继上次学习过Java8中的非常重要的Lambda表达式之后,接下来就要学习另一个也比较重要的知识啦,也就如标题所示:Stream,而它的学习是完全依赖于之前学习的Lambda表达式。
Java 8 API添加了一个新的抽象称为流Stream,可以让你以一种声明的方式处理数据。
Stream 使用一种类似用 SQL 语句从数据库查询数据的直观方式来提供一种对 Java 集合运算和表达的高阶抽象。
Stream API可以极大提高Java程序员的生产力,让程序员写出高效率、干净、简洁的代码。
这种风格将要处理的元素集合看作一种流, 流在管道中传输, 并且可以在管道的节点上进行处理, 比如筛选, 排序,聚合等。
元素流在管道中经过中间操作(intermediate operation)的处理,最后由最终操作(terminal operation)得到前面处理的结果。
+--------------------+ +------+ +------+ +---+ +-------+ | stream of elements +-----> |filter+-> |sorted+-> |map+-> |collect| +--------------------+ +------+ +------+ +---+ +-------+
以上的流程转换为 Java 代码为:
class Apple{
private int weigth;
private String color;
public int getWeigth() {
return weigth;
}
public void setWeigth(int weigth) {
this.weigth = weigth;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Apple(int weigth, String color) {
this.weigth = weigth;
this.color = color;
}
}
@Test
public void testStream(){
List<Apple> transactionsIds = new ArrayList<>();
transactionsIds.add(new Apple(1,"红色"));
transactionsIds.add(new Apple(2,"绿色"));
transactionsIds.add(new Apple(3,"绿色"));
transactionsIds.add(new Apple(2,"绿色"));
int weight= transactionsIds.stream()
.filter(app ->app.getColor().equals("绿色"))
.sorted(( app1, app2)->app2.getWeigth()-app1.getWeigth())
.mapToInt(Apple::getWeigth)
.sum();
System.out.println(weight);
}
以上代码的写法可读性比较高,几乎一眼能看出做了哪些操作。
简介
Stream(流)是一个来自数据源的元素队列并支持聚合操作
- 元素队列元素是特定类型的对象,形成一个队列。 Java中的Stream并不会存储元素,而是按需计算。
- 数据源 流的来源。 可以是集合,数组,I/O channel, 产生器generator 等。
- 聚合操作 类似SQL语句一样的操作, 比如filter, map, reduce, find, match, sorted等。
和以前的Collection操作不同, Stream操作还有两个基础的特征:
- Pipelining: 中间操作都会返回流对象本身。 这样多个操作可以串联成一个管道, 如同流式风格(fluent style)。 这样做可以对操作进行优化, 比如延迟执行(laziness)和短路( short-circuiting)。
- 内部迭代: 以前对集合遍历都是通过Iterator或者For-Each的方式, 显式的在集合外部进行迭代, 这叫做外部迭代。 Stream提供了内部迭代的方式, 通过访问者模式(Visitor)实现。
实例
生成流
在 Java 8 中, 集合接口有两个方法来生成流:
-
stream() − 为集合创建串行流。
-
parallelStream() − 为集合创建并行流。
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
List<String> filtered = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList());
forEach
Stream 提供了新的方法 'forEach' 来迭代流中的每个数据。以下代码片段使用 forEach 输出了10个随机数:
Random random = new Random(); random.ints().limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
map
map 方法用于映射每个元素到对应的结果,以下代码片段使用 map 输出了元素对应的平方数:
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 2, 2, 3, 7, 3, 5); // 获取对应的平方数
List<Integer> squaresList = numbers.stream().map( i -> i*i).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
filter
filter 方法用于通过设置的条件过滤出元素。以下代码片段使用 filter 方法过滤出空字符串:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
// 获取空字符串的数量
int count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();
limit
limit 方法用于获取指定数量的流。 以下代码片段使用 limit 方法打印出 10 条数据:
Random random = new Random(); random.ints().limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
sorted
sorted 方法用于对流进行排序。以下代码片段使用 sorted 方法对输出的 10 个随机数进行排序:
Random random = new Random(); random.ints().limit(10).sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
并行(parallel)程序
parallelStream 是流并行处理程序的代替方法。以下实例我们使用 parallelStream 来输出空字符串的数量:
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
// 获取空字符串的数量
int count = strings.parallelStream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();
我们可以很容易的在顺序运行和并行直接切换。
Collectors
Collectors 类实现了很多归约操作,例如将流转换成集合和聚合元素。Collectors 可用于返回列表或字符串:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
List<String> filtered = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("筛选列表: " + filtered);
String mergedString = strings.stream().filter(string -> !string.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
System.out.println("合并字符串: " + mergedString);
统计
另外,一些产生统计结果的收集器也非常有用。它们主要用于int、double、long等基本类型上,它们可以用来产生类似如下的统计结果。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 2, 2, 3, 7, 3, 5);
IntSummaryStatistics stats = numbers.stream().mapToInt((x) -> x).summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("列表中最大的数 : " + stats.getMax());
System.out.println("列表中最小的数 : " + stats.getMin());
System.out.println("所有数之和 : " + stats.getSum());
System.out.println("平均数 : " + stats.getAverage());
分析
一、stream支持并行,这个怎么验证呢?可以通过下面两张图可知
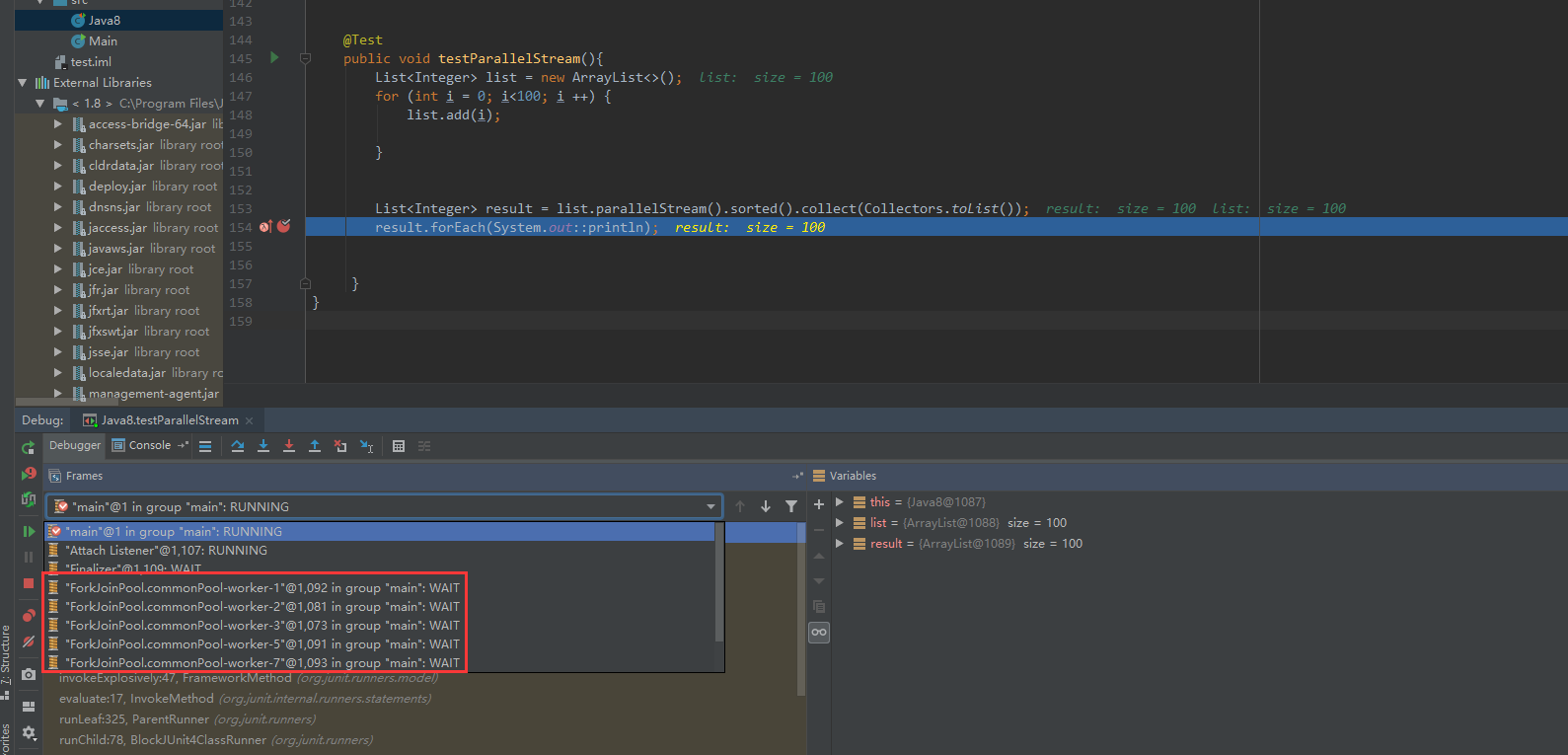
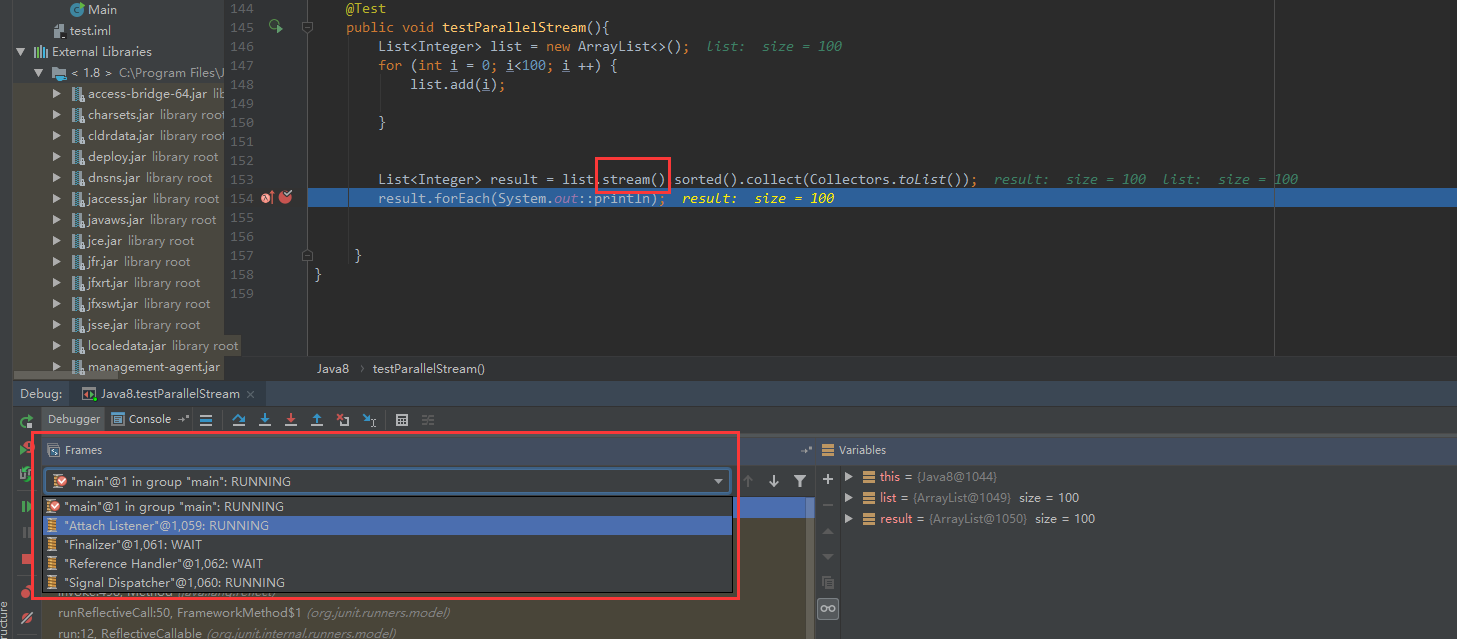
二、stream到底如何工作的?
下图很清晰的展示了stream的工作方式,并且是一次性的,即操作过的stream无法再次被操作。

三、stream有啥好处?
下图可以说明stream的优势,很明显,就是速度要快,因为stream只操作符合条件的数据,有短路的特点。
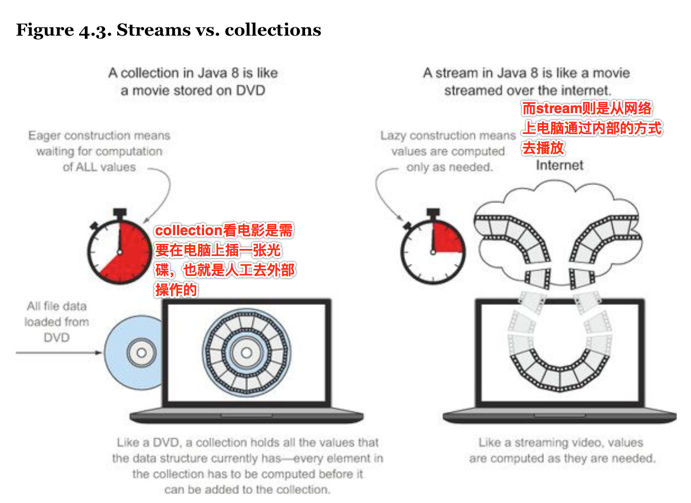
四、stream的迭代方式变化,也就是上文提及的由以前的“外部迭代”改成了“内部迭代”

五、stream的方法分为两种,一种是Intermediate Operations(中间操作),一种是terminal operations(终止操作),这个应该好理解,继续操作的命令就是中间操作。这里为什么要区分这两种操作的,因为stream操作是属于延迟操作,也就是说这段链式代码必须遇到terminal operations才会去执行,否则是不会有任何效果,这个是容易踩得坑。

这里大致列一下,其实每个方法上大神都有说明是什么操作,另外我们根据返回类型也能确定是属于什么操作。

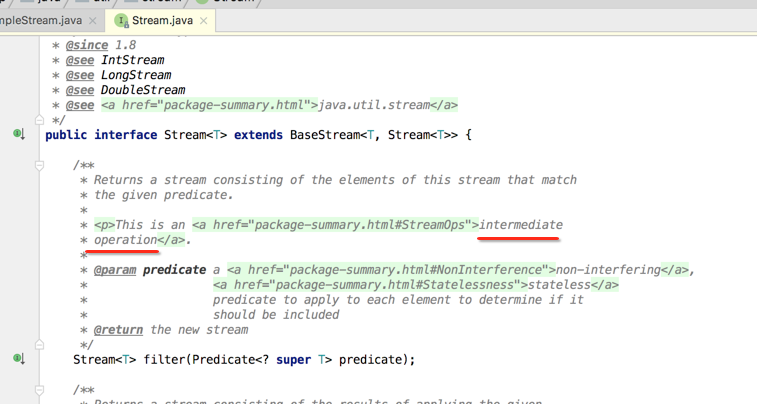
六、stream的中间操作是不停的for循环吗?
对于一个流可能有若干个中间操作,对于这些操作并非降低了整体的执行性能,反而会有提升,比如说增加了三个中间操作,可能感受会有三次循环,但是实际上最终只会循环一次,可以这么简单的理解,以于这些中间操作的行为都是存放于Stream中的一个容器当中,一旦遇到终止操作时,则会将这些行为按照咱们写的顺序逐个的应用到集合当中的每一个元素上,所以说性能上不会有任何影响。
七、stream会修改源数据吗?
并不会修改底层的数据源,集合可以作为流的底层数据源
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/webor2006/p/7887244.html,https://www.runoob.com/java/java8-streams.html
