译注:原文英语不地道,翻译也就比较乱,后面几个小节内容干脆省略了。
理解 Spring Security 架构
这篇指南是对 Spring Security 框架的初阶讲解,有对该框架设计思想的解读以及基础模块的介绍。即便仅覆盖了应用安全领域非常基础的内容,应该已经能帮开发者理清 Spring Security 框架使用过程中的一些混乱体验了。
本指南不能作为一份完整手册,仅能解决最基础的问题,但是对初学者及专家都有用。文中会经常引用 Spring Boot,因为它针对安全应用提供了一些默认行为,而这些默认行为有助于理解如何适配上述架构。
注:所有这些原理也能很好的应用于未使用 Spring Boot 的应用程序。
认证与访问控制(Authentication and Access Control)
应用程序的安全可以归结为两个独立的问题:认证(你是谁?)及授权(你能干嘛?)。人们有时会用”访问控制(access control)“的说法来代替”授权“,这会导致概念混乱,但是更有助于理解,因为 "authorization" 实在是在其它场合被过度使用了。Spring Security 框架设计了一个架构用于分离认证和授权,并且针对二者均提供了相应策略及扩展点。
认证(Authentication)
认证的主要策略接口是 AuthenticationManager,仅需实现一个方法:
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
在 AuthenticationManager 的实现类方法 authenticate() 里可以执行三件事:
- 返回
Authentication(即authenticated=true),若被验证为有效身份 - 抛出
AuthenticationException异常,若确定输入数据为无效身份 - 返回
null,若无法作出判定
AuthenticationException 是一种运行时异常,通常由应用程序统一按需捕捉处理,即不需要在用户的业务逻辑中进行捕捉和处理,如在有Web UI的场景,就自动渲染一个提示认证失败的页面,在纯后端HTTP服务场景时可能就只响应一个401状态码。
AuthenticationManager 最常用的实现类是 ProviderManager,它代理了一系列 AuthenticationProvider 实例。
AuthenticationProvider 有点像 AuthenticationManager,但它额外还有一个方法,允许调用者查询其是否支持指定的 Authentication 类型:
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
supports() 方法中的 Class<?> 参数其实应该是 Class<? extends Authentication>。在同一个应用中,通过 AuthenticationProviders 链式委托的方式,ProviderManager 可以支持多种不同的认证机制。如果 ProviderManager 识别不了某个特定的 Authentication 实例类型,就跳过。
ProviderManager 可以有一个父级容器,用来判断是否所有 provider 返回 null,如该父级容器不可用,null 的 Authentication 会导致 AuthenticationException 异常。
有时,应用中会对受保护资源进行逻辑分组,比如所有Web资源匹配一个路径模式如 /api/{all}),且每组资源可以有独立的 AuthenticationManager。 通常,它们是 ProviderManager,且共享同一个 父级容器。这种父级容器即为一种全局资源,作为所有 provider 的备选方案。
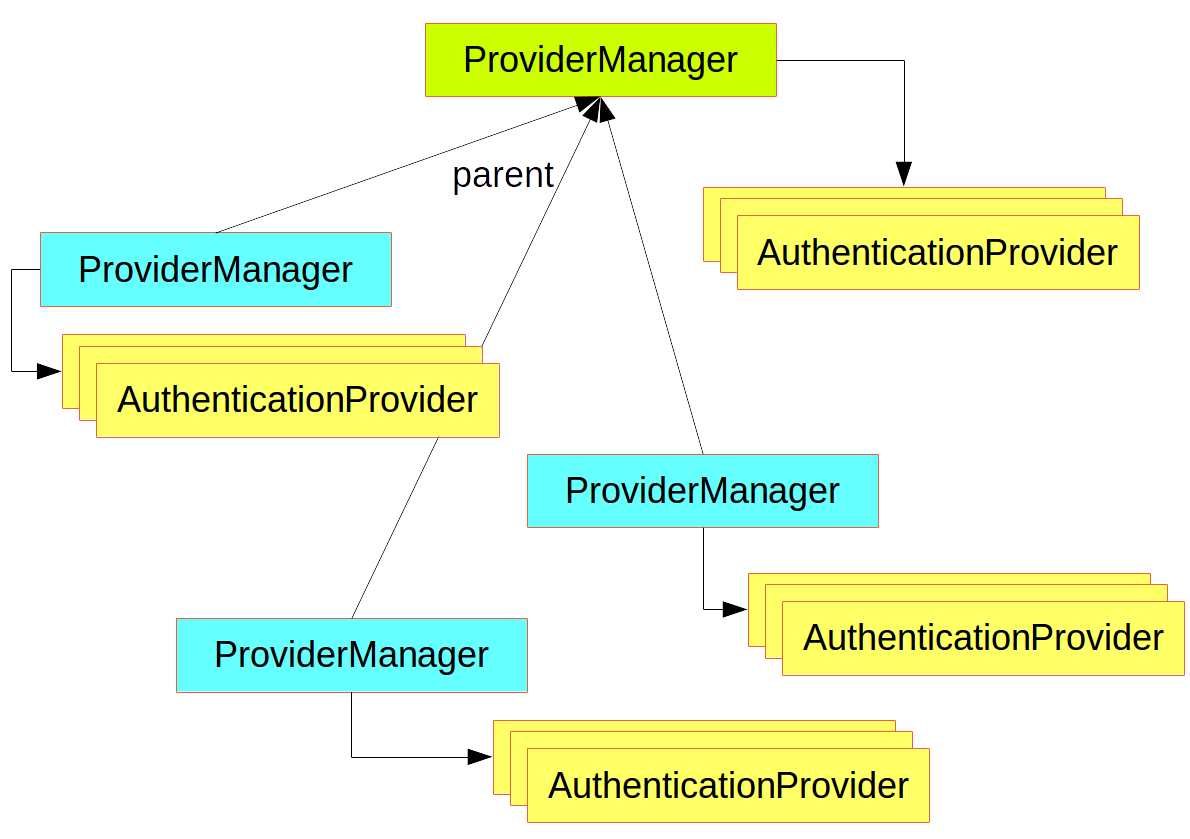
自定义认证管理器
Spring Security 框架提供了一些配置助手,便于快速配置一些常规认证管理器特性。其中最常用的助手为 AuthenticationManagerBuilder:设置内存、JDBC或LDAP等数据源的用户详情,或用于添加自定义 UserDetailsService。下例展示了配置全局(父级)AuthenticationManager 的应用:
@Configuration
public class ApplicationSecurity extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
... // web stuff here
@Autowired
public void initialize(AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder, DataSource dataSource) {
builder.jdbcAuthentication().dataSource(dataSource).withUser("dave")
.password("secret").roles("USER");
}
}
虽然仅在Web应用的场景做了展示,但 AuthenticationManagerBuilder 的用处非常广泛。
注意:AuthenticationManagerBuilder 是通过 @Autowired 的方式注入到 @Bean 的方法中的 - 这种方式构造了全局(父级)AuthenticationManager。对照另一种情况看看:
@Configuration
public class ApplicationSecurity extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
... // web stuff here
@Override
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder) {
builder.jdbcAuthentication().dataSource(dataSource).withUser("dave")
.password("secret").roles("USER");
}
}
若我们用了对方法 @Override 的方式配置, AuthenticationManagerBuilder 就会仅构造出一个局部认证管理器 - 作为全局认证管理器的子级。在 Spring Boot 应用中, 可以将全局认证管理器 @Autowired 到另一个 bean 中,但无法对局部认证管理器做同样操作,除非你自己显式将其暴露访问权限。
除非你通过提供了 自定义 AuthenticationManager bean 的方式提前对之做了清空处理,Spring Boot 提供了一个默认的全局 AuthenticationManager (仅针对一个用户),并且其足够安全,无需太多关注。若要构建AuthenticationManager配置,通常只需对受保护的相关资源做局部处理即可。
授权/访问控制(Authorization / Access Control)
授权其核心策略为 AccessDecisionManager。框架提供了三套相应实现形式,且均委托给 AccessDecisionVoter 实例链,有点像 ProviderManager 委托给 AuthenticationProviders 的情形。
一个 AccessDecisionVoter 要考量一个 Authentication 及一个安全对象 Object。Authentication代表一个用户身份,Object 被修饰为 ConfigAttributes。
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
int vote(Authentication authentication, S object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes);
在 AccessDecisionManager 及 AccessDecisionVoter 的签名中 Object 式完全通用的类型。Object 代表用户可能要访问的任意Web资源或Java类方法。ConfigAttributes 也是完全任意,代表安全对象Object的修饰名-决定访问该对象的需要的许可级别。
ConfigAttribute 为接口,它仅有一个方法,返回 String,这些字符串以同样的方式编码,表达资源拥有者的意图,表达出允许访问它的规则。典型的 ConfigAttribute 就是时用户角色名,如 ROLE_ADMIN 或 ROLE_AUDIT,且通常有些特定格式(如 ROLE_ 前缀)或表示规则。
多数人会使用默认的 AccessDecisionManager - 平权式(若任意voter返回肯定,访问即意味着被同意)。
ConfigAttributes 通常使用 SpEL (Spring Expression Language) 表达式,例如:isFullyAuthenticated() && hasRole('user'),这种机制由 AccessDecisionVoter 提供支持,它可以处理表达式并为之创建上下文语境。要扩展表达式的处理范围,需要自定义实现 SecurityExpressionRoot 或者 SecurityExpressionHandler。
[[web-security]]
Web 安全
Spring Security 框架在Web层(包括UI及HTTP后端)是基于 Servlet 的 Filters 实现的,所以先看看 Filters 会有帮助。下图展示了单个HTTP请求下的典型处理层级。
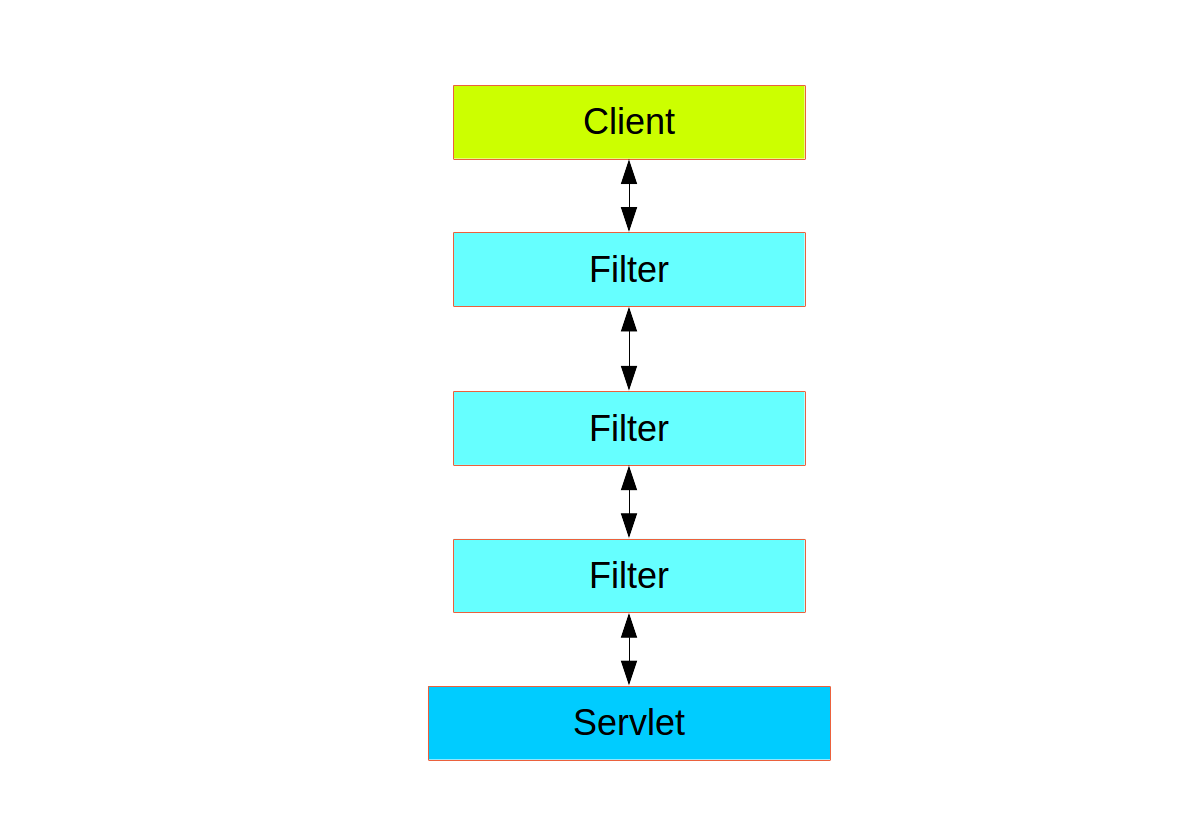
客户端发送请求到应用,容器根据请求URI的路径部分,来决定对应的的filter和servlet,多数情况下,一个servlet 仅处理单个请求,但是filter却是一连串的,因此这些filter需要进行排序。实际上,当filter想自行处理该请求时,会中断余下filter链的执行。 filter 也可以修改下游 filter 及 servle t中用到的请求或响应。filter链的排序非常重要, Spring Boot 通过两种机制进行管理:
Filter类型的@Beans:用@Order注解或实现Ordered接口;- 作为
FilterRegistrationBean的一部分,其API中本身带有排序
一些现成的 filter 定义了内置的常量,帮助标记彼此的相对排序,如 Spring Session 框架中的 SessionRepositoryFilter 其 DEFAULT_ORDER 值为 Integer.MIN_VALUE + 50,这个值告知我们它处于链的前部,但它不会阻止其它 filter 排到它前面。
Spring Security 框架仅作为整个Filter链中的单独一个Filter存在,它的表现形式为 FilterChainProxy。在 Spring Boot 应用中, 安全 filter 作为一个 @Bean 存在于 ApplicationContext 中,且默认被装入以便它被应用到每个请求。它的装入位置被定义为 SecurityProperties.DEFAULT_FILTER_ORDER,转而通过 FilterRegistrationBean.REQUEST_WRAPPER_FILTER_MAX_ORDER 常量(这个是Spring Boot应用程序中的filter可以指定的最大排序值)确定最终值。虽然从容器的角度, Spring Security 框架存在一个独立的 filter 中,但是在内部,还有其它额外的 filter - 每个都起到一些特殊的作用。下图展示了它们的关系:
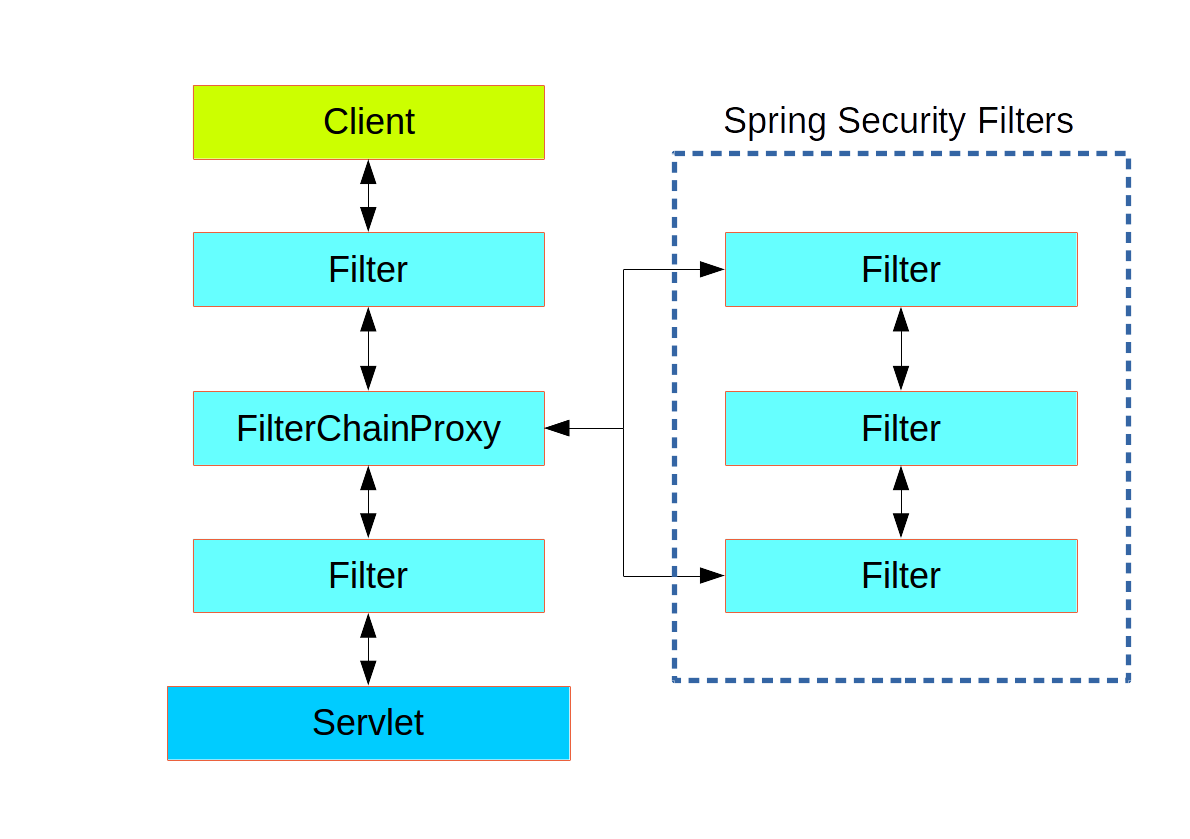
其实,在安全filter中,间接还有一层:容器中它常被装入为 DelegatingFilterProxy, 它是不必成为 Spring @Bean的。 该代理对象委托给 FilterChainProxy - 它倒总是 @Bean 形式, 通常有个固定的名字 springSecurityFilterChain。 FilterChainProxy 包含了所有的安全逻辑,内部以filter 链的形式排列。所有的 filter 具有同样的 API - 实现 Servlet 规范中的 Filter 接口,且均有中断余下链执行的机会。
在同一顶级 FilterChainProxy中,由 Spring Security 框架管理的 filter 链可以有很多个,且对于容器来说是未知的。 Spring Security 框架中的 filter 包含了一个 filter 链的列表,并将请求调度给匹配的第一个链。这个调度过程中,最重要的特性是:仅一个链会被调度来处理请求。如下图:

不带自定义安全配置的情况下,一个Spring Boot 应用,有N个(N通常等于6)filter链。第一个链(N-1)一般用来忽略静态资源如/css/{all} 、 /images/{all},以及错误视图 /error。最后的链匹配模糊匹配路径 (/{all}) ,包含认证逻辑、授权、异常处理、会话处理、header信息写入;
创建及自定义过滤器链(Filter Chains)
Spring Boot 应用中,filter链的默认方案带有预定义的排序 SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER。这个是可以通过设置完全关闭的:security.basic.enabled=false,或者也可以保留,同时再定义其它更低排序值的规则-给WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 或
WebSecurityConfigurer 加上 @Bean 注解,并加上 @Order注解:
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER - 10)
public class ApplicationConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/match1/**")
...;
}
}
这个bean就让 Spring Security 添加了新的 filter 链,并排在默认方案之前。
很多应用需要对资源进行完全不同的访问规则定义,比如一个同时包含UI和后端API的应用,UI部分可能要支持基于cookie的认证,便于跳转到登录页,API部分则是基于Token的认证,当接收到未授权的请求时要返回401代码。这样,每套资源需要拥有自己的 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,有独立的排序,及自己的请求匹配规则。若匹配规则重叠,则最先设置排序的filter链优先生效。
匹配请求(Request Matching for Dispatch and Authorization)
安全相关的filter链具有一个请求匹配器,用于判定是否应用到某一个HTTP请求。一旦做出决策,要应用一个特定的filter链,其它链就不会被应用。尽管如此,在filter链里面,你可以拥有更多细致的授权控制,这一点可以在 HttpSecurity 配置器中通过设置额外的匹配器来实现:
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER - 10)
public class ApplicationConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/match1/**")
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/match1/user").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/match1/spam").hasRole("SPAM")
.anyRequest().isAuthenticated();
}
}
最容易犯的错误是,在配置Spring Security框架时,这些匹配器是应用到不同的过程上的:一个是对整个filter链的,另一个仅针对访问规则生效。
组合 Actuator 与 Application Security 规则
略.......
@Configuration
@Order(ManagementServerProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER + 1)
public class ApplicationConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/foo/**")
...;
}
}
方法的安全性
略......
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SampleSecureApplication {
}
@Service
public class MyService {
@Secured("ROLE_USER")
public String secure() {
return "Hello Security";
}
}
处理有线程的情况
略......
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
assert(authentication.isAuthenticated);
@RequestMapping("/foo")
public String foo(@AuthenticationPrincipal User user) {
... // do stuff with user
}
@RequestMapping("/foo")
public String foo(Principal principal) {
Authentication authentication = (Authentication) principal;
User = (User) authentication.getPrincipal();
... // do stuff with user
}
处理异步方法的安全问题
略......
@Configuration
public class ApplicationConfiguration extends AsyncConfigurerSupport {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
return new DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5));
}
}
原文:https://spring.io/guides/topicals/spring-security-architecture/