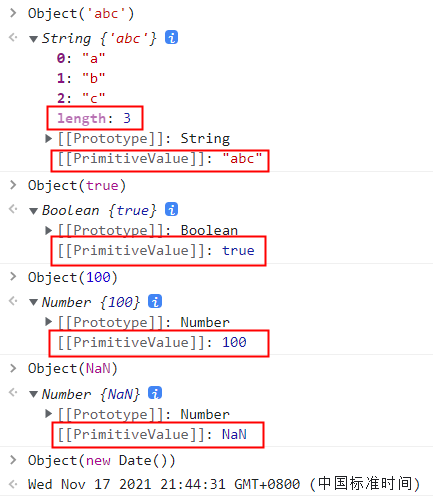
使用Object()将字符串、数字、布尔值、NaN、Date转成对应的包装对象,可以看到它们的原始值都在包装对象的内部属性 [[PrimitiveValue]] 上面,这个属性是不会被Object.assign()拷贝的。只有字符串的包装对象,会产生可枚举的实义属性,这些属性才可以被拷贝
原型链上的属性不会被Object.assign()拷贝
Object.prototype.age = 100 const target = {} const source = { name: '小明' } Object.assign(target, source) console.log(target) // {name: '小明'}
不可枚举属性不会被Object.assign()拷贝
const target = {} const source = { name: '小明' } Object.defineProperty(source, 'latent', { value: '我是一个隐藏的属性', enumerable: false // 默认为false,不可枚举 }) Object.assign(target, source) console.log(target) // { name: '小明' }
属性名为Symbol值的属性,会被Object.assign()拷贝
const target = {} const source = { name: '小明' } Object.defineProperty(source, 'latent', { value: '我是一个隐藏的属性', enumerable: true }) Object.assign(target, source, { [Symbol('xx')]: 'xx' }) console.log(target) // {name: '小明', latent: '我是一个隐藏的属性', Symbol(xx): 'xx'}
注意:
1、Object.assign()是浅拷贝
const target = {} const source = { name: '小明', hobby: { one: 'one', two: 'two' } } Object.assign(target, source) source.name = '小小明' target.hobby.one = 'oneone' console.log(target) // {name: '小明', hobby: {one: 'oneone', two: 'two'}} console.log(source) // {name: '小明', hobby: {one: 'oneone', two: 'two'}}
2、同名属性的替换
const target = { name: '小明' }
const source = { name: '小小明', age: 10 }
const source1 = { age: 18 }
Object.assign(target, source, source1)
console.log(target) // { name: '小小明', age: 18 }
3、数组的处理
const target = [1, 2, 3] const source = [4, 5] Object.assign(target, source) console.log(target) // [4, 5, 3]
Object.assign()会将[1, 2, 3]视为{ 0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3 },因此源数组的0号属性4覆盖了目标数组的0号属性1
const target = { 0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3 }
const source = { 0: 4, 1: 5 }
Object.assign(target, source)
console.log(target) // {0: 4, 1: 5, 2: 3}
4、函数取值的处理:Object.assign()只能进行值的复制,如果要复制的值是一个取值函数,那么将求值后再复制
const target = {} const source = { get fn() { return 1 } } Object.assign(target, source) console.log(target) // {fn: 1}
常见用途:
1、为对象添加属性
class Person { constructor(name, age) { // this.name = name // this.age = age Object.assign(this, { name, age }) } }
2、为对象添加方法
class Person {} Object.assign(Person.prototype, { sayHi() { console.log('hi') } }) // 等同于下面的写法 Person.prototype.sayHi = function() { console.log('hi') }