Nginx调优
前言:
最近相对比较闲,整理下以前工作中学到的东西,将接触到生产环境中的内容都深入学习一下,nginx与tomcat的优化是在山西ott项目上接触到的,直接操作配置文件很容易,但更多的配置参数与优化方式还是需要了解的,先得知道问题在哪里,然后再做。
Nginx调优
目录
软件调优
1.隐藏 Nginx 版本号
2.隐藏 Nginx 版本号和软件名
3.更改 Nginx 服务的默认用户
4.优化 Nginx worker 进程数
5.绑定 Nginx 进程到不同的 CPU 上
6.优化 Nginx 处理事件模型
7.优化 Nginx 单个进程允许的最大连接数
8.优化 Nginx worker 进程最大打开文件数
9.优化服务器域名的散列表大小
10.开启高效文件传输模式
11.优化 Nginx 连接超时时间
12.限制上传文件的大小
13.FastCGI 相关参数调优
14.配置 Nginx gzip 压缩
15.配置 Nginx expires 缓存
16.优化 Nginx日志(日志切割)
17.优化 Nginx 站点目录
18.配置 Nginx 防盗链
19.配置 Nginx 错误页面优雅显示
20.优化 Nginx 文件权限
21.Nginx 防爬虫优化
22.控制 Nginx 并发连接数
23. 集群代理优化
系统内核参数优化
Nginx软件调优
1. 隐藏 Nginx 版本号
为什么要隐藏 Nginx 版本号:一般来说,软件的漏洞都与版本有关,隐藏版本号是为了防止恶意用户利用软件漏洞进行攻击
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server_tokens off; # 隐藏版本号 server { listen 80; server_name www.abc.com; location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; } } } ...[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload[root@localhost ~]# curl -I 127.0.0.1 # 查看是否隐藏版本号HTTP/1.1 404 Not FoundServer: nginx Date: Thu, 25 May 2017 05:23:03 GMTContent-Type: text/htmlContent-Length: 162Connection: keep-alive |
2.隐藏 Nginx 版本号和软件名
为什么要隐藏 Nginx 版本号和软件名:一般来说,软件的漏洞都与版本有关,隐藏版本号是为了防止恶意用户利用软件漏洞进行攻击,而软件名可以进行修改,否则黑客知道是 Nginx 服务器更容易进行攻击,需要注意的是,隐藏 Nginx 软件名需要重新编译安装 Nginx ,如果没有该方面需求尽量不要做
1) 修改:/usr/local/src/nginx-1.6.3/src/core/nginx.h
|
1
2
3
|
#define NGINX_VERSION "8.8.8.8" # 修改为想要显示的版本号#define NGINX_VER "Google/" NGINX_VERSION # 修改为想要显示的软件名#define NGINX_VAR "Google" # 修改为想要显示的软件名 |
2) 修改:/usr/local/src/nginx-1.6.3/src/http/ngx_http_header_filter_module.c
|
1
2
|
static char ngx_http_server_string[] = "Server: Google" CRLF; # 修改为想要显示的软件名static char ngx_http_server_full_string[] = "Server: " NGINX_VER CRLF; |
3) 修改:/usr/local/src/nginx-1.6.3/src/http/ngx_http_special_response.c
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
static u_char ngx_http_error_full_tail[] ="<hr><center>" NGINX_VER "(www.google.com)</center>" CRLF # 此行定义对外展示的内容"</body>" CRLF"</html>" CRLF;static u_char ngx_http_error_tail[] ="<hr><center>Google</center>" CRLF # 此行定义对外展示的软件名"</body>" CRLF"</html>" CRLF; |
4) 重新编译 Nginx
|
1
2
3
4
|
cd /usr/local/src/nginx-1.6.3./configure --user=nginx --group=nginx --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_modulemake && make install/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx |
3.更改 Nginx 服务的默认用户
为什么要更改 Nginx 服务的默认用户:就像更改 ssh 的默认 22 端口一样,增加安全性,Nginx 服务的默认用户是 nobody ,我们更改为 nginx
1) 添加 nginx 用户
|
1
|
useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M nginx |
2) 更改 Nginx 配置文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.confworker_processes 1;user nginx nginx; # 指定Nginx服务的用户和用户组events { worker_connections 1024;}http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server_tokens off; server { listen 80; server_name www.abc.com; location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; } }} |
3) 重新加载 Nginx
|
1
2
|
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload |
4) 验证是否生效
|
1
2
3
|
[root@localhost ~]# ps aux | grep nginx root 8901 0.0 0.1 45036 1784 ? Ss 13:54 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginxnginx 8909 0.0 0.1 45460 1828 ? S 13:59 0:00 nginx: worker process # Nginx进程的所属用户为nginx |
4.优化 Nginx worker 进程数
Nginx 有 Master 和 worker 两种进程,Master 进程用于管理 worker 进程,worker 进程用于 Nginx 服务
worker 进程数应该设置为等于 CPU 的核数,高流量并发场合也可以考虑将进程数提高至 CPU 核数 * 2
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
[root@localhost ~]# grep -c processor /proc/cpuinfo # 查看CPU核数2[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf # 设置worker进程数worker_processes 2;user nginx nginx;......[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t # 重新加载Nginx[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload[root@localhost ~]# ps -ef | grep nginx | grep -v grep # 验证是否为设置的进程数root 8901 1 0 13:54 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginxnginx 8937 8901 0 14:14 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process nginx 8938 8901 0 14:14 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process |
5.绑定 Nginx 进程到不同的 CPU 上
为什么要绑定 Nginx 进程到不同的 CPU 上 :默认情况下,Nginx 的多个进程有可能跑在某一个 CPU 或 CPU 的某一核上,导致 Nginx 进程使用硬件的资源不均,因此绑定 Nginx 进程到不同的 CPU 上是为了充分利用硬件的多 CPU 多核资源的目的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
[root@localhost ~]# grep -c processor /proc/cpuinfo # 查看CPU核数2worker_processes 2; # 2核CPU的配置worker_cpu_affinity 01 10;worker_processes 4; # 4核CPU的配置worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000; worker_processes 8; # 8核CPU的配置worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000 00010000 00100000 01000000 1000000;[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/src/ # 进行压力测试,教程:http://os.51cto.com/art/201202/317803.htm[root@localhost src]# wget http://home.tiscali.cz/~cz210552/distfiles/webbench-1.5.tar.gz [root@localhost src]# tar -zxvf webbench-1.5.tar.gz[root@localhost src]# cd webbench-1.5[root@localhost src]# yum install -y ctags gcc[root@localhost src]# mkdir -m 644 -p /usr/local/man/man1[root@localhost src]# make && make install[root@localhost src]# webbench -c 10000 -t 60 http://192.168.5.131/ |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
[root@localhost ~]# top # 按1查看CPU调度结果,这里是虚拟机测试,效果并不太明显top - 14:44:46 up 4:40, 3 users, load average: 0.01, 0.32, 0.24Tasks: 85 total, 1 running, 84 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombieCpu0 : 0.8%us, 0.8%sy, 0.0%ni, 97.9%id, 0.3%wa, 0.0%hi, 0.2%si, 0.0%stCpu1 : 0.6%us, 0.7%sy, 0.0%ni, 98.1%id, 0.0%wa, 0.0%hi, 0.5%si, 0.0%stMem: 1534840k total, 304824k used, 1230016k free, 3932k buffersSwap: 204792k total, 0k used, 204792k free, 191364k cachedPID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND 4319 root 20 0 98308 3932 2964 S 3.2 0.3 0:15.76 sshd 18989 root 20 0 15016 1292 1008 R 1.6 0.1 0:00.04 top 1 root 20 0 19232 1388 1112 S 0.0 0.1 0:02.19 init 2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.08 kthreadd 3 root RT 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.61 migration/04 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:03.60 ksoftirqd/05 root RT 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 migration/06 root RT 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.50 watchdog/0 |
6.优化 Nginx 处理事件模型
Nginx 的连接处理机制在不同的操作系统会采用不同的 I/O 模型,要根据不同的系统选择不同的事件处理模型,可供选择的事件处理模型有:kqueue 、rtsig 、epoll 、/dev/poll 、select 、poll ,其中 select 和 epoll 都是标准的工作模型,kqueue 和 epoll 是高效的工作模型,不同的是 epoll 用在 Linux 平台上,而 kqueue 用在 BSD 系统中。
(1) 在 Linux 下,Nginx 使用 epoll 的 I/O 多路复用模型
(2) 在 Freebsd 下,Nginx 使用 kqueue 的 I/O 多路复用模型
(3) 在 Solaris 下,Nginx 使用 /dev/poll 方式的 I/O 多路复用模型
(4) 在 Windows 下,Nginx 使用 icop 的 I/O 多路复用模型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf......events { use epoll;}...... |
7.优化 Nginx 单个进程允许的最大连接数
(1) 控制 Nginx 单个进程允许的最大连接数的参数为 worker_connections ,这个参数要根据服务器性能和内存使用量来调整
(2) 进程的最大连接数受 Linux 系统进程的最大打开文件数限制,只有执行了 "ulimit -HSn 65535" 之后,worker_connections 才能生效
(3) 连接数包括代理服务器的连接、客户端的连接等,Nginx 总并发连接数 = worker 数量 * worker_connections, 总数保持在3w左右
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.confworker_processes 2;worker_cpu_affinity 01 10;user nginx nginx;events { use epoll; worker_connections 15000;}...... |
8.优化 Nginx worker 进程最大打开文件数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.confworker_processes 2;worker_cpu_affinity 01 10;worker_rlimit_nofile 65535; # worker 进程最大打开文件数,可设置为优化后的 ulimit -HSn 的结果user nginx nginx;events { worker_connections 1024;}http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server_tokens off; server { listen 80; server_name www.abc.com; location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; } }} |
9.优化服务器域名的散列表大小
如下,如果在 server_name 中配置了一个很长的域名,那么重载 Nginx 时会报错,因此需要使用 server_names_hash_max_size 来解决域名过长的问题,该参数的作用是设置存放域名的最大散列表的存储的大小,根据 CPU 的一级缓存大小来设置。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
server { listen 80; server_name www.abcdefghijklmnopqrst.com; # 配置一个很长的域名 location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; } } |
|
1
2
3
|
[root@localhost conf]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t # 如果配置的域名很长会出现如下错误nginx: [emerg] could not build the server_names_hash, you should increase server_names_hash_bucket_size: 64nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test failed |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf......http { include mime.types; server_names_hash_bucket_size 512; # 配置在 http 区块,默认是 512kb ,一般设置为 cpu 一级缓存的 4-5 倍,一级缓存大小可以用 lscpu 命令查看 default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server_tokens off; include vhosts/*.conf;} |
10.开启高效文件传输模式
(1) sendfile 参数用于开启文件的高效传输模式,该参数实际上是激活了 sendfile() 功能,sendfile() 是作用于两个文件描述符之间的数据拷贝函数,这个拷贝操作是在内核之中的,被称为 "零拷贝" ,sendfile() 比 read 和 write 函数要高效得多,因为 read 和 write 函数要把数据拷贝到应用层再进行操作
(2) tcp_nopush 参数用于激活 Linux 上的 TCP_CORK socket 选项,此选项仅仅当开启 sendfile 时才生效,tcp_nopush 参数可以允许把 http response header 和文件的开始部分放在一个文件里发布,以减少网络报文段的数量
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf......http { include mime.types; server_names_hash_bucket_size 512; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; # 开启文件的高效传输模式 tcp_nopush on; # 激活 TCP_CORK socket 选择 tcp_nodelay on; #数据在传输的过程中不进缓存 keepalive_timeout 65; server_tokens off; include vhosts/*.conf;} |
11.优化 Nginx 连接超时时间
1. 什么是连接超时
(1) 举个例子,某饭店请了服务员招待顾客,但是现在饭店不景气,因此要解雇掉一些服务员,这里的服务员就相当于 Nginx 服务建立的连接
(2) 当服务器建立的连接没有接收处理请求时,可以在指定的时间内让它超时自动退出
2. 连接超时的作用
(1) 将无用的连接设置为尽快超时,可以保护服务器的系统资源(CPU、内存、磁盘)
(2) 当连接很多时,及时断掉那些建立好的但又长时间不做事的连接,以减少其占用的服务器资源
(3) 如果黑客攻击,会不断地和服务器建立连接,因此设置连接超时以防止大量消耗服务器的资源
(4) 如果用户请求了动态服务,则 Nginx 就会建立连接,请求 FastCGI 服务以及后端 MySQL 服务,设置连接超时,使得在用户容忍的时间内返回数据
3. 连接超时存在的问题
(1) 服务器建立新连接是要消耗资源的,因此,连接超时时间不宜设置得太短,否则会造成并发很大,导致服务器瞬间无法响应用户的请求
(2) 有些 PHP 站点会希望设置成短连接,因为 PHP 程序建立连接消耗的资源和时间相对要少些
(3) 有些 Java 站点会希望设置成长连接,因为 Java 程序建立连接消耗的资源和时间要多一些,这时由语言的运行机制决定的
4. 设置连接超时
(1) keepalive_timeout :该参数用于设置客户端连接保持会话的超时时间,超过这个时间服务器会关闭该连接
(2) client_header_timeout :该参数用于设置读取客户端请求头数据的超时时间,如果超时客户端还没有发送完整的 header 数据,服务器将返回 "Request time out (408)" 错误
(3) client_body_timeout :该参数用于设置读取客户端请求主体数据的超时时间,如果超时客户端还没有发送完整的主体数据,服务器将返回 "Request time out (408)" 错误
(4) send_timeout :用于指定响应客户端的超时时间,如果超过这个时间,客户端没有任何活动,Nginx 将会关闭连接
(5) tcp_nodelay :默认情况下当数据发送时,内核并不会马上发送,可能会等待更多的字节组成一个数据包,这样可以提高 I/O 性能,但是,在每次只发送很少字节的业务场景中,使用 tcp_nodelay 功能,等待时间会比较长
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf......http { include mime.types; server_names_hash_bucket_size 512; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; tcp_nodelay on; client_header_timeout 15; client_body_timeout 15; send_timeout 25; include vhosts/*.conf;} |
12.限制上传文件的大小
client_max_body_size 用于设置最大的允许客户端请求主体的大小,在请求首部中有 "Content-Length" ,如果超过了此配置项,客户端会收到 413 错误,即请求的条目过大
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
worker_processes 2;worker_cpu_affinity 01 10;user nginx nginx;error_log logs/error.log error;events { use epoll; worker_connections 20480;}http { include mime.types; server_names_hash_bucket_size 512; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server_tokens off; client_max_body_size 8m; # 设置客户端最大的请求主体大小为8M include vhosts/*.conf;} |
13.FastCGI 相关参数调优
当 LNMP 组合工作时,首先是用户通过浏览器输入域名请求 Nginx Web 服务,如果请求的是静态资源,则由 Nginx 解析返回给用户;如果是动态请求(如 PHP),那么 Nginx 就会把它通过 FastCGI 接口发送给 PHP 引擎服务(即 php-fpm)进行解析,如果这个动态请求要读取数据库数据,那么 PHP 就会继续向后请求 MySQL 数据库,以读取需要的数据,并最终通过 Nginx 服务把获取的数据返回给用户,这就是 LNMP 环境的基本请求流程。
FastCGI 介绍:CGI 通用网关接口,是 HTTP 服务器与其他机器上的程序服务通信交流的一种工具,CGI 接口的性能较差,每次 HTTP 服务器遇到动态程序时都需要重新启动解析器来执行解析,之后结果才会被返回 HTTP 服务器,因此就有了 FastCGI ,FastCGI 是一个在 HTTP 服务器和动态脚本语言间通信的接口,主要是把动态语言和 HTTP 服务器分离开来,使得 HTTP 服务器专一地处理静态请求,提高整体性能,在 Linux 下,FastCGI 接口即为 socket ,这个 socket 可以是文件 socket 也可以是 IP socket
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.confworker_processes 1;events { worker_connections 1024;}http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; fastcgi_connect_timeout 240; # Nginx服务器和后端FastCGI服务器连接的超时时间 fastcgi_send_timeout 240; # Nginx允许FastCGI服务器返回数据的超时时间,即在规定时间内后端服务器必须传完所有的数据,否则Nginx将断开这个连接 fastcgi_read_timeout 240; # Nginx从FastCGI服务器读取响应信息的超时时间,表示连接建立成功后,Nginx等待后端服务器的响应时间 fastcgi_buffer_size 64k; # Nginx FastCGI 的缓冲区大小,用来读取从FastCGI服务器端收到的第一部分响应信息的缓冲区大小 fastcgi_buffers 4 64k; # 设定用来读取从FastCGI服务器端收到的响应信息的缓冲区大小和缓冲区数量 fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k; # 用于设置系统很忙时可以使用的 proxy_buffers 大小 fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k; # FastCGI 临时文件的大小# fastcti_temp_path /data/ngx_fcgi_tmp; # FastCGI 临时文件的存放路径 fastcgi_cache_path /data/ngx_fcgi_cache levels=2:2 keys_zone=ngx_fcgi_cache:512m inactive=1d max_size=40g; # 缓存目录 server { listen 80; server_name www.abc.com; location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; } location ~ .*.(php|php5)?$ { root html/www; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; include fastcgi.conf; fastcgi_cache ngx_fcgi_cache; # 缓存FastCGI生成的内容,比如PHP生成的动态内容 fastcgi_cache_valid 200 302 1h; # 指定http状态码的缓存时间,这里表示将200和302缓存1小时 fastcgi_cache_valid 301 1d; # 指定http状态码的缓存时间,这里表示将301缓存1天 fastcgi_cache_valid any 1m; # 指定http状态码的缓存时间,这里表示将其他状态码缓存1分钟 fastcgi_cache_min_uses 1; # 设置请求几次之后响应被缓存,1表示一次即被缓存 fastcgi_cache_use_stale error timeout invalid_header http_500; # 定义在哪些情况下使用过期缓存 fastcgi_cache_key http://$host$request_uri; # 定义 fastcgi_cache 的 key } }} |
|
1
2
|
[root@localhost ~]# pkill php-fpm[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/php/sbin/php-fpm |
14.配置 Nginx gzip 压缩
Nginx gzip 压缩模块提供了压缩文件内容的功能,用户请求的内容在发送到客户端之前,Nginx 服务器会根据一些具体的策略实施压缩,以节约网站出口带宽,同时加快数据传输效率,来提升用户访问体验,需要压缩的对象有 html 、js 、css 、xml 、shtml ,图片和视频尽量不要压缩,因为这些文件大多都是已经压缩过的,如果再压缩可能反而变大,另外,压缩的对象必须大于 1KB,由于压缩算法的特殊原因,极小的文件压缩后可能反而变大
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf......http { gzip on; # 开启压缩功能 gzip_min_length 1k; # 允许压缩的对象的最小字节 gzip_buffers 4 32k; # 压缩缓冲区大小,表示申请4个单位为16k的内存作为压缩结果的缓存 gzip_http_version 1.1; # 压缩版本,用于设置识别HTTP协议版本 gzip_comp_level 9; # 压缩级别,1级压缩比最小但处理速度最快,9级压缩比最高但处理速度最慢 gzip_types text/css text/xml application/javascript; # 允许压缩的媒体类型 gzip_vary on; # 该选项可以让前端的缓存服务器缓存经过gzip压缩的页面,例如用代理服务器缓存经过Nginx压缩的数据} |
检查压缩:可以用 Google 浏览器按 F12 查看,也可以在 Google 浏览器安装 yslow 插件(yslow.org)
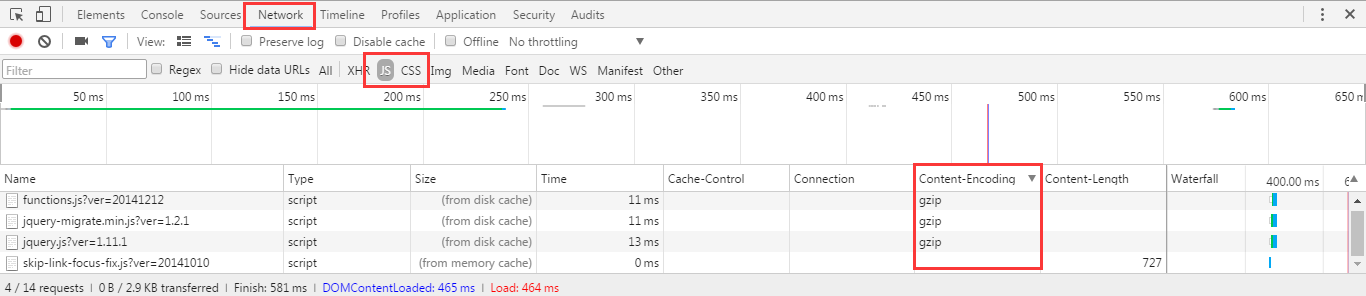

15.配置 Nginx expires 缓存
(1) Nginx expires 的功能就是为用户访问的网站内容设定一个过期时间,当用户第一次访问这些内容时,会把这些内容存储在用户浏览器本地,这样用户第二次及以后继续访问该网站时,浏览器会检查加载已经缓存在用户浏览器本地的内容,就不会去服务器下载了,直到缓存的内容过期或被清除为止
(2) 不希望被缓存的内容:广告图片、网站流量统计工具、更新很频繁的文件
(3) 缓存日期参考:51CTO 缓存 1 周,新浪缓存 15 天,京东缓存 25 年,淘宝缓存 10 年
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
server { listen 80; server_name www.abc.com abc.com; root html/www; location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|js|css)$ # 缓存的对象 { expires 3650d; # 缓存的时间,3650天,即10年 }} |
使用 Google 浏览器安装 yslow 插件来查看:
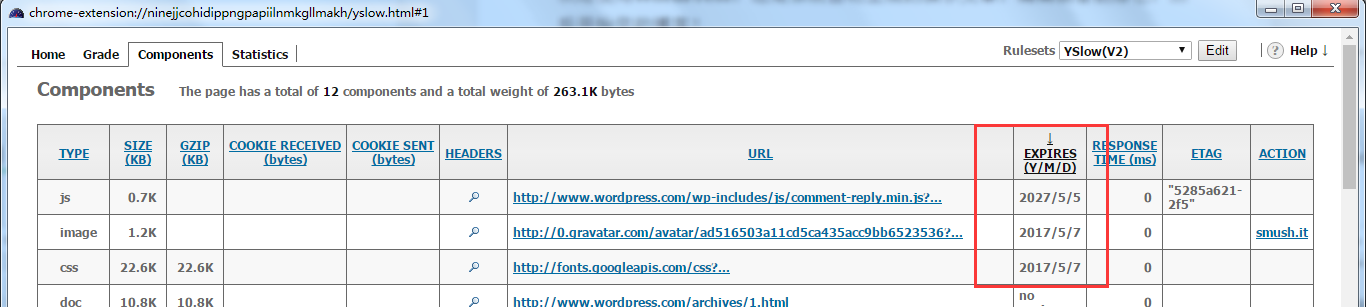
16.优化 Nginx access 日志
1. 配置日志切割
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/cut_nginx_log.sh#!/bin/bashsavepath_log='/usr/local/clogs'nglogs='/usr/local/nginx/logs'mkdir -p $savepath_log/$(date +%Y)/$(date +%m)mv $nglogs/access.log $savepath_log/$(date +%Y)/$(date +%m)/access.$(date +%Y%m%d).logmv $nglogs/error.log $savepath_log/$(date +%Y)/$(date +%m)/error.$(date +%Y%m%d).logkill -USR1 `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid` |
|
1
2
|
[root@localhost ~]# crontab -e # 每天凌晨0点执行脚本0 0 * * * /bin/sh /usr/local/nginx/conf/cut_nginx_log.sh > /dev/null 2>&1 |
2. 不记录不需要的访问日志
|
1
2
3
|
location ~ .*.(js|jpg|JPG|jpeg|JPEG|css|bmp|gif|GIF)$ { access_log off;} |
3. 设置访问日志的权限
|
1
2
|
chown -R root.root /usr/local/nginx/logschmod -R 700 /usr/local/nginx/logs |
17.优化 Nginx 站点目录
1. 禁止解析指定目录下的指定程序
|
1
2
3
|
location ~ ^/data/.*.(php|php5|sh|pl|py)$ { # 根据实际来禁止哪些目录下的程序,且该配置必须写在 Nginx 解析 PHP 的配置前面 deny all;} |
2. 禁止访问指定目录
|
1
2
3
|
location ~ ^/data/.*.(php|php5|sh|pl|py)$ { # 根据实际来禁止哪些目录下的程序,且该配置必须写在 Nginx 解析 PHP 的配置前面 deny all;} |
3. 限制哪些 IP 不能访问网站
|
1
2
3
4
|
location ~ ^/wordpress { # 相对目录,表示只允许 192.168.1.1 访问网站根目录下的 wordpress 目录 allow 192.168.1.1/24; deny all;} |
18.配置 Nginx 防盗链
什么是防盗链:简单地说,就是某些不法网站未经许可,通过在其自身网站程序里非法调用其他网站的资源,然后在自己的网站上显示这些调用的资源,使得被盗链的那一端消耗带宽资源 (1) 根据 HTTP referer 实现防盗链:referer 是 HTTP的一个首部字段,用于指明用户请求的 URL 是从哪个页面通过链接跳转过来的
(2) 根据 cookie 实现防盗链:cookie 是服务器贴在客户端身上的 "标签" ,服务器用它来识别客户端
根据 referer 配置防盗链:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#第一种,匹配后缀location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bm|swf|flv|rar|zip|gz|bz2)$ { # 指定需要使用防盗链的媒体资源 access_log off; # 不记录防盗链的日志 expires 15d; # 设置缓存时间 valid_referers none blocked *.test.com *.abc.com; # 表示这些地址可以访问上面的媒体资源 if ($invalid_referer) { # 如果地址不如上面指定的地址就返回403 return 403 }}#第二种,绑定目录location /images { root /web/www/img; vaild_referers nono blocked *.spdir.com *.spdir.top; if ($invalid_referer) { return 403; }} |
19.配置 Nginx 错误页面优雅显示
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf......http { location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; error_page 400 401 402 403 404 405 408 410 412 413 414 415 500 501 502 503 506 = http://www.xxxx.com/error.html; # 将这些状态码的页面链接到 http://www.xxxx.com/error.html ,也可以单独指定某个状态码的页面,如 error_page 404 /404.html }} |
20.优化 Nginx 文件权限
为了保证网站不受木马入侵,所有文件的用户和组都应该为 root ,所有目录的权限是 755 ,所有文件的权限是 644
|
1
2
3
|
[root@localhost ~]# chown -R root.root /usr/local/nginx/.... # 根据实际来调整[root@localhost ~]# chmod 755 /usr/local/nginx/....[root@localhost ~]# chmod 644 /usr/local/nginx/.... |
21.Nginx 防爬虫优化
我们可以根据客户端的 user-agents 首部字段来阻止指定的爬虫爬取我们的网站
|
1
2
3
|
if ($http_user_agent ~* "qihoobot|Baiduspider|Googlebot|Googlebot-Mobile|Googlebot-Image|Mediapartners-Google|Adsbot-Google|Yahoo! Slurp China|YoudaoBot|Sosospider|Sogou spider|Sogou web spider|MSNBot") { return 403;} |
22.控制 Nginx 并发连接数
1. 限制单个 IP 的并发连接数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf....http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m; # 用于设置共享内存区域,addr 是共享内存区域的名称,10m 表示共享内存区域的大小 server { listen 80; server_name www.abc.com; location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; limit_conn addr 1; # 限制单个IP的并发连接数为1 } }} |
2. 限制虚拟主机总连接数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
....http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=perserver:10m; server { listen 80; server_name www.abc.com; location / { root html/www; index index.html index.htm; limit_conn perserver 2; # 设置虚拟主机连接数为2 } }} |
23. 集群代理优化
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
upstream bbs_com_pool{ #定义服务器池 ip_hash; #会话保持(当服务器集群中没有会话池时,且代理的是动态数据就必须写ip_hash,反之什么也不用写) #fair #智能分配(第三方,需要下载upstream_fair模块)根据后端服务器的响应时间来调度 #url_hash #更具URL的结果来分配请求(每个url定向到同一个服务器,提高后端缓存服务器的效率,本身不支持,需要安装nginx_hash) #当算法为ip_hash不能有 weight backup server 192.168.10.1:80; #默认weight为1 server 192.168.10.3:80 weight=5; #weight表示权重 server 192.168.10.4:80 down; #down:不参与本次轮询 server 192.168.10.5:80 down backup; #backup:当任何一台主机出现故障,将进行切换替换 server 192.168.10.6:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=20s; #max_fails最大失败请求次数(默认为1),fail_timeout失败超时时间 server 192.168.10.7:8080; } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
stream{ upstream cluster { # hash $remote_addr consistent; //保持 session 不变,四层开启 server 192.168.1.2:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s; server 192.168.1.3:80 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s; } server { listen 80; proxy_pass cluster; proxy_connect_timeout 1s; proxy_timeout 3s; } location { proxy_next_upstream http_500 http_502 http_503 error timeout invalid_header; 当发生其中任何一种错误,将转交给下一个服务器 proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host &$host; #设置后端服务器的真实地址 proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded_For &proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; client_body_buffer_size 128k; #缓冲区大小,本地保存大小 proxy_connect_timeout 90; #发起握手等待的响应时间 proxy_read_timeout 90; #建立连接后等待后端服务器响应时间(其实是后端等候处理的时间) proxy_send_timeout 90; #给定时间内后端服务器必须响应,否则断开 proxy_buffer_size 4k; #proxy缓冲区大小 proxy_buffers 4 32k; #缓冲区个数和大小 proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; #系统繁忙时buffer的临时大小,官方要求proxy_buffer_size*2 proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; #proxy临时文件的大小 }} |
系统内核参数优化
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
vim /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 fs.file-max = 999999 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 6000 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1 net.core.somaxconn=262114 net.core.netdev_max_backlog=262114 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 262114 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans=262114 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries=1 net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries=1 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 30 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 10240 87380 12582912 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 10240 87380 12582912 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 8096 net.core.rmem_default = 6291456 net.core.wmem_default = 6291456 net.core.rmem_max = 12582912 net.core.wmem_max = 12582912 |
参数详解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1:选项用于设置开启SYN cookies,当出现SYN等待队列溢出时,启用cookies进行处理;fs.file-max = 999999:这个参数表示进程(比如一个worker进程)可以同时打开的最大句柄数,这个参数直线限制最大并发连接数,需根据实际情况配置;net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets =6000:这个参数用来设定timewait数量,如果超过这个数字,TIME_WAIT套接字将立刻被清除并打印警告信息。该参数默认为180 000,过多的TIME_WAIT套接字会使Web服务器变慢;net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle=1:这个参数用于设置启用timewait快速回收;net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1:这个参数设置为1,表示允许将TIME-WAIT状态的socket重新用于新的TCP连接,这对于服务器来说很有意义,因为服务器上总会有大量TIME-WAIT状态的连接;net.core.somaxconn=262114 :选项默认值是128,这个参数用于调节系统同时发起的TCP连接数,在高并发的请求中,默认的值可能会导致链接超时或者重传,因此需要结合高并发请求数来调节此值;net.core.netdev_max_backlog=262114:该选项表示每个网络接口接收数据包的速率比内核处理这些包的速率快时,允许发送到队列数据包的最大数目;net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog =262114:这个参数表示TCP三次握手建立阶段接受SYN请求队列的最大长度,默认为1024,将其设置得大一些可以使出现Nginx繁忙来不及accept新连接的情况时,Linux不至于丢失客户端发起的连接请求;net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans=262114:选项用于设定系统中最多有多少个TCP套接字不被关联到任何一个用户文件句柄上。如果超过这个数字,孤立链接将立即被复位并输出警告信息。这个限制指示为了防止简单的DOS攻击,不用过分依靠这个限制甚至认为的减小这个值,更多的情况是增加这个值;net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries=1:内核放弃连接之前发送SYN+ACK包的数量;net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries=1:内核放弃连接之前发送SYN包的数量;net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600:这个参数表示当keepalive启用时,TCP发送keepalive消息的频度。默认是2小时,若将其设置的小一些,可以更快地清理无效的连接;net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 30:这个参数表示当服务器主动关闭连接时,socket保持在FIN-WAIT-2状态的最大时间;net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 61000:这个参数定义了在UDP和TCP连接中本地(不包括连接的远端)端口的取值范围;net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 10240 87380 12582912:这个参数定义了TCP接受缓存(用于TCP接受滑动窗口)的最小值、默认值、最大值;net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 10240 87380 12582912:这个参数定义了TCP发送缓存(用于TCP发送滑动窗口)的最小值、默认值、最大值;net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 8096:当网卡接受数据包的速度大于内核处理的速度时,会有一个队列保存这些数据包。这个参数表示该队列的最大值;net.core.rmem_default = 6291456:这个参数表示内核套接字接受缓存区默认的大小;net.core.wmem_default = 6291456:这个参数表示内核套接字发送缓存区默认的大小;net.core.rmem_max = 12582912:这个参数表示内核套接字接受缓存区的最大大小;net.core.wmem_max = 12582912:这个参数表示内核套接字发送缓存区的最大大小;net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1:该参数与性能无关,用于解决TCP的SYN攻击; |
注意:滑动窗口的大小与套接字缓存区会在一定程度上影响并发连接的数目。每个TCP连接都会为维护TCP滑动窗口而消耗内存,这个窗口会根据服务器的处理速度收缩或扩张。 参数net.core.wmem_max = 12582912的设置,需要平衡物理内存的总大小、Nginx并发处理的最大连接数量而确定。当然,如果仅仅为了提供并发量使服务器不出现Out Of Memory问题而去降低滑动窗口大小,那么并不合适,因为滑动窗过小会影响大数据量的传输速度。net.core.rmem_default = 6291456、net.core.wmem_default = 6291456、 net.core.rmem_max = 12582912和net.core.wmem_max = 12582912这4个参数的设置需要根据我们的业务特性以及实际的硬件成本来综合考虑。 Nginx并发处理的最大连接量:由nginx.conf中的work_processes和work_connections参数决定。