【正文】
这份笔记整理了整整一个星期,每一行代码都是自己默写完成,并测试运行成功,同时也回顾了一下《剑指offer》这本书中和链表有关的讲解,希望对笔试和面试有所帮助。OMG!
本文包含链表的以下内容:
1、单链表的创建和遍历
2、求单链表中节点的个数
3、查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点(剑指offer,题15)
4、查找单链表中的中间结点
5、合并两个有序的单链表,合并之后的链表依然有序【出现频率高】(剑指offer,题17)
6、单链表的反转【出现频率最高】(剑指offer,题16)
7、从尾到头打印单链表(剑指offer,题5)
8、判断单链表是否有环
9、取出有环链表中,环的长度
10、单链表中,取出环的起始点(剑指offer,题56)。本题需利用上面的第8题和第9题。
11、判断两个单链表相交的第一个交点(剑指offer,题37)
此外,《剑指offer》中还有如下和链表相关的题目暂时还没有收录:(以后再收录)
剑指offer,题13:在O(1)时间删除链表结点
剑指offer,题26:复杂链表的复制
剑指offer,题45:圆圈中最后剩下的数字
剑指offer,题57:删除链表中
1、单链表的创建和遍历:
1 public class LinkList {
2 public Node head;
3 public Node current;
4
5 //方法:向链表中添加数据
6 public void add(int data) {
7 //判断链表为空的时候
8 if (head == null) {//如果头结点为空,说明这个链表还没有创建,那就把新的结点赋给头结点
9 head = new Node(data);
10 current = head;
11 } else {
12 //创建新的结点,放在当前节点的后面(把新的结点合链表进行关联)
13 current.next = new Node(data);
14 //把链表的当前索引向后移动一位
15 current = current.next; //此步操作完成之后,current结点指向新添加的那个结点
16 }
17 }
18
19 //方法:遍历链表(打印输出链表。方法的参数表示从节点node开始进行遍历
20 public void print(Node node) {
21 if (node == null) {
22 return;
23 }
24
25 current = node;
26 while (current != null) {
27 System.out.println(current.data);
28 current = current.next;
29 }
30 }
31
32
33 class Node {
34 //注:此处的两个成员变量权限不能为private,因为private的权限是仅对本类访问。
35 int data; //数据域
36 Node next;//指针域
37
38 public Node(int data) {
39 this.data = data;
40 }
41 }
42
43
44 public static void main(String[] args) {
45 LinkList list = new LinkList();
46 //向LinkList中添加数据
47 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
48 list.add(i);
49 }
50
51 list.print(list.head);// 从head节点开始遍历输出
52 }
53
54 }
上方代码中,这里面的Node节点采用的是内部类来表示(33行)。使用内部类的最大好处是可以和外部类进行私有操作的互相访问。
注:内部类访问的特点是:内部类可以直接访问外部类的成员,包括私有;外部类要访问内部类的成员,必须先创建对象。
为了方便添加和遍历的操作,在LinkList类中添加一个成员变量current,用来表示当前节点的索引(03行)。
这里面的遍历链表的方法(20行)中,参数node表示从node节点开始遍历,不一定要从head节点遍历。
2、求单链表中节点的个数:
注意检查链表是否为空。时间复杂度为O(n)。这个比较简单。
核心代码:
1 //方法:获取单链表的长度
2 public int getLength(Node head) {
3 if (head == null) {
4 return 0;
5 }
6
7 int length = 0;
8 Node current = head;
9 while (current != null) {
10 length++;
11 current = current.next;
12 }
13
14 return length;
15 }
3、查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点:
3.1 普通思路:
先将整个链表从头到尾遍历一次,计算出链表的长度size,得到链表的长度之后,就好办了,直接输出第(size-k)个节点就可以了(注意链表为空,k为0,k为1,k大于链表中节点个数时的情况
)。时间复杂度为O(n),大概思路如下:
1 public int findLastNode(int index) { //index代表的是倒数第index的那个结点
2
3 //第一次遍历,得到链表的长度size
4 if (head == null) {
5 return -1;
6 }
7
8 current = head;
9 while (current != null) {
10 size++;
11 current = current.next;
12 }
13
14 //第二次遍历,输出倒数第index个结点的数据
15 current = head;
16 for (int i = 0; i < size - index; i++) {
17 current = current.next;
18 }
19
20 return current.data;
21 }
如果面试官不允许你遍历链表的长度,该怎么做呢?接下来就是。
3.2 改进思路:(这种思路在其他题目中也有应用)
这里需要声明两个指针:即两个结点型的变量first和second,首先让first和second都指向第一个结点,然后让second结点往后挪k-1个位置,此时first和second就间隔了k-1个位置,然后整体向后移动这两个节点,直到second节点走到最后一个结点的时候,此时first节点所指向的位置就是倒数第k个节点的位置。时间复杂度为O(n)
代码实现:(初版)
1 public Node findLastNode(Node head, int index) {
2
3 if (node == null) {
4 return null;
5 }
6
7 Node first = head;
8 Node second = head;
9
10 //让second结点往后挪index个位置
11 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
12 second = second.next;
13 }
14
15 //让first和second结点整体向后移动,直到second结点为Null
16 while (second != null) {
17 first = first.next;
18 second = second.next;
19 }
20
21 //当second结点为空的时候,此时first指向的结点就是我们要找的结点
22 return first;
23 }
代码实现:(最终版)(考虑k大于链表中结点个数时的情况时,抛出异常)
上面的代码中,看似已经实现了功能,其实还不够健壮:
要注意k等于0的情况;
如果k大于链表中节点个数时,就会报空指针异常,所以这里需要做一下判断。
核心代码如下:
1 public Node findLastNode(Node head, int k) {
2 if (k == 0 || head == null) {
3 return null;
4 }
5
6 Node first = head;
7 Node second = head;
8
9 //让second结点往后挪k-1个位置
10 for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
11 System.out.println("i的值是" + i);
12 second = second.next;
13 if (second == null) { //说明k的值已经大于链表的长度了
14 //throw new NullPointerException("链表的长度小于" + k); //我们自己抛出异常,给用户以提示
15 return null;
16 }
17 }
18
19 //让first和second结点整体向后移动,直到second走到最后一个结点
20 while (second.next != null) {
21 first = first.next;
22 second = second.next;
23 }
24
25 //当second结点走到最后一个节点的时候,此时first指向的结点就是我们要找的结点
26 return first;
27 }
4、查找单链表中的中间结点:
同样,面试官不允许你算出链表的长度,该怎么做呢?
思路:
和上面的第2节一样,也是设置两个指针first和second,只不过这里是,两个指针同时向前走,second指针每次走两步,first指针每次走一步,直到second指针走到最后一个结点时,此时first指针所指的结点就是中间结点。注意链表为空,链表结点个数为1和2的情况。时间复杂度为O(n)。
代码实现:
1 //方法:查找链表的中间结点
2 public Node findMidNode(Node head) {
3
4 if (head == null) {
5 return null;
6 }
7
8 Node first = head;
9 Node second = head;
10 //每次移动时,让second结点移动两位,first结点移动一位
11 while (second != null && second.next != null) {
12 first = first.next;
13 second = second.next.next;
14 }
15
16 //直到second结点移动到null时,此时first指针指向的位置就是中间结点的位置
17 return first;
18 }
上方代码中,当n为偶数时,得到的中间结点是第n/2 + 1个结点。比如链表有6个节点时,得到的是第4个节点。
5、合并两个有序的单链表,合并之后的链表依然有序:
这道题经常被各公司考察。
例如:
链表1:
1->2->3->4
链表2:
2->3->4->5
合并后:
1->2->2->3->3->4->4->5
解题思路:
挨着比较链表1和链表2。
这个类似于归并排序。尤其要注意两个链表都为空、和其中一个为空的情况。只需要O (1) 的空间。时间复杂度为O (max(len1,len2))
代码实现:
1 //两个参数代表的是两个链表的头结点
2 public Node mergeLinkList(Node head1, Node head2) {
3
4 if (head1 == null && head2 == null) { //如果两个链表都为空
5 return null;
6 }
7 if (head1 == null) {
8 return head2;
9 }
10 if (head2 == null) {
11 return head1;
12 }
13
14 Node head; //新链表的头结点
15 Node current; //current结点指向新链表
16
17 // 一开始,我们让current结点指向head1和head2中较小的数据,得到head结点
18 if (head1.data < head2.data) {
19 head = head1;
20 current = head1;
21 head1 = head1.next;
22 } else {
23 head = head2;
24 current = head2;
25 head2 = head2.next;
26 }
27
28 while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
29 if (head1.data < head2.data) {
30 current.next = head1; //新链表中,current指针的下一个结点对应较小的那个数据
31 current = current.next; //current指针下移
32 head1 = head1.next;
33 } else {
34 current.next = head2;
35 current = current.next;
36 head2 = head2.next;
37 }
38 }
39
40 //合并剩余的元素
41 if (head1 != null) { //说明链表2遍历完了,是空的
42 current.next = head1;
43 }
44
45 if (head2 != null) { //说明链表1遍历完了,是空的
46 current.next = head2;
47 }
48
49 return head;
50 }
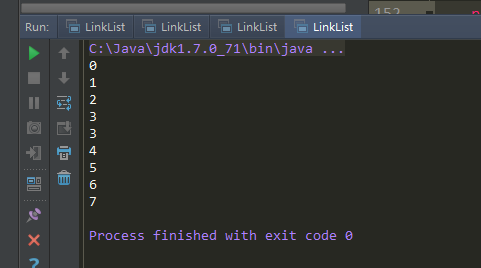
代码测试:
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 LinkList list1 = new LinkList();
3 LinkList list2 = new LinkList();
4 //向LinkList中添加数据
5 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
6 list1.add(i);
7 }
8
9 for (int i = 3; i < 8; i++) {
10 list2.add(i);
11 }
12
13 LinkList list3 = new LinkList();
14 list3.head = list3.mergeLinkList(list1.head, list2.head); //将list1和list2合并,存放到list3中
15
16 list3.print(list3.head);// 从head节点开始遍历输出
17 }
上方代码中用到的add方法和print方法和第1小节中是一致的。
运行效果:
注:《剑指offer》中是用递归解决的,感觉有点难理解。
6、单链表的反转:【出现频率最高】
例如链表:
1->2->3->4
反转之后:
4->3->2->1
思路:
从头到尾遍历原链表,每遍历一个结点,将其摘下放在新链表的最前端。注意链表为空和只有一个结点的情况。时间复杂度为O(n)
方法1:(遍历)
1 //方法:链表的反转
2 public Node reverseList(Node head) {
3
4 //如果链表为空或者只有一个节点,无需反转,直接返回原链表的头结点
5 if (head == null || head.next == null) {
6 return head;
7 }
8
9 Node current = head;
10 Node next = null; //定义当前结点的下一个结点
11 Node reverseHead = null; //反转后新链表的表头
12
13 while (current != null) {
14 next = current.next; //暂时保存住当前结点的下一个结点,因为下一次要用
15
16 current.next = reverseHead; //将current的下一个结点指向新链表的头结点
17 reverseHead = current;
18
19 current = next; // 操作结束后,current节点后移
20 }
21
22 return reverseHead;
23 }
上方代码中,核心代码是第16、17行。
方法2:(递归)
这个方法有点难,先不讲了。
7、从尾到头打印单链表:
对于这种颠倒顺序的问题,我们应该就会想到栈,后进先出。所以,这一题要么自己使用栈,要么让系统使用栈,也就是递归。注意链表为空的情况。时间复杂度为O(n)
注:不要想着先将单链表反转,然后遍历输出,这样会破坏链表的结构,不建议。
方法1:(自己新建一个栈)
1 //方法:从尾到头打印单链表
2 public void reversePrint(Node head) {
3
4 if (head == null) {
5 return;
6 }
7
8 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); //新建一个栈
9 Node current = head;
10
11 //将链表的所有结点压栈
12 while (current != null) {-
13 stack.push(current); //将当前结点压栈
14 current = current.next;
15 }
16
17 //将栈中的结点打印输出即可
18 while (stack.size() > 0) {
19 System.out.println(stack.pop().data); //出栈操作
20 }
21 }
方法2:(使用系统的栈:递归,代码优雅简洁)
1 public void reversePrint(Node head) {
2
3
4 if (head == null) {
5 return;
6 }
7 reversePrint(head.next);
8 System.out.println(head.data);
9 }
总结:方法2是基于递归实现的,戴安看起来简洁优雅,但有个问题:当链表很长的时候,就会导致方法调用的层级很深,有可能造成栈溢出。而方法1的显式用栈,是基于循环实现的,代码的鲁棒性要更好一些。
8、判断单链表是否有环:
这里也是用到两个指针,如果一个链表有环,那么用一个指针去遍历,是永远走不到头的。
因此,我们用两个指针去遍历:first指针每次走一步,second指针每次走两步,如果first指针和second指针相遇,说明有环。时间复杂度为O (n)。
方法:
1 //方法:判断单链表是否有环
2 public boolean hasCycle(Node head) {
3
4 if (head == null) {
5 return false;
6 }
7
8 Node first = head;
9 Node second = head;
10
11 while (second != null) {
12 first = first.next; //first指针走一步
13 second = second.next.next; second指针走两步
14
15 if (first == second) { //一旦两个指针相遇,说明链表是有环的
16 return true;
17 }
18 }
19
20 return false;
21 }
完整版代码:(包含测试部分)
这里,我们还需要加一个重载的add(Node node)方法,在创建单向循环链表时要用到。
LinkList.java:
1 public class LinkList {
2 public Node head;
3 public Node current;
4
5 //方法:向链表中添加数据
6 public void add(int data) {
7 //判断链表为空的时候
8 if (head == null) {//如果头结点为空,说明这个链表还没有创建,那就把新的结点赋给头结点
9 head = new Node(data);
10 current = head;
11 } else {
12 //创建新的结点,放在当前节点的后面(把新的结点合链表进行关联)
13 current.next = new Node(data);
14 //把链表的当前索引向后移动一位
15 current = current.next;
16 }
17 }
18
19
20 //方法重载:向链表中添加结点
21 public void add(Node node) {
22 if (node == null) {
23 return;
24 }
25
26 if (head == null) {
27 head = node;
28 current = head;
29 } else {
30 current.next = node;
31 current = current.next;
32 }
33 }
34
35
36 //方法:遍历链表(打印输出链表。方法的参数表示从节点node开始进行遍历
37 public void print(Node node) {
38 if (node == null) {
39 return;
40 }
41
42 current = node;
43 while (current != null) {
44 System.out.println(current.data);
45 current = current.next;
46 }
47 }
48
49 //方法:检测单链表是否有环
50 public boolean hasCycle(Node head) {
51
52 if (head == null) {
53 return false;
54 }
55
56 Node first = head;
57 Node second = head;
58
59 while (second != null) {
60 first = first.next; //first指针走一步
61 second = second.next.next; //second指针走两步
62
63 if (first == second) { //一旦两个指针相遇,说明链表是有环的
64 return true;
65 }
66 }
67
68 return false;
69 }
70
71 class Node {
72 //注:此处的两个成员变量权限不能为private,因为private的权限是仅对本类访问。
73 int data; //数据域
74 Node next;//指针域
75
76 public Node(int data) {
77 this.data = data;
78 }
79 }
80
81 public static void main(String[] args) {
82 LinkList list = new LinkList();
83 //向LinkList中添加数据
84 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
85 list.add(i);
86 }
87
88 list.add(list.head); //将头结点添加到链表当中,于是,单链表就有环了。备注:此时得到的这个环的结构,是下面的第8小节中图1的那种结构。
89
90 System.out.println(list.hasCycle(list.head));
91 }
92 }
检测单链表是否有环的代码是第50行。
88行:我们将头结点继续往链表中添加,此时单链表就环了。最终运行效果为true。
如果删掉了88行代码,此时单链表没有环,运行效果为false。
9、取出有环链表中,环的长度:
我们平时碰到的有环链表是下面的这种:(图1)
上图中环的长度是4。
但有可能也是下面的这种:(图2)
此时,上图中环的长度就是3了。
那怎么求出环的长度呢?
思路:
这里面,我们需要先利用上面的第7小节中的hasCycle方法(判断链表是否有环的那个方法),这个方法的返回值是boolean型,但是现在要把这个方法稍做修改,让其返回值为相遇的那个结点。然后,我们拿到这个相遇的结点就好办了,这个结点肯定是在环里嘛,我们可以让这个结点对应的指针一直往下走,直到它回到原点,就可以算出环的长度了。
方法:
1 //方法:判断单链表是否有环。返回的结点是相遇的那个结点
2 public Node hasCycle(Node head) {
3
4 if (head == null) {
5 return null;
6 }
7
8 Node first = head;
9 Node second = head;
10
11 while (second != null) {
12 first = first.next;
13 second = second.next.next;
14
15 if (first == second) { //一旦两个指针相遇,说明链表是有环的
16 return first; //将相遇的那个结点进行返回
17 }
18 }
19
20 return null;
21 }
22
23 //方法:有环链表中,获取环的长度。参数node代表的是相遇的那个结点
24 public int getCycleLength(Node node) {
25
26 if (head == null) {
27 return 0;
28 }
29
30 Node current = node;
31 int length = 0;
32
33 while (current != null) {
34 current = current.next;
35 length++;
36 if (current == node) { //当current结点走到原点的时候
37 return length;
38 }
39 }
40
41 return length;
42 }
完整版代码:(包含测试部分)
1 public class LinkList {
2 public Node head;
3 public Node current;
4
5 public int size;
6
7 //方法:向链表中添加数据
8 public void add(int data) {
9 //判断链表为空的时候
10 if (head == null) {//如果头结点为空,说明这个链表还没有创建,那就把新的结点赋给头结点
11 head = new Node(data);
12 current = head;
13 } else {
14 //创建新的结点,放在当前节点的后面(把新的结点合链表进行关联)
15 current.next = new Node(data);
16 //把链表的当前索引向后移动一位
17 current = current.next; //此步操作完成之后,current结点指向新添加的那个结点
18 }
19 }
20
21
22 //方法重载:向链表中添加结点
23 public void add(Node node) {
24 if (node == null) {
25 return;
26 }
27 if (head == null) {
28 head = node;
29 current = head;
30 } else {
31 current.next = node;
32 current = current.next;
33 }
34 }
35
36
37 //方法:遍历链表(打印输出链表。方法的参数表示从节点node开始进行遍历
38 public void print(Node node) {
39 if (node == null) {
40 return;
41 }
42
43 current = node;
44 while (current != null) {
45 System.out.println(current.data);
46 current = current.next;
47 }
48 }
49
50 //方法:判断单链表是否有环。返回的结点是相遇的那个结点
51 public Node hasCycle(Node head) {
52
53 if (head == null) {
54 return null;
55 }
56
57 Node first = head;
58 Node second = head;
59
60 while (second != null) {
61 first = first.next;
62 second = second.next.next;
63
64 if (first == second) { //一旦两个指针相遇,说明链表是有环的
65 return first; //将相遇的那个结点进行返回
66 }
67 }
68
69 return null;
70 }
71
72 //方法:有环链表中,获取环的长度。参数node代表的是相遇的那个结点
73 public int getCycleLength(Node node) {
74
75 if (head == null) {
76 return 0;
77 }
78
79 Node current = node;
80 int length = 0;
81
82 while (current != null) {
83 current = current.next;
84 length++;
85 if (current == node) { //当current结点走到原点的时候
86 return length;
87 }
88 }
89
90 return length;
91 }
92
93 class Node {
94 //注:此处的两个成员变量权限不能为private,因为private的权限是仅对本类访问。
95 int data; //数据域
96 Node next;//指针域
97
98 public Node(int data) {
99 this.data = data;
100 }
101 }
102
103
104 public static void main(String[] args) {
105 LinkList list1 = new LinkList();
106
107 Node second = null; //把第二个结点记下来
108
109 //向LinkList中添加数据
110 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
111 list1.add(i);
112
113 if (i == 1) {
114 second = list1.current; //把第二个结点记下来
115 }
116 }
117
118 list1.add(second); //将尾结点指向链表的第二个结点,于是单链表就有环了,备注:此时得到的环的结构,是本节中图2的那种结构
119 Node current = list1.hasCycle(list1.head); //获取相遇的那个结点
120
121 System.out.println("环的长度为" + list1.getCycleLength(current));
122 }
123
124 }
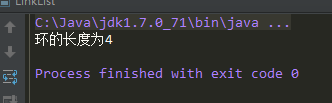
运行效果:
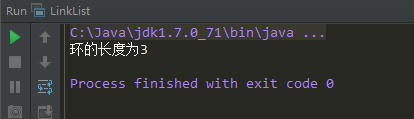
如果将上面的104至122行的测试代码改成下面这样的:(即:将图2中的结构改成图1中的结构)
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 LinkList list1 = new LinkList();
3 //向LinkList中添加数据
4 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
5 list1.add(i);
6 }
7
8 list1.add(list1.head); //将头结点添加到链表当中(将尾结点指向头结点),于是,单链表就有环了。备注:此时得到的这个环的结构,是本节中图1的那种结构。
9
10 Node current = list1.hasCycle(list1.head);
11
12 System.out.println("环的长度为" + list1.getCycleLength(current));
13 }
运行结果:
如果把上面的代码中的第8行删掉,那么这个链表就没有环了,于是运行的结果为0。
10、单链表中,取出环的起始点:
我们平时碰到的有环链表是下面的这种:(图1)
上图中环的起始点1。
但有可能也是下面的这种:(图2)
此时,上图中环的起始点是2。
方法1:
这里我们需要利用到上面第8小节的取出环的长度的方法getCycleLength,用这个方法来获取环的长度length。拿到环的长度length之后,需要用到两个指针变量first和second,先让second指针走length步;然后让first指针和second指针同时各走一步,当两个指针相遇时,相遇时的结点就是环的起始点。
注:为了找到环的起始点,我们需要先获取环的长度,而为了获取环的长度,我们需要先判断是否有环。所以这里面其实是用到了三个方法。
代码实现:
方法1的核心代码:
1 //方法:获取环的起始点。参数length表示环的长度
2 public Node getCycleStart(Node head, int cycleLength) {
3
4 if (head == null) {
5 return null;
6 }
7
8 Node first = head;
9 Node second = head;
10 //先让second指针走length步
11 for (int i = 0; i < cycleLength; i++) {
12 second = second.next;
13 }
14
15 //然后让first指针和second指针同时各走一步
16 while (first != null && second != null) {
17 first = first.next;
18 second = second.next;
19
20 if (first == second) { //如果两个指针相遇了,说明这个结点就是环的起始点
21 return first;
22 }
23 }
24
25 return null;
26 }
完整版代码:(含测试部分)
1 public class LinkList {
2 public Node head;
3 public Node current;
4
5 public int size;
6
7 //方法:向链表中添加数据
8 public void add(int data) {
9 //判断链表为空的时候
10 if (head == null) {//如果头结点为空,说明这个链表还没有创建,那就把新的结点赋给头结点
11 head = new Node(data);
12 current = head;
13 } else {
14 //创建新的结点,放在当前节点的后面(把新的结点合链表进行关联)
15 current.next = new Node(data);
16 //把链表的当前索引向后移动一位
17 current = current.next; //此步操作完成之后,current结点指向新添加的那个结点
18 }
19 }
20
21
22 //方法重载:向链表中添加结点
23 public void add(Node node) {
24 if (node == null) {
25 return;
26 }
27 if (head == null) {
28 head = node;
29 current = head;
30 } else {
31 current.next = node;
32 current = current.next;
33 }
34 }
35
36
37 //方法:遍历链表(打印输出链表。方法的参数表示从节点node开始进行遍历
38 public void print(Node node) {
39 if (node == null) {
40 return;
41 }
42
43 current = node;
44 while (current != null) {
45 System.out.println(current.data);
46 current = current.next;
47 }
48 }
49
50
51 //方法:判断单链表是否有环。返回的结点是相遇的那个结点
52 public Node hasCycle(Node head) {
53
54 if (head == null) {
55 return null;
56 }
57
58 Node first = head;
59 Node second = head;
60
61 while (second != null) {
62 first = first.next;
63 second = second.next.next;
64
65 if (first == second) { //一旦两个指针相遇,说明链表是有环的
66 return first; //将相遇的那个结点进行返回
67 }
68 }
69
70 return null;
71 }
72 //方法:有环链表中,获取环的长度。参数node代表的是相遇的那个结点
73 public int getCycleLength(Node node) {
74
75 if (head == null) {
76 return 0;
77 }
78
79 Node current = node;
80 int length = 0;
81
82 while (current != null) {
83 current = current.next;
84 length++;
85 if (current == node) { //当current结点走到原点的时候
86 return length;
87 }
88 }
89
90 return length;
91 }
92
93 //方法:获取环的起始点。参数length表示环的长度
94 public Node getCycleStart(Node head, int cycleLength) {
95
96 if (head == null) {
97 return null;
98 }
99
100 Node first = head;
101 Node second = head;
102 //先让second指针走length步
103 for (int i = 0; i < cycleLength; i++) {
104 second = second.next;
105 }
106
107 //然后让first指针和second指针同时各走一步
108 while (first != null && second != null) {
109 first = first.next;
110 second = second.next;
111
112 if (first == second) { //如果两个指针相遇了,说明这个结点就是环的起始点
113 return first;
114 }
115 }
116
117 return null;
118 }
119
120 class Node {
121 //注:此处的两个成员变量权限不能为private,因为private的权限是仅对本类访问。
122 int data; //数据域
123 Node next;//指针域
124
125 public Node(int data) {
126 this.data = data;
127 }
128 }
129
130
131 public static void main(String[] args) {
132 LinkList list1 = new LinkList();
133
134 Node second = null; //把第二个结点记下来
135
136 //向LinkList中添加数据
137 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
138 list1.add(i);
139
140 if (i == 1) {
141 second = list1.current; //把第二个结点记下来
142 }
143 }
144
145 list1.add(second); //将尾结点指向链表的第二个结点,于是单链表就有环了,备注:此时得到的环的结构,是本节中图2的那种结构
146 Node current = list1.hasCycle(list1.head); //获取相遇的那个结点
147
148 int length = list1.getCycleLength(current); //获取环的长度
149
150 System.out.println("环的起始点是" + list1.getCycleStart(list1.head, length).data);
151
152 }
153
154 }
11、判断两个单链表相交的第一个交点:
《剑指offer》P193,5.3,面试题37就有这道题。
面试时,很多人碰到这道题的第一反应是:在第一个链表上顺序遍历每个结点,每遍历到一个结点的时候,在第二个链表上顺序遍历每个结点。如果在第二个链表上有一个结点和第一个链表上的结点一样,说明两个链表在这个结点上重合。显然该方法的时间复杂度为O(len1 * len2)。
方法1:采用栈的思路
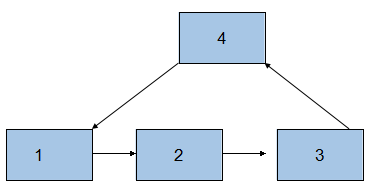
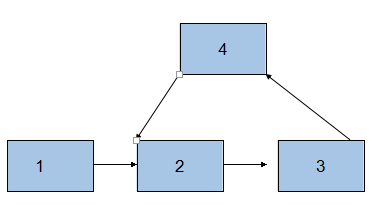
我们可以看出两个有公共结点而部分重合的链表,拓扑形状看起来像一个Y,而不可能是X型。 如下图所示:
如上图所示,如果单链表有公共结点,那么最后一个结点(结点7)一定是一样的,而且是从中间的某一个结点(结点6)开始,后续的结点都是一样的。
现在的问题是,在单链表中,我们只能从头结点开始顺序遍历,最后才能到达尾结点。最后到达的尾节点却要先被比较,这听起来是不是像“先进后出”?于是我们就能想到利用栈的特点来解决这个问题:分别把两个链表的结点放入两个栈中,这样两个链表的尾结点就位于两个栈的栈顶,接下来比较下一个栈顶,直到找到最后一个相同的结点。
这种思路中,我们需要利用两个辅助栈,空间复杂度是O(len1+len2),时间复杂度是O(len1+len2)。和一开始的蛮力法相比,时间效率得到了提高,相当于是利用空间消耗换取时间效率。
那么,有没有更好的方法呢?接下来要讲。
方法2:判断两个链表相交的第一个结点:用到快慢指针,推荐(更优解)
我们在上面的方法2中,之所以用到栈,是因为我们想同时遍历到达两个链表的尾结点。其实为解决这个问题我们还有一个更简单的办法:首先遍历两个链表得到它们的长度。在第二次遍历的时候,在较长的链表上走 |len1-len2| 步,接着再同时在两个链表上遍历,找到的第一个相同的结点就是它们的第一个交点。
这种思路的时间复杂度也是O(len1+len2),但是我们不再需要辅助栈,因此提高了空间效率。当面试官肯定了我们的最后一种思路的时候,就可以动手写代码了。
核心代码:
1 //方法:求两个单链表相交的第一个交点
2 public Node getFirstCommonNode(Node head1, Node head2) {
3 if (head1 == null || head == null) {
4 return null;
5 }
6
7 int length1 = getLength(head1);
8 int length2 = getLength(head2);
9 int lengthDif = 0; //两个链表长度的差值
10
11 Node longHead;
12 Node shortHead;
13
14 //找出较长的那个链表
15 if (length1 > length2) {
16 longHead = head1;
17 shortHead = head2;
18 lengthDif = length1 - length2;
19 } else {
20 longHead = head2;
21 shortHead = head1;
22 lengthDif = length2 - length1;
23 }
24
25 //将较长的那个链表的指针向前走length个距离
26 for (int i = 0; i < lengthDif; i++) {
27 longHead = longHead.next;
28 }
29
30 //将两个链表的指针同时向前移动
31 while (longHead != null && shortHead != null) {
32 if (longHead == shortHead) { //第一个相同的结点就是相交的第一个结点
33 return longHead;
34 }
35 longHead = longHead.next;
36 shortHead = shortHead.next;
37 }
38
39 return null;
40 }
41
42
43 //方法:获取单链表的长度
44 public int getLength(Node head) {
45 if (head == null) {
46 return 0;
47 }
48
49 int length = 0;
50 Node current = head;
51 while (current != null) {
52
53 length++;
54 current = current.next;
55 }
56
57 return length;

![d28e487b-e5c1-4f4b-99a0-7c5d3d0e7b20[1] d28e487b-e5c1-4f4b-99a0-7c5d3d0e7b20[1]](https://images2015.cnblogs.com/blog/641601/201509/641601-20150904234341279-1087249137.png)
![062fff31-70cc-45fe-aef8-80ed6d51b666[1] 062fff31-70cc-45fe-aef8-80ed6d51b666[1]](https://images2015.cnblogs.com/blog/641601/201509/641601-20150904234342076-1178947722.png)