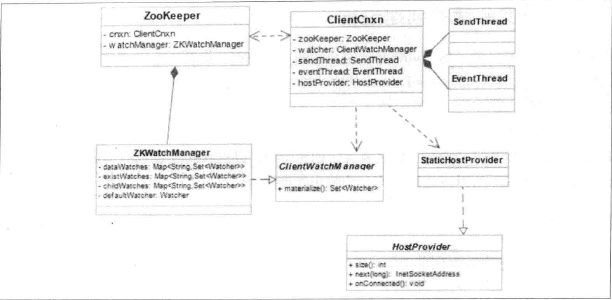
客户端是开发人员使用Zookeeper的主要的途径,以下内容将对Zookeeper的内部原理进行详细的学习和讲解。ZooKeeper的客户端主要有一下几个核心组件组成:
- Zookeeper:提供客户端访问ZooKeeper服务器的API.
- ClientWatchManager:负责管理客户端注册的Watcher.
- HostProvider:客户端地址列表管理器。
- ClientCnxn:客户端核心线程,其内部包含连个线程及SendThread和EvnentThread。SendThread是一个IO线程主要负责客户端和服务端之间的网络通信;后者是一个事件处理线程,主要负责对服务端时间进行处理。
客户端的整体架构如下:
实例
下面使用具体的实例结合源码来分析Zookeeper源码创建的过程:如下代码是一个单例的ZooKeeperSupport可以用来回去Zookeeper客户端对象:

1 public class ZookeeperSupport { 2 private static volatile ZooKeeper zooKeeper = null; // zookeeper连接,在初始化zk配置时设置 3 public static final Integer zooKeeperLock = new Integer(1); 4 public static boolean isUseZk = true; // 是否使用zk,默认使用,当zk连接发生异常时不再使用 5 public static final long ZK_CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 1L; //zk连接的超时时间设置,单位为秒 6 7 public static ZooKeeper getZooKeeper() { 8 // 如果zookeeper为null 或者连接不可用,则重新获取连接,一般情况下,不会触发 9 if (zooKeeper == null || !zooKeeper.getState().isAlive()) { 10 synchronized (zooKeeperLock) { 11 // 如果发现zk不再使用,则不再创建新的zk,直接返回 12 if (isUseZk) { 13 if (zooKeeper == null || !zooKeeper.getState().isAlive()) { 14 try { 15 zooKeeper = createNewZookeper(); 16 } catch (Exception e) { 17 Constant.log_cron.error("[initZkConfig] error happen where new zookeeper", e); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 return zooKeeper; 24 } 25 26 public static void setZooKeeper(ZooKeeper zooKeeper) { 27 ZookeeperSupport.zooKeeper = zooKeeper; 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * zookeeper启动时,异步启动两个线程,所以new之后并不代表连接已经建立,此时如果调用zk的一些方法会抛ConnectionLoss的异常 32 * 为了避免这种情况,封装new方法,每次new的时候去等待连接已经建立才做后面的步骤 33 * 34 * @return 35 * @throws Exception 36 */ 37 public static ZooKeeper createNewZookeper() throws Exception { 38 CountDownLatch connectedLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); 39 ZooKeeper zooKeeper = new ZooKeeper(ZKConfig.getInstance().getConnectUrl(), ZKConfig.getInstance().getTimeout(), new DefaultWatcher(connectedLatch)); 40 if (States.CONNECTING == zooKeeper.getState()) { 41 boolean ret = connectedLatch.await(ZK_CONNECT_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 42 // 如果等待超时了,还没有收到连接成功的通知,则说明zk不可用,直接不用zk,并报警 43 if(!ret){ 44 isUseZk = false; 45 } 46 } 47 return zooKeeper; 48 } 49 }
为了使用Zookeeper服务,必需创建一个Zookeeper类的对象。在创建Zookeeper类的对象时客户端Session的建立是一个异步的过程,构造方法可能会在回话完成建立完成前立即返回,构造方法中的Watcher就是处理连接状态通知的接口。下面给出了DefaultWatcher实现:

1 public class DefaultWatcher implements Watcher { 2 private CountDownLatch connectedLatch; 3 public DefaultWatcher(CountDownLatch connectedLatch) { 4 this.connectedLatch = connectedLatch; 5 } 6 // 监控所有被触发的事件 7 @Override 8 public void process(WatchedEvent event) { 9 if (connectedLatch != null && event.getState() == KeeperState.SyncConnected) { 10 connectedLatch.countDown(); 11 } 12 } 13 }
源码分析
Zookeeper类一共有9个构造函数,具体参数的意义如下:

由上面的实例可知,在创建Zookeeper对象时最终调用了如下的构造函数:

1 可以看到上面的实例中最终调用了这个构造方法: 2 public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher, 3 boolean canBeReadOnly, HostProvider aHostProvider, 4 ZKClientConfig clientConfig) throws IOException { 5 if (clientConfig == null) { 6 clientConfig = new ZKClientConfig(); 7 } 8 this.clientConfig = clientConfig; 9 //1.初始化watcherManger 10 watchManager = defaultWatchManager(); 11 //2.为watchManager设置设置默认的Watcher 12 watchManager.defaultWatcher = watcher; 13 //3.解析服务器串 14 ConnectStringParser connectStringParser = new ConnectStringParser( 15 connectString); 16 hostProvider = aHostProvider; 17 //4.创建ClientCnxn对象,并启动 18 cnxn = new ClientCnxn(connectStringParser.getChrootPath(), 19 hostProvider, sessionTimeout, this, watchManager, 20 getClientCnxnSocket(), canBeReadOnly); 21 cnxn.start(); 22 }
根据如上源码可知在初始化Zookeeper对象时主要做了三件事情:
- 初始化ZKWatcherManager
- 解析服务器串,并初始化hostprovider
- 初始化并启动ClientCnxn
1.初始化ZKWatcherManager
下面针对上面三个步骤注意分析。WatchManager主要负责管理客户端注册的Wathcr。首先看看 defaultWatchManager()方法,

1 protected ZKWatchManager defaultWatchManager() { 2 return new ZKWatchManager(getClientConfig().getBoolean(ZKClientConfig.DISABLE_AUTO_WATCH_RESET)); 3 }
该方法创建了一个ZKWatchManager对象, ZKWatchManager实现了ClientWatchManager接口,ClientWatchManager接口只有一个materialize()方法,该方法根据keeperState、eventType和path返回应该被通知的Watcher集合。其声明如下:

public interface ClientWatchManager { public Set<Watcher> materialize(Watcher.Event.KeeperState state, Watcher.Event.EventType type, String path); }
接下来看看ZKWatchManager的实现,在ZKWatchManager中包含了五个属性:

1 private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> dataWatches =new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>(); 2 private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> existWatches =new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>(); 3 private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> childWatches =new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>(); 4 private boolean disableAutoWatchReset;//用于禁止在Client重连是在服务端重建watch 5 protected volatile Watcher defaultWatcher;//默认的watcher
在ZKWatchManager中最重要的方法是materialize()方法,下面结合源码进行分析:

public Set<Watcher> materialize(Watcher.Event.KeeperState state, Watcher.Event.EventType type,String clientPath){ //用于存储返回结果 Set<Watcher> result = new HashSet<Watcher>(); //根据EventType进行不同的操作 switch (type) { case None: //将defaultWatcher返回 result.add(defaultWatcher); //如果KeeperState不是SyncConnected,并且disableAutoWatchReset为true返回所有的watcher,并清空 boolean clear = disableAutoWatchReset && state != Watcher.Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected; synchronized(dataWatches) { for(Set<Watcher> ws: dataWatches.values()) { result.addAll(ws); } if (clear) { dataWatches.clear(); } } synchronized(existWatches) { for(Set<Watcher> ws: existWatches.values()) { result.addAll(ws); } if (clear) { existWatches.clear(); } } synchronized(childWatches) { for(Set<Watcher> ws: childWatches.values()) { result.addAll(ws); } if (clear) { childWatches.clear(); } } return result; //如果EventType是NodeDataChanged或者NodeCreated,将dataWatches和existWatches case NodeDataChanged: case NodeCreated: synchronized (dataWatches) { addTo(dataWatches.remove(clientPath), result); } synchronized (existWatches) { addTo(existWatches.remove(clientPath), result); } break; //如果EventType是NodeChildrenChanged,将childWatches返回 case NodeChildrenChanged: synchronized (childWatches) { addTo(childWatches.remove(clientPath), result); } break; //如果EventType是NodeDeleted,将dataWatches返回 case NodeDeleted: synchronized (dataWatches) { addTo(dataWatches.remove(clientPath), result); } synchronized (existWatches) { Set<Watcher> list = existWatches.remove(clientPath); if (list != null) { addTo(existWatches.remove(clientPath), result); } } synchronized (childWatches) { addTo(childWatches.remove(clientPath), result); } break; default: throw new RuntimeException(msg); } return result; } }
在看了ZKWatcherManager代码之后,那么产生一个疑问Watcher是在什么时候添加到ZKWatcherManager中的,以Zookeeper接口中的getData()为例:

public void getData(final String path, Watcher watcher,DataCallback cb, Object ctx){ … //在此处创建了WatchRegistration对象 WatchRegistration wcb = null; if (watcher != null) { wcb = new DataWatchRegistration(watcher, clientPath); } … //调用clientCnxn的queuePacket方法 cnxn.queuePacket(h,newReplyHeader(),request,response,cb,clientPath,serverPath, ctx, wcb); }
从上面可以看到在getData()方法中中创建了一个DataWatchRegistration对象,接下来再分析一下DataWatchRegistration。DataWatchRegistration继承了WatchRegistration类,WatchRegistration有一个抽象方法如下:

1 abstract protected Map<String, Set<Watcher>> getWatches(int rc);
该方法从ZKWatcherManager中获取一个合适的Map。除此之外还有个register方法,真正的向ZKWatcherManager中注册Watcher,其具体代码如下:

public void register(int rc) { if (shouldAddWatch(rc)) { Map<String, Set<Watcher>> watches = getWatches(rc); synchronized(watches) { Set<Watcher> watchers = watches.get(clientPath); if (watchers == null) { watchers = new HashSet<Watcher>(); watches.put(clientPath, watchers); } watchers.add(watcher); } } }
现在再看一下DataWatchRegistration中是如何实现getWatches(int rc)方法:

protected Map<String, Set<Watcher>> getWatches(int rc) { return watchManager.dataWatches; }
在DataWatchRegistration中直接返回了watchManager.dataWatches register()方法在finishPacket会调用。
2.ClinetCnxn的创建
在Zookeeper的构造函数中,创建并启动ClientCnxn的代码如下:

cnxn = new ClientCnxn(connectStringParser.getChrootPath(), hostProvider, sessionTimeout, this, watchManager, getClientCnxnSocket(), canBeReadOnly); cnxn.start();
在构造方法中调用的getClientCnxnSocket()方法,该方法根据系统配置创建一个ClientCnxnSocket对象,具体代码如下:

1 private ClientCnxnSocket getClientCnxnSocket() throws IOException { 2 String clientCnxnSocketName = getClientConfig().getProperty( 3 ZKClientConfig.ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_CNXN_SOCKET); 4 //默认使用ClientCnxnSocketNIO 5 if (clientCnxnSocketName == null) { 6 clientCnxnSocketName = ClientCnxnSocketNIO.class.getName(); 7 } 8 try { 9 //反射获取构造函数 10 Constructor<?> clientCxnConstructor = Class.forName(clientCnxnSocketName). 11 getDeclaredConstructor(ZKClientConfig.class); 12 //创建对象 13 ClientCnxnSocket clientCxnSocket = (ClientCnxnSocket) clientCxnConstructor. 14 newInstance(getClientConfig()); 15 return clientCxnSocket; 16 } catch (Exception e) { 17 IOException ioe = new IOException("Couldn't instantiate " 18 + clientCnxnSocketName); 19 ioe.initCause(e); 20 throw ioe; 21 } 22 }
接下来看一下ClientCnxn的构造方法:

public ClientCnxn(String chrootPath, HostProvider hostProvider, int sessionTimeout, ZooKeeper zooKeeper,ClientWatchManager watcher, ClientCnxnSocket clientCnxnSocket, long sessionId, byte[] sessionPasswd, boolean canBeReadOnly) { … connectTimeout = sessionTimeout / hostProvider.size(); readTimeout = sessionTimeout * 2 / 3; … //初始化sendThread和EventThread sendThread = new SendThread(clientCnxnSocket); eventThread = new EventThread(); this.clientConfig=zooKeeper.getClientConfig(); }
关于sendThread和EventThread暂时先不分析,接下来看看ClientCnxn的start()方法,该方法主要用于启动sendThread线程和eventThread线程。

1 public void start() { 2 sendThread.start(); 3 eventThread.start(); 4 }
EventThread
EventThread:主要用于处理Zookeeper客户端的各种事件,需要注意的是EventThread是一个守护线程。在EventThread内部主要包含以下几个属性:

1 //保存一个待处理的时间的队列 2 final LinkedBlockingQueue<Object> waitingEvents =new LinkedBlockingQueue<Object>(); 3 private volatile KeeperState sessionState = KeeperState.Disconnected; 4 private volatile boolean wasKilled = false;// 判断EventThread是否被杀掉 5 private volatile boolean isRunning = false;//判断EventThread是否还在运行
同时在EventThread内部有几个方法将不同待处理事件添加到waitingEvents,这些方法我们暂时不做分析。接下来看看EventThread的run()方法:

1 public void run() { 2 try { 3 isRunning = true; 4 while (true) { 5 //从任务队列中取出待处理任务 6 Object event = waitingEvents.take(); 7 if (event == eventOfDeath) { 8 wasKilled = true; 9 } else { 10 //处理事务 11 processEvent(event); 12 } 13 if (wasKilled) 14 synchronized (waitingEvents) { 15 if (waitingEvents.isEmpty()) { 16 isRunning = false; 17 break; 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 … 23 } 24 … 25 }
processEvent()方法比较简单,就是调用相应的对象执行相应的处理。
SendThread
SendThread主要负责客户端与服务器端的IO和心跳消息。SendThread主要包含以下四个属性:

private long lastPingSentNs;//记录上一次心跳发送时间 private final ClientCnxnSocket clientCnxnSocket;//在ClientCnxn构造时传入的 private Random r = new Random(System.nanoTime()); private boolean isFirstConnect = true;
SendThread的构造方法如下:

SendThread(ClientCnxnSocket clientCnxnSocket) { uper(makeThreadName("-SendThread()")); state = States.CONNECTING;//将ClientCnxn中state由Not_connected设置为CONNECTING this.clientCnxnSocket = clientCnxnSocket; etDaemon(true);//设置为守护线程 }
接下来看看SendThread的run方法,其中这段代码比较长先进行逐一分析:

clientCnxnSocket.introduce(this, sessionId, outgoingQueue); clientCnxnSocket.updateNow(); clientCnxnSocket.updateLastSendAndHeard(); int to; long lastPingRwServer = Time.currentElapsedTime(); final int MAX_SEND_PING_INTERVAL = 10000; //10 seconds
接下来进入While循环,在循环的第一部分判断socket连接是否建立,如果没有建立就建立连接,改代码主要如下

if (!clientCnxnSocket.isConnected()) { // don't re-establish connection if we are closing if (closing) { break; } startConnect(); lientCnxnSocket.updateLastSendAndHeard(); }
进入startConnect继续跟踪,发现startConnect()最终调用了ClientCnxnSocketNIO的connect方法,在connect()方法内部先调用了createSock()方法创建一个Sockect对象,其具体实现如下:

SocketChannel createSock() throws IOException { SocketChannel sock; sock = SocketChannel.open(); sock.configureBlocking(false); sock.socket().setSoLinger(false, -1); sock.socket().setTcpNoDelay(true); return sock; }
接下来connect()方法继续调用registerAndConnect,该方法真正的向服务器端建立连接:

void registerAndConnect(SocketChannel sock, InetSocketAddress addr) throws IOException { sockKey = sock.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); boolean immediateConnect = sock.connect(addr); if (immediateConnect) { sendThread.primeConnection(); } }
可以看到在registerAndConnect方法中又调用了SendThread的primeConnection()方法,在primeConnection()方法中主要初始化Session、Watch和权限信息,同时注册ClientCnxnSocketNIO对读时间和写时间的监听。继续回到SendThread的run()方法。接下来继续判断连接状态,如果是state.isConnected()会进行一系列的操作,其中最重要的是调用sendPing()方法和clientCnxnSocket.doTransport(to, pendingQueue, ClientCnxn.this);,再此主要分析一下doTransport()方法,

1 void doTransport(int waitTimeOut, List<Packet> pendingQueue, ClientCnxn cnxn) 2 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 3 selector.select(waitTimeOut); 4 Set<SelectionKey> selected; 5 synchronized (this) { 6 selected = selector.selectedKeys(); 7 } 8 updateNow(); 9 for (SelectionKey k : selected) { 10 SocketChannel sc = ((SocketChannel) k.channel()); 11 //如果是连接事件 12 if ((k.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) { 13 if (sc.finishConnect()) { 14 updateLastSendAndHeard(); 15 updateSocketAddresses(); 16 sendThread.primeConnection(); 17 } 18 } 19 //如果是读写事件 20 else f((k.readyOps() & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE)) != 0) { 21 doIO(pendingQueue, cnxn); 22 } 23 } 24 if (sendThread.getZkState().isConnected()) { 25 if (findSendablePacket(outgoingQueue, 26 sendThread.tunnelAuthInProgress()) != null) { 27 enableWrite(); 28 } 29 } 30 selected.clear(); 31 }
可以看到最重要的方法是doIO(),在doIO()方法中主要进行读写操作.继续回到SendThread的run方法,看看run()方法在结束时做什么工作,在run()方法,跳出while循环时代码如下

synchronized (state) { // When it comes to this point, it guarantees that later queued // packet to outgoingQueue will be notified of death. cleanup(); } //调用selector.close() clientCnxnSocket.close(); if (state.isAlive()) { //添加Disconnected事件 eventThread.queueEvent(new WatchedEvent(Event.EventType.None, Event.KeeperState.Disconnected, null)); }
在SendThread的run()结束前很重要的一步操作是调用cleanup()方法:

1 private void cleanup() { 2 //关闭网络连接 3 clientCnxnSocket.cleanup(); 4 synchronized (pendingQueue) { 5 //遍历pendingQueue,执行conLossPacket 6 for (Packet p : pendingQueue) { 7 conLossPacket(p); 8 } 9 //清除pendingQueue 10 pendingQueue.clear(); 11 } 12 // We can't call outgoingQueue.clear() here because 13 // between iterating and clear up there might be new 14 // packets added in queuePacket(). 15 Iterator<Packet> iter = outgoingQueue.iterator(); 16 while (iter.hasNext()) { 17 Packet p = iter.next(); 18 conLossPacket(p); 19 iter.remove(); 20 } 21 }
在cleanUp方法中最主要的是循环和遍历pendingQueue和outgoingQueue,并针对两个队列中每一个Packet调用conLossPacket(p)方法,最后清空两个队列,现在具体看一看conLossPacket(p)中具体做了什么事情,在conLossPacket(p)主要调用了finishPacket(p),现在进finishPacket(p)方法进行分析:

private void finishPacket(Packet p) { int err = p.replyHeader.getErr(); //watcher的注册于取消注册 …. //判断是否有异步的回调,如果没有将finished设置为true,唤醒所有等待的事件 if (p.cb == null) { synchronized (p) { p.finished = true; p.notifyAll(); } } else { //有异步回调,将finished设置为true,并将packet加入到EventThread的队列 p.finished = true; eventThread.queuePacket(p); } }
至此真个Zookeeper连接的建立过程就完成了。
