LinkedList及常用API
① LinkedList----链表
② LinkedList类扩展AbstractSequentialList并实现List接口
③ LinkedList提供了一个链表数据结构
④ LinkedList有两个构造方法
a) LinkedList()
b) LinkedList(Collection c)
⑤ 除了继承的方法之外,LinkedList类还定义了一些有用的方法用于操作和访问容器中的数据;
a) void addFirst(E e)
b) void addLast(E e)
c) E removeFirst()
d) E removeLast()
1 LinkedList<String> sList = new LinkedList<String>();
2 sList.add("zhangsan");// 将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾
3 sList.add("lisi");
4 sList.add("wangwu");
5 sList.add("rose");
6 sList.add("mary");
7 sList.add("jack");
8 sList.addFirst("jay");// 将指定元素插入此列表的开头
9 sList.addLast("jhon");// 将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾
10 for (String name : sList) {
11 System.out.println(name);
12 }
13
14 System.out.println("****************************************");
15 System.out.println(sList.removeFirst());//移除并返回此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,NoSuchElementException
16 sList.clear();
17 System.out.println(sList.size());//返回此列表的元素数
18 System.out.println(sList.pollFirst());//获取并移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null
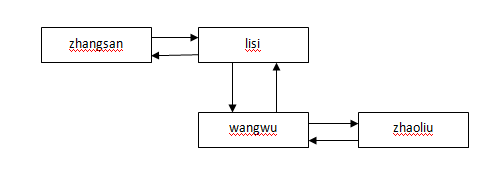
Linked中链表结构如下:
LinkedList中的 remove(Object)方法如下:
1 public boolean remove(Object o) {
2 if (o == null) {
3 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
4 if (x.item == null) {
5 unlink(x);
6 return true;
7 }
8 }
9 } else {
10 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
11 if (o.equals(x.item)) {
12 unlink(x);
13 return true;
14 }
15 }
16 }
17 return false;
18 }
再找到unlink方法
1 E unlink(Node<E> x) {
2 // assert x != null;
3 final E element = x.item;
4 final Node<E> next = x.next;
5 final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
6
7 if (prev == null) {
8 first = next;
9 } else {
10 prev.next = next;
11 x.prev = null;
12 }
13
14 if (next == null) {
15 last = prev;
16 } else {
17 next.prev = prev;
18 x.next = null;
19 }
20
21 x.item = null;
22 size--;
23 modCount++;
24 return element;
25 }
从中可以看到删除时做的操作是,将要删除的元素b设为null,并且将其上一个元素a指向b的下一个元素c,将c指向a;
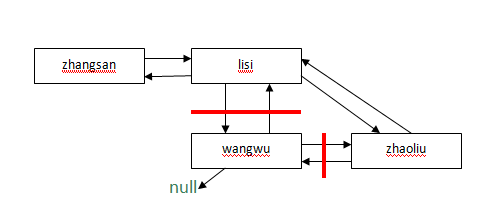
总结:
内部封装的是双向链表数据结构
每个节点是一个Node对象,Node对象中封装的是你要添加的元素
还有一个指向上一个Node对象的引用和指向下一个Node对象的引用
不同的容器有不同的数据结构,不同的数据结构操作起来性能是不同的
链表数据结构,做插入,删除的效率比较高,但查询效率比较低
数组结构,它做查询的效率高,因为可以通过下标直接找到元素
但插入删除效率比较低,因为要做移位操作
二:用LinkedList实现栈和队列
栈的特点,后进先出

栈的方法:
1 class MyStack<T>{
2 private LinkedList<T> data=null;
3 public MyStack() {
4 data=new LinkedList<T>();
5 }
6
7 //压栈的方法
8 public void push(T obj) {
9 data.addFirst(obj);
10 }
11
12 public T pop() {
13 return data.removeFirst();
14 }
15
16 public Iterator<T> iterator() {
17 return data.iterator();
18 }
19 }
main函数中添加及使用:
1 MyStack<String> mystack=new MyStack<String>();
2 mystack.push("zhangsan");
3 mystack.push("lisi");
4 mystack.push("wangwu");
5 mystack.push("zhaoliu");
6 mystack.pop();
7 mystack.pop();
8 Iterator<String> it=mystack.iterator();
9 while(it.hasNext()){
10 System.out.println(it.next());
11 }
输出结果:
lisi
zhangsan
队列的特点:先进先出
队列的方法:
1 class myQueue<T>{
2 private LinkedList<T> data=null;
3 public myQueue(){
4 data=new LinkedList<T>();
5 }
6
7 public void push(T obj) {
8 data.addFirst(obj);
9 }
10
11 public T pop() {
12 return data.removeLast();
13 }
14
15 public Iterator<T> iterotor() {
16 return data.iterator();
17 }
18 }
main函数中添加及使用:
1 myQueue<Integer> myQueue=new myQueue<Integer>();
2 myQueue.push(1);
3 myQueue.push(2);
4 myQueue.push(3);
5 myQueue.push(4);
6 myQueue.push(5);
7 myQueue.pop();
8 myQueue.pop();
9 Iterator<Integer> it= myQueue.iterotor();
10 while (it.hasNext()) {
11 System.out.println(it.next());
12 }
输出结果:
5
4
3