单表查询
单表查询的语法:
SELECT 字段1,字段2... FROM 表名 WHERE 条件 GROUP BY field HAVING 筛选 ORDER BY field LIMIT 限制条数
关键字的执行优先级:
from > where > group by > having > select > distinct > order by > limit
简单查询
create table employee(
id int not null primary key auto_increment,
name char(16) not null,
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int(3) unsigned not null default 28,
hire_date date not null,
post char(50),
post_comment char(100),
salary double(15,2),
office int,
depart_id int
);
insert into employee(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values
('egon','male',18,'20170301','教导主任',7300.33,401,1), #以下是教学部
('alex','male',78,'20150302','teacher',1000000.31,401,1),
('wupeiqi','male',81,'20130305','teacher',8300,401,1),
('yuanhao','male',73,'20140701','teacher',3500,401,1),
('liwenzhou','male',28,'20121101','teacher',2100,401,1),
('jingliyang','female',18,'20110211','teacher',9000,401,1),
('jinxin','male',18,'19000301','teacher',30000,401,1),
('成龙','male',48,'20101111','teacher',10000,401,1),
('歪歪','female',48,'20150311','sale',3000.13,402,2),#以下是销售部门
('丫丫','female',38,'20101101','sale',2000.35,402,2),
('丁丁','female',18,'20110312','sale',1000.37,402,2),
('星星','female',18,'20160513','sale',3000.29,402,2),
('格格','female',28,'20170127','sale',4000.33,402,2),
('张野','male',28,'20160311','operation',10000.13,403,3), #以下是运营部门
('程咬金','male',18,'19970312','operation',20000,403,3),
('程咬银','female',18,'20130311','operation',19000,403,3),
('程咬铜','male',18,'20150411','operation',18000,403,3),
('程咬铁','female',18,'20140512','operation',17000,403,3)
;
#简单查询
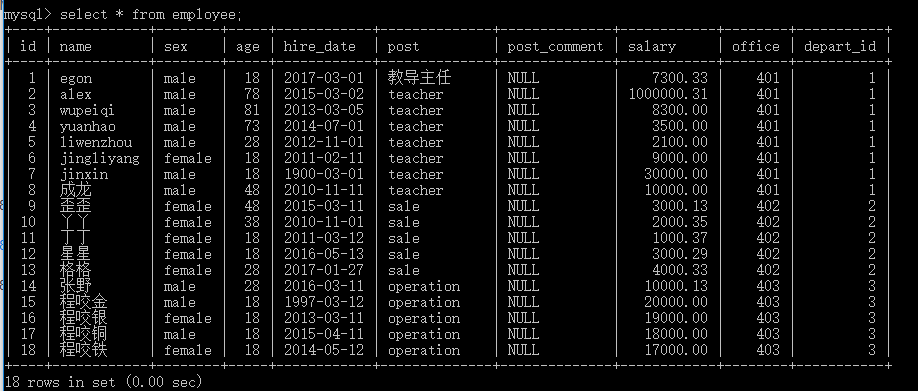
select id,name,sex,age,hire_date,post,post_comment,salary,office,depart_id from employee;
select name,salary from employee;
#避免重复DISTINCT
select distinct post FROM employee;
#通过四则运算查询
SELECT name, salary*12 FROM employee;
SELECT name, salary*12 AS Annual_salary FROM employee;
SELECT name, salary*12 Annual_salary FROM employee;
#定义显示格式
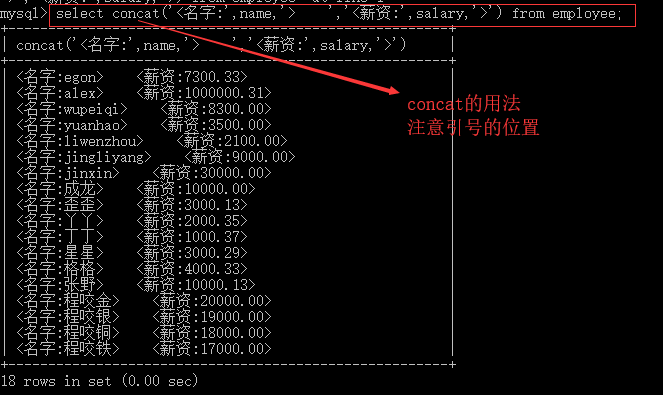
CONCAT() 函数用于连接字符串
SELECT CONCAT('姓名: ',name,' 年薪: ', salary*12) AS Annual_salary FROM employee;
CONCAT_WS() 第一个参数为分隔符
SELECT CONCAT_WS(':',name,salary*12) AS Annual_salary FROM employee;
查出所有员工的名字,薪资,格式为<名字:egon>,<薪资:3000>
select concat('<名字:',name,'> ','<薪资:',salary,'>') from employee;
查出所有的岗位(去掉重复)
select distinct depart_id from employee;
查出所有员工名字,以及他们的年薪,年薪的字段名为annual_year
select name,salary*12 as annual_salary from employee;

where 约束
where字句中可以使用:
比较运算符:><>= <= <> != between 80 and 100 值在10到20之间 in(80,90,100) 值是10或20或30 like 'egon%' pattern可以是%或_,%表示任意多字符,_表示一个字符 逻辑运算符:在多个条件直接可以使用逻辑运算符 and or not
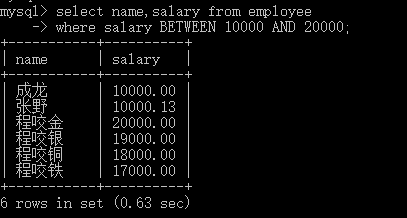
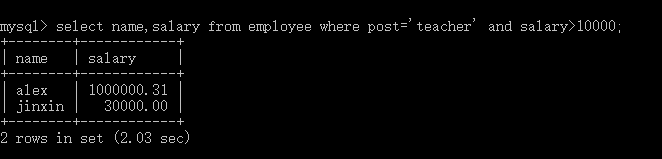
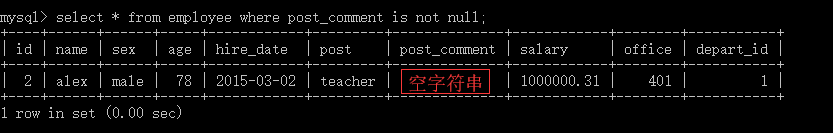
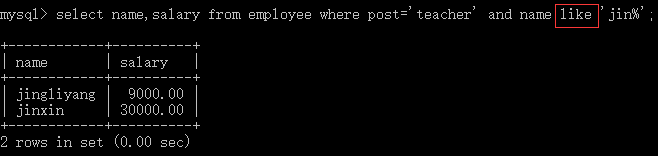
#1:单条件查询 select name from employee where post='sale'; #2:多条件查询 select name,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary>10000; #3:关键字BETWEEN AND select name,salary from employee where salary BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000; select name,salary from employee where salary NOT BETWEEN 10000 AND 20000; #4:关键字IS NULL(判断某个字段是否为NULL不能用等号,需要用IS) select name,post_comment from employee where post_comment IS NULL; select name,post_comment from employee where post_comment IS NOT NULL; select name,post_comment from employee where post_comment=''; #注意''是空字符串,不是null #执行 update employee set post_comment='' where id=2; select name,post_comment from employee where post_comment='';#有结果了 #5:关键字IN集合查询 select name,salary from employee where salary=3000 OR salary=3500 OR salary=4000 OR salary=9000 ; select name,salary from employee where salary in (3000,3500,4000,9000) ; select name,salary from employee where salary not in (3000,3500,4000,9000) ; #6:关键字LIKE模糊查询 通配符’%’ select * from employee where name LIKE 'eg%'; 通配符’_’ select * from employee where name LIKE 'al__';
分组查询:group by
分组指的是:将所有记录按照某个相同字段进行归类,比如针对员工信息表的职位分组,或者按照性别进行分组等
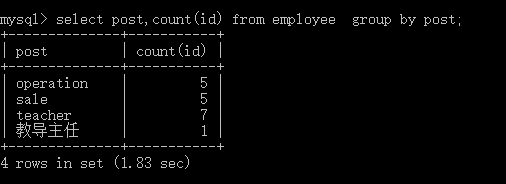
小窍门:‘每’这个字后面的字段,就是我们分组的依据 1.单独使用GROUP BY关键字分组 SELECT post FROM employee GROUP BY post; 2.GROUP BY关键字和GROUP_CONCAT()函数一起使用 SELECT post,GROUP_CONCAT(name) FROM employee GROUP BY post;#按照岗位分组,并查看组内成员名 SELECT post,GROUP_CONCAT(name) as emp_members FROM employee GROUP BY post; 3.GROUP BY与聚合函数一起使用 select post,count(id) as count from employee group by post;#按照岗位分组,并查看每个组有多少人
设置ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY set global sql_mode='ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY'; quit #设置成功后,一定要退出,然后重新登录方可生效

聚合函数
聚合函数聚合的是组的内容,若是没有分组,则默认一组
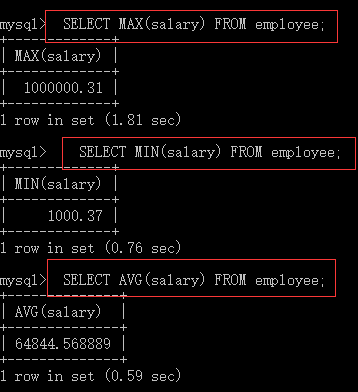
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=1; SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employee; SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employee; SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employee; SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee; SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employee WHERE depart_id=3;
having过滤
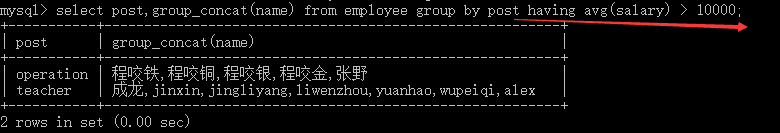
执行优先级从高到低:where > group by > having #1. Where 发生在分组group by之前,因而Where中可以有任意字段,但是绝对不能使用聚合函数。 #2. Having发生在分组group by之后,因而Having中可以使用分组的字段,无法直接取到其他字段,可以使用聚合函数 select @@global.sql_mode; select * from employee where salary > 100000; select * from employee having salary > 100000;#错误 select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post having salary > 10000;#错误,分组后无法直接取到salary字段 select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post having avg(salary) > 10000;
查询排序:order by
按单列排序
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary; SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary ASC; SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC;
按多列排序:先按照age排序,如果年纪相同,则按照薪资排序
SELECT * from employee ORDER BY age, salary DESC;
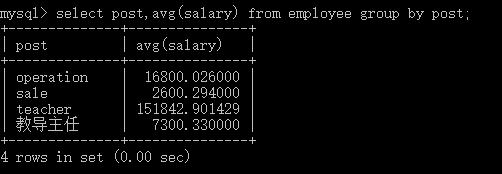
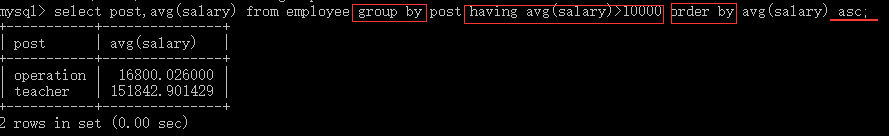
1. 查询所有员工信息,先按照age升序排序,如果age相同则按照hire_date降序排序 select * from employee order by age asc,hire_date desc; 2. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资,结果按平均薪资升序排列 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary)>10000 order by avg(salary) desc;
限制查询记录数
SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 3; #默认初始位置为0 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 0,5; #从第0开始,即先查询出第一条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条 SELECT * FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 5,5; #从第5开始,即先查询出第6条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条

使用正则表达式查询
select * from employee where name REGEXP '^ale';
select * from employee where name REGEXP 'on$';
select * from employee where name REGEXP 'm{2}';
查看所有员工中名字是jin开头,n或者g结果的员工信息
select * from employee where name regexp '^jin.*[gn]$';
多表连接查询
准备表
#建表
create table department(
id int,
name varchar(20)
);
create table employee(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int,
dep_id int
);
#插入数据
insert into department values
(200,'技术'),
(201,'人力资源'),
(202,'销售'),
(203,'运营');
insert into employee(name,sex,age,dep_id) values
('egon','male',18,200),
('alex','female',48,201),
('wupeiqi','male',38,201),
('yuanhao','female',28,202),
('liwenzhou','male',18,200),
('jingliyang','female',18,204)
;
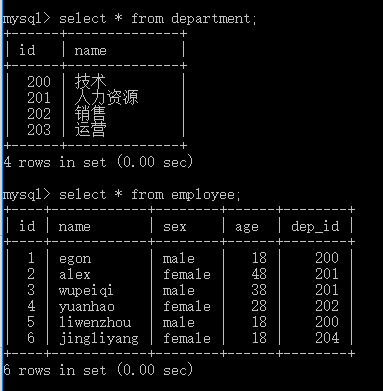
查询表
desc department;
desc employee;
select * from department;
select * from employee;
多表连接查询
外链接语法
select 字段列表 from 表1 inner|left|right join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
交叉连接:不适用任何匹配条件。生成笛卡尔积
select * from employee,department;
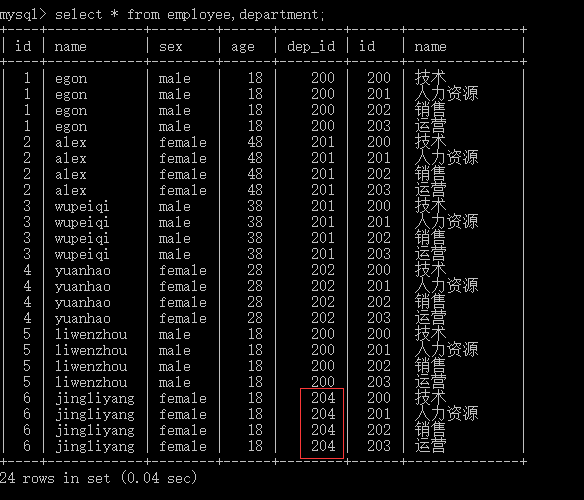
内连接:只连接匹配的行
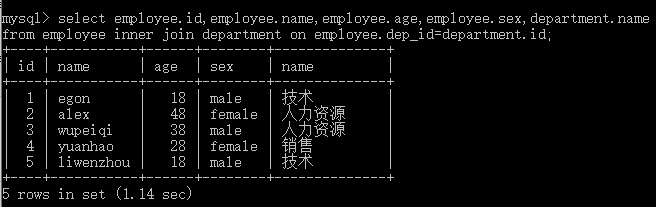
#找两张表共有的部分,相当于利用条件从笛卡尔积结果中筛选出了正确的结果 select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee,department where employee.dep_id=department.id; select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
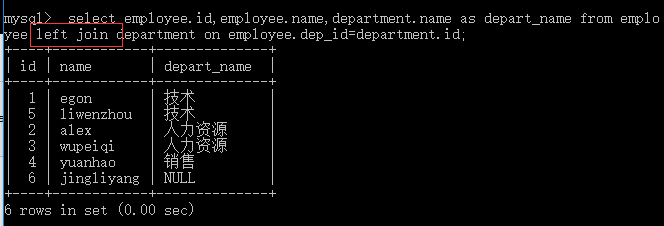
外链接之左连接:优先显示左表全部记录
#以左表为准,即找出所有员工信息,当然包括没有部门的员工 select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee left join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
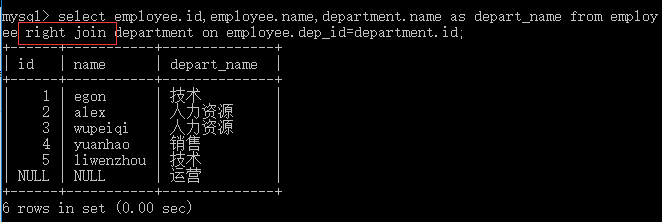
外链接之右连接:优先显示右表全部记录
select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee right join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
全外连接:显示左右两个表全部记录
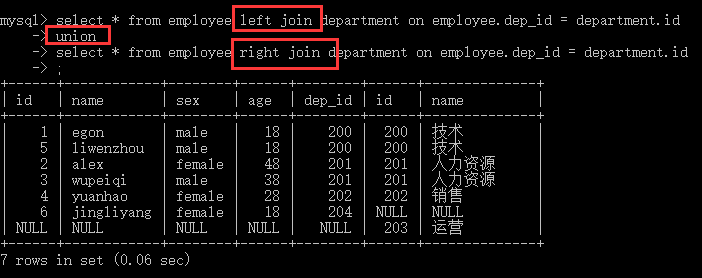
#注意:mysql不支持全外连接 full JOIN select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id = department.id union select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id = department.id ; #注意 union与union all的区别:union会去掉相同的纪录
子查询
#1:子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。 #2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。 #3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字 #4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等
带IN关键字的子查询
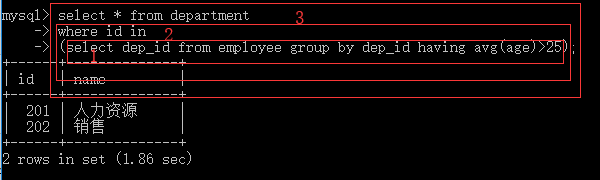
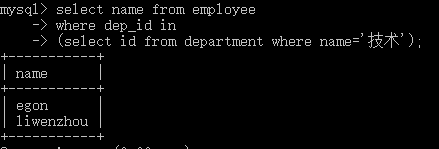
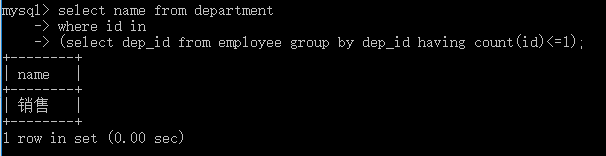
#查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名 select id,name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25); #查看技术部员工姓名 select name from employee where dep_id in (select id from department where name='技术'); #查看不足1人的部门名 select name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(id) <=1);
带比较运算符的子查询
#查询大于所有人平均年龄的员工名与年龄 select name,age from employee where age > (select avg(age) from employee); #查询大于部门内平均年龄的员工名、年龄 select t1.name,t1.age from emp t1 inner join (select dep_id,avg(age) avg_age from emp group by dep_id) t2 on t1.dep_id = t2.dep_id where t1.age > t2.avg_age;
带EXISTS关键字的子查询
EXISTS关字键字表示存在。在使用EXISTS关键字时,内层查询语句不返回查询的记录。
而是返回一个真假值。
True或False当返回True时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回值为False时,外层查询语句不进行查询
select * from employee where exists (select id from department where id=203);#结果为True 若把id=205,结果为false
视图
是一个虚拟表,其内容由查询定义。同真实的表一样,视图包含一系列带有名称的列和行数据
视图有如下特点; 1. 视图的列可以来自不同的表,是表的抽象和逻辑意义上建立的新关系。 2. 视图是由基本表(实表)产生的表(虚表)。 3. 视图的建立和删除不影响基本表。 4. 对视图内容的更新(添加、删除和修改)直接影响基本表。 5. 当视图来自多个基本表时,不允许添加和删除数据。
创建视图 create view 视图名称 as sql 查询语句 使用视图 select * from 视图名称; 修改视图 alter view 视图名称 AS SQL语句 删除视图 drop view 视图名称;
create view emp_view as select * from employee; select * from emp_view; update emp_view set name='blueky' where id=5; select * from employee;#epmloyee表中的字段也变成blueky alter view emp_view as select * from employee where age>28; drop view emp_view;
触发器:监视某种情况,并触发某种操作。
触发器创建语法四要素:1.监视地点(table) 2.监视事件(insert/update/delete) 3.触发时间(after/before) 4.触发事件(insert/update/delete)
创建触发器语法
create trigger triggerName after/before insert/update/delete on 表名 for each row #这句话是固定的 begin #需要执行的sql语句 end #注意1:after/before: 只能选一个 ,after 表示 后置触发, before 表示前置触发 #注意2:insert/update/delete:只能选一个
#准备表
CREATE TABLE cmd (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
USER CHAR (32),
priv CHAR (10),
cmd CHAR (64),
sub_time datetime, #提交时间
success enum ('yes', 'no') #0代表执行失败
);
CREATE TABLE errlog (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
err_cmd CHAR (64),
err_time datetime
);
#创建触发器
delimiter //
CREATE TRIGGER tri_after_insert_cmd AFTER INSERT ON cmd FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF NEW.success = 'no' THEN #等值判断只有一个等号
INSERT INTO errlog(err_cmd, err_time) VALUES(NEW.cmd, NEW.sub_time) ; #必须加分号
END IF ; #必须加分号
END//
delimiter ;
#往表cmd中插入记录,触发触发器,根据IF的条件决定是否插入错误日志
INSERT INTO cmd (
USER,
priv,
cmd,
sub_time,
success
)
VALUES
('egon','0755','ls -l /etc',NOW(),'yes'),
('egon','0755','cat /etc/passwd',NOW(),'no'),
('egon','0755','useradd xxx',NOW(),'no'),
('egon','0755','ps aux',NOW(),'yes');
#删除触发器
drop trigger tri_after_insert_cmd;
事务
事务用于将某些操作的多个SQL作为原子性操作,一旦有某一个出现错误,即可回滚到原来的状态,从而保证数据库数据完整性。
事物的特性:原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性。
在 MySQL 中只有使用了 Innodb 数据库引擎的数据库或表才支持事务。 事务处理可以用来维护数据库的完整性,保证成批的 SQL 语句要么全部执行,要么全部不执行。 事务用来管理 insert,update,delete 语句 SET AUTOCOMMIT=0 ;禁止自动提交 和 SET AUTOCOMMIT=1 开启自动提交.
数据锁
当并发事务同时访问一个资源时,有可能导致数据不一致,就需要一种机制来将数据访问顺序化,以保证数据库数据的一致性
多个事务同时读取一个对象的时候,是不会有冲突的。同时读和写,或者同时写才会产生冲突。
因此为了提高数据库的并发性能,通常会定义两种锁:共享锁和排它锁。
共享锁:共享锁(S)表示对数据进行读操作。因此多个事务可以同时为一个对象加共享锁。 排他锁:排他锁(X)表示对数据进行写操作。如果一个事务对 对象加了排他锁,其他事务就不能再给它加任何锁了。

1 1. 查看岗位是teacher的员工姓名、年龄 2 select name,age from employee where post='teacher'; 3 4 2. 查看岗位是teacher且年龄大于30岁的员工姓名、年龄 5 select name,age from employee where post='teacher' and age>30; 6 7 3. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资在9000-1000范围内的员工姓名、年龄、薪资 8 select name,age,salary from employee where salary between 9000 and 10000; 9 10 4. 查看岗位描述不为NULL的员工信息 11 select * from employee where post_comment is not null; 12 13 5. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资是10000或9000或30000的员工姓名、年龄、薪资 14 select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary in(10000,9000,30000); 15 16 6. 查看岗位是teacher且薪资不是10000或9000或30000的员工姓名、年龄、薪资 17 select name,age,salary from employee where post='teacher' and salary not in(10000,9000,30000); 18 19 20 7. 查看岗位是teacher且名字是jin开头的员工姓名、年薪 21 #select name,salary from employee where post='teacher' and name like 'jin_'; 22 select name,salary from employee where post='teacher' and name like 'jin%'; 23 24 25 26 27 1. 查询岗位名以及岗位包含的所有员工名字 28 select post,group_concat(name) from employee group by post; 29 30 2. 查询岗位名以及各岗位内包含的员工个数 31 select post,count(id) from employee group by post; 32 33 3. 查询公司内男员工和女员工的个数 34 select sex,count(id) from employee group by sex; 35 4. 查询岗位名以及各岗位的平均薪资 36 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post; 37 38 5. 查询岗位名以及各岗位的最高薪资 39 select post,max(salary) from employee group by post; 40 41 6. 查询岗位名以及各岗位的最低薪资 42 select post,min(salary) from employee group by post; 43 44 45 7. 查询男员工与男员工的平均薪资,女员工与女员工的平均薪资 46 select sex,avg(salary) from employee group by sex; 47 48 49 1. 查询各岗位内包含的员工个数小于2的岗位名、岗位内包含员工名字、个数 50 select post,group_concat(name),count(id) from employee group by post having count(id)<2; 51 2. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资 52 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary)>10000; 53 3. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000且小于20000的岗位名、平均工资 54 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary)>10000 and avg(salary)<20000; 55 56 57 58 1. 查询所有员工信息,先按照age升序排序,如果age相同则按照hire_date降序排序 59 select * from employee order by age asc,hire_date desc; 60 61 2. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资,结果按平均薪资升序排列 62 select post,avg(salary) from employee where avg(salary)>10000 group by post order by avg(salary) asc;#错误 63 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary)>10000 order by avg(salary) asc; 64 65 3. 查询各岗位平均薪资大于10000的岗位名、平均工资,结果按平均薪资降序排列 66 select post,avg(salary) from employee group by post having avg(salary)>10000 order by avg(salary) desc; 67 68 69 1. 分页显示,每页5条 70 select * from employee limit 0,5; 71 select * from employee limit 5,5; 72 select * from employee limit 10,5; 73 74 1.以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且employee表中的age字段值必须大于25, 75 即找出年龄大于25岁的员工以及员工所在的部门 76 select employee.name,department.name from employee 77 inner join department on employee dep_id=department.id where age>25; 78 79 2.以内连接的方式查询employee和department表,并且以age字段的升序方式显示 80 select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,department.name from employee,department 81 where employee dep_id=department.id 82 and age>25 83 order by age asc; 84 85 1.查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名 86 select * from department 87 where id in 88 (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age)>25); 89 90 2.查看技术部员工姓名 91 select name from employee 92 where dep_id in 93 (select id from department where name='技术'); 94 95 3.查看不足1人的部门名 96 select name from department 97 where id in 98 (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(id)<=1);
