一、定义
提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素, 而又无须暴露该对象的内部表示;
主要解决:不同的方式来遍历整个整合对象。
何时使用:遍历一个聚合对象。
如何解决:把在元素之间游走的责任交给迭代器,而不是聚合对象。
二、结构
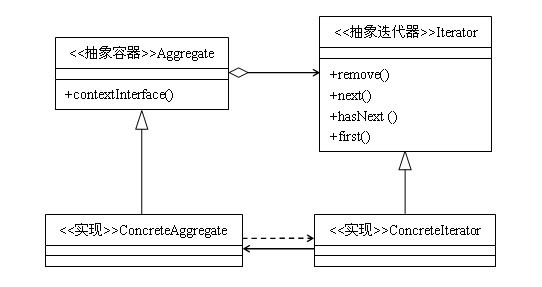
组成:
抽象容器:一般是一个接口,提供一个iterator()方法,例如java中的Collection接口,List接口,Set接口等。
具体容器:就是抽象容器的具体实现类,比如List接口的有序列表实现ArrayList,List接口的链表实现LinkList,Set接口的哈希列表的实现HashSet等。
抽象迭代器:定义遍历元素所需要的方法,一般来说会有这么三个方法:取得第一个元素的方法first(),取得下一个元素的方法next(),判断是否遍历结束的方法hasNext(),移出当前对象的方法remove(),
迭代器实现:实现迭代器接口中定义的方法,完成集合的迭代。
三、适用场景
1、访问一个聚合对象的内容而无须暴露它的内部表示。
2、需要为聚合对象提供多种遍历方式。
3、为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口。
四、优缺点
优点:
1、它支持以不同的方式遍历一个聚合对象。
2、迭代器简化了聚合类。
3、在同一个聚合上可以有多个遍历。
4、在迭代器模式中,增加新的聚合类和迭代器类都很方便,无须修改原有代码。
5、系统需要访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示。
缺点:
由于迭代器模式将存储数据和遍历数据的职责分离,增加新的聚合类需要对应增加新的迭代器类,类的个数成对增加,这在一定程度上增加了系统的复杂性。
迭代器模式在遍历的同时更改迭代器所在的集合结构会导致出现异常。所以使用foreach语句只能在对集合进行遍历,不能在遍历的同时更改集合中的元素。
五、实现
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace DesignPatterns.Iterator { // 抽象聚合类 public interface IListCollection { Iterator GetIterator(); } // 迭代器抽象类 public interface Iterator { bool MoveNext(); Object GetCurrent(); void Next(); void Reset(); } // 具体聚合类 public class ConcreteList : IListCollection { int[] collection; public ConcreteList() { collection = new int[] { 2, 4, 6, 8 }; } public Iterator GetIterator() { return new ConcreteIterator(this); } public int Length { get { return collection.Length; } } public int GetElement(int index) { return collection[index]; } } // 具体迭代器类 public class ConcreteIterator : Iterator { // 迭代器要集合对象进行遍历操作,自然就需要引用集合对象 private ConcreteList _list; private int _index; public ConcreteIterator(ConcreteList list) { _list = list; _index = 0; } public bool MoveNext() { if (_index < _list.Length) { return true; } return false; } public object GetCurrent() { return _list.GetElement(_index); } public void Reset() { _index = 0; } public void Next() { if (_index < _list.Length) { _index++; } } } // 客户端 class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Iterator iterator; IListCollection list = new ConcreteList(); iterator = list.GetIterator(); while (iterator.MoveNext()) { int i = (int)iterator.GetCurrent(); Console.WriteLine(i.ToString()); iterator.Next(); } Console.Read(); } } }
参考
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhili/p/IteratorPattern.html