大厂算法面试之leetcode精讲14.排序算法
视频讲解(高效学习):点击学习
目录:
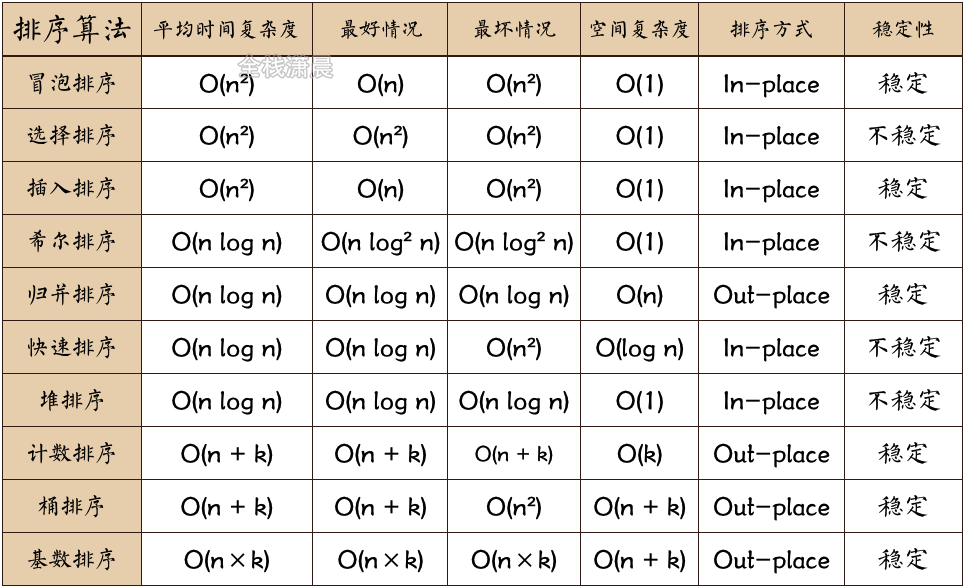
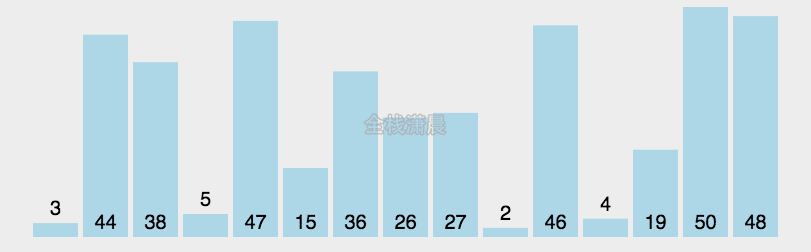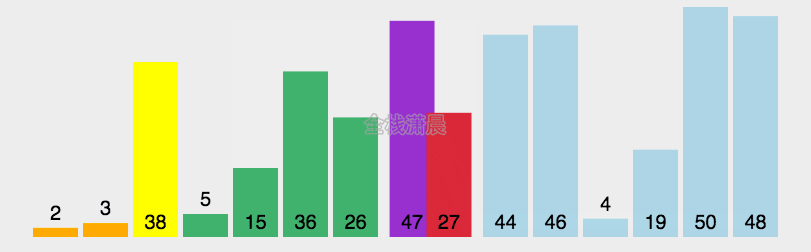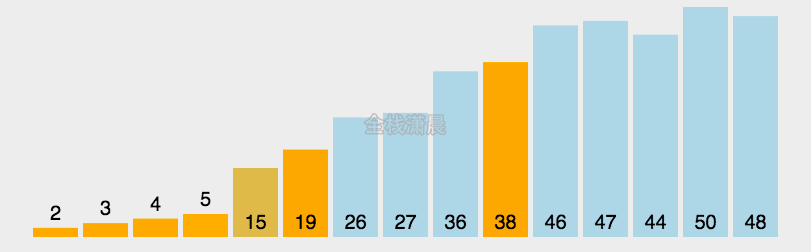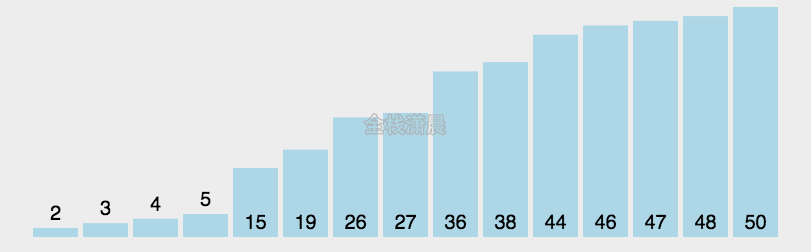
常见排序算法复杂度
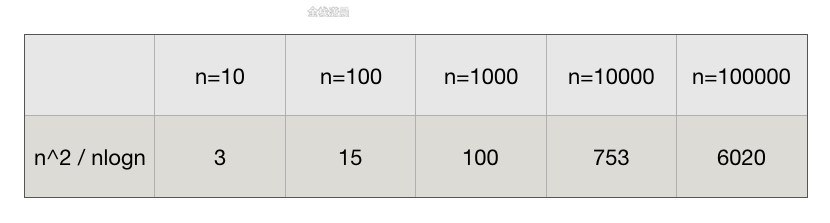
n^2除nlogn在不同数据规模下的结果
常见排序算法
算法可视化来源:http://visualgo.net/
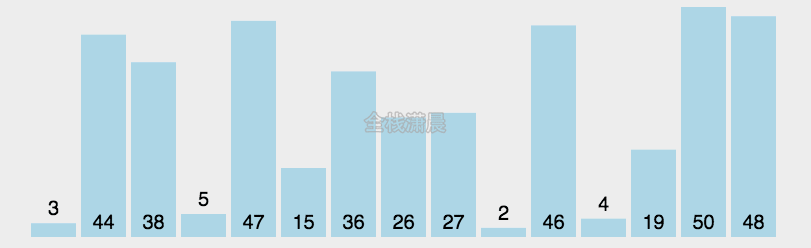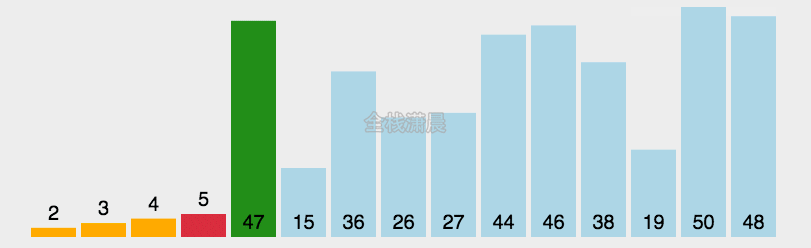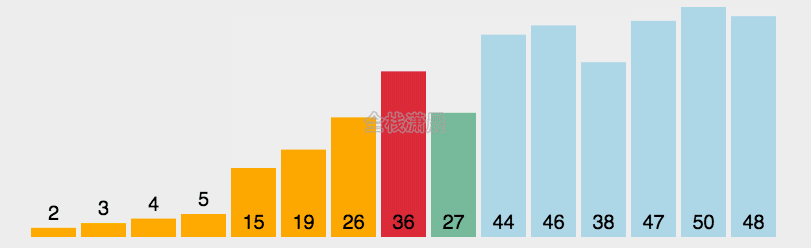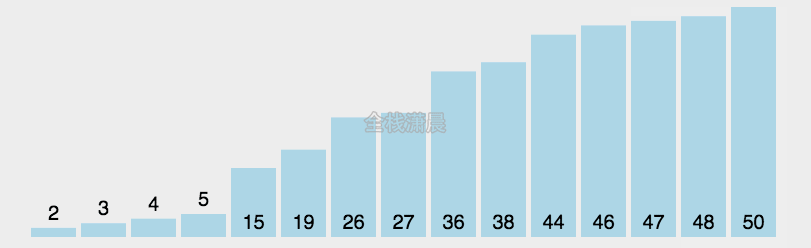
冒泡排序:时间复杂度O(n^2)
- 比较相邻元素,如果第一个比第二个大,则交换他们
- 一轮下来,可以保证最后一个数是最大的
- 执行n-1轮,就可以完成排序
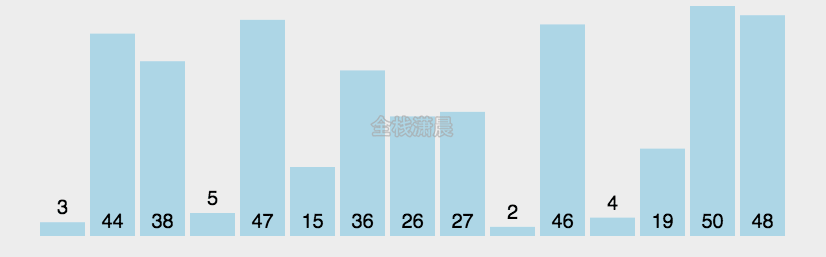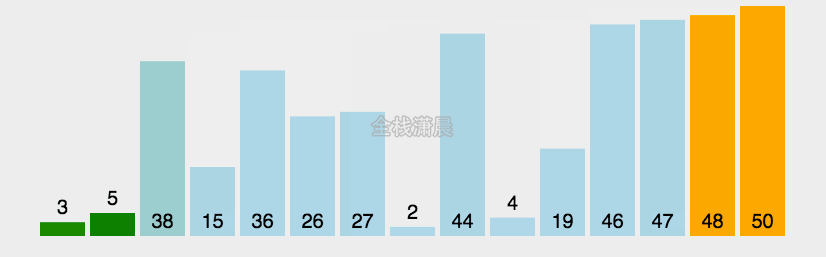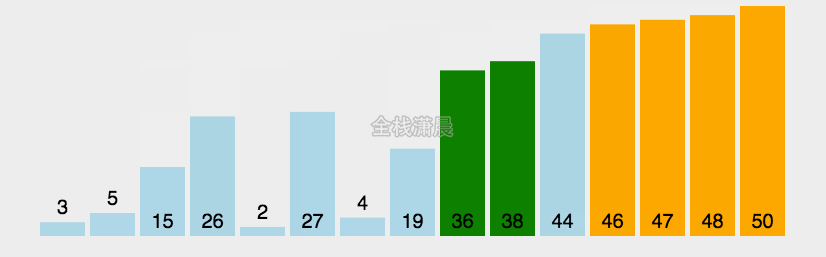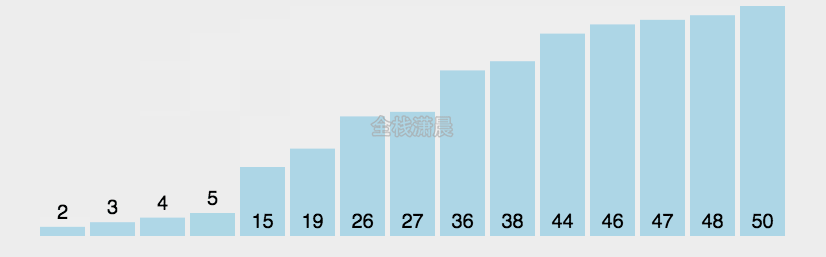
function bubbleSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length;
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) { //相邻元素两两对比
var temp = arr[j+1]; //元素交换
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
选择排序:时间复杂度O(n^2)
- 找到数组中的最小值,将它放在第一位
- 接着找到第二小的值,将它放在第二位
- 依次类推,执行n-1轮
function selectionSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length;
var minIndex, temp;
for (var i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
minIndex = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { //寻找最小的数
minIndex = j; //将最小数的索引保存
}
}
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
return arr;
}
插入排序:时间复杂度O(n^2)
- 从第二个数开始往前比
- 比它大就往后排
- 以此类推直到最后一个数
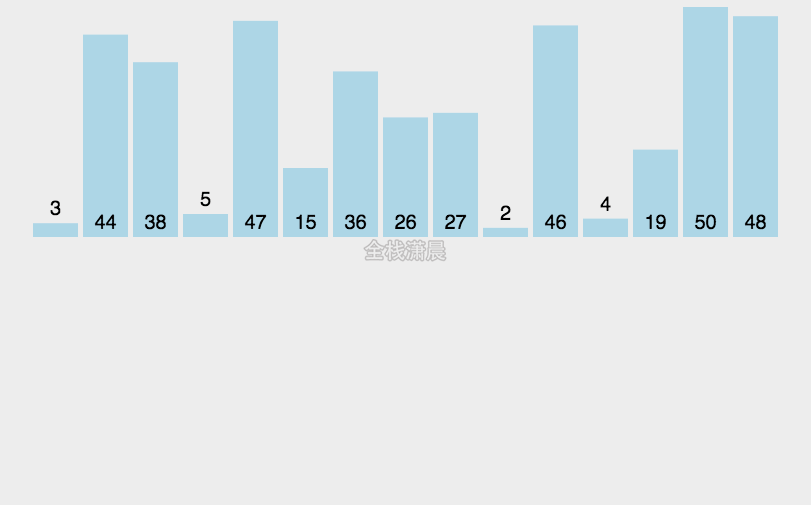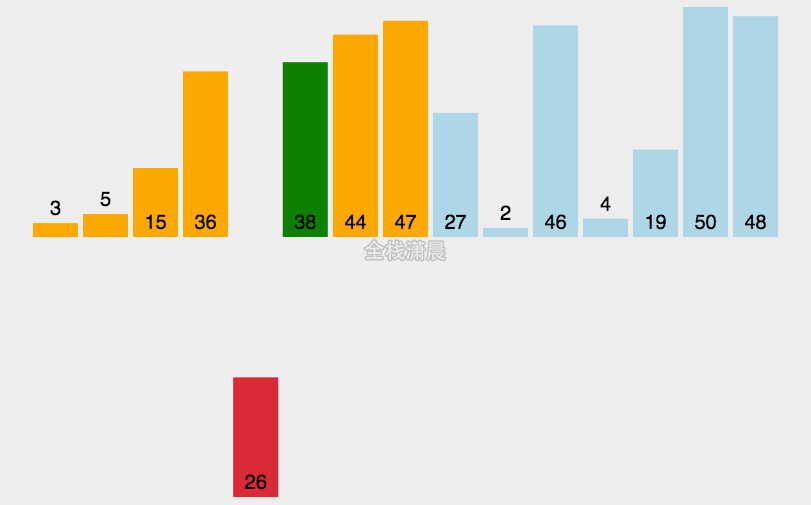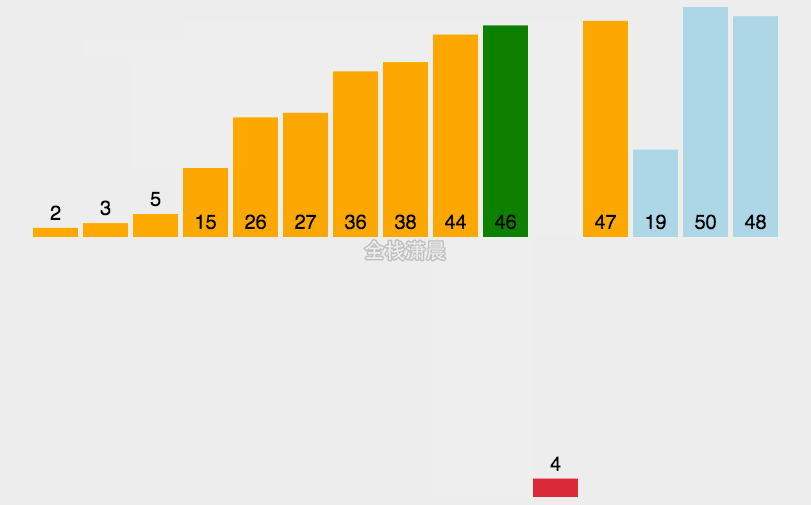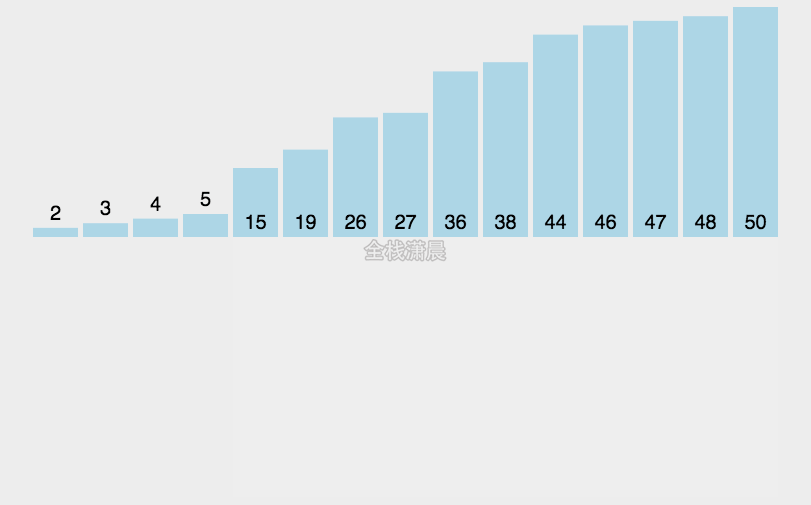
function insertionSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length;
var preIndex, current;
for (var i = 1; i < len; i++) {
preIndex = i - 1;
current = arr[i];
while(preIndex >= 0 && arr[preIndex] > current) {
arr[preIndex+1] = arr[preIndex];
preIndex--;
}
arr[preIndex+1] = current;
}
return arr;
}
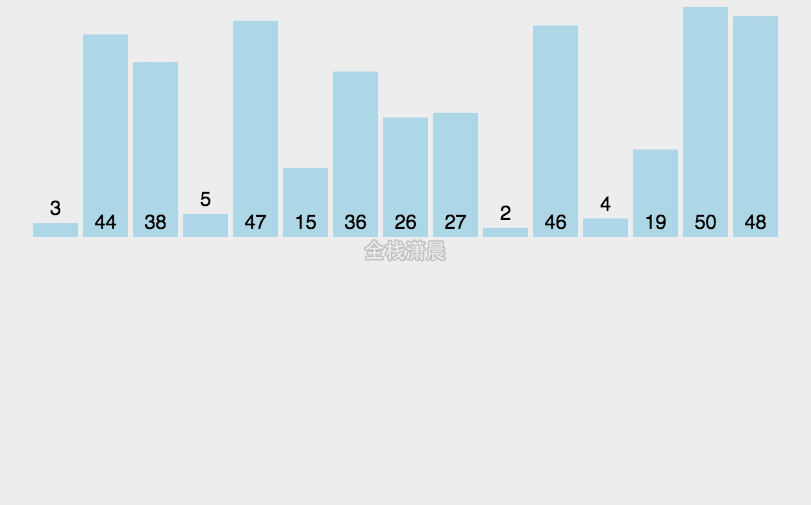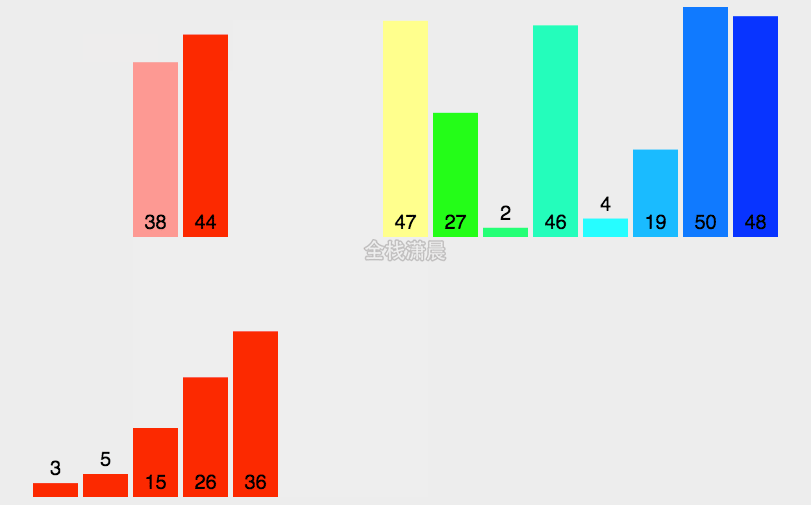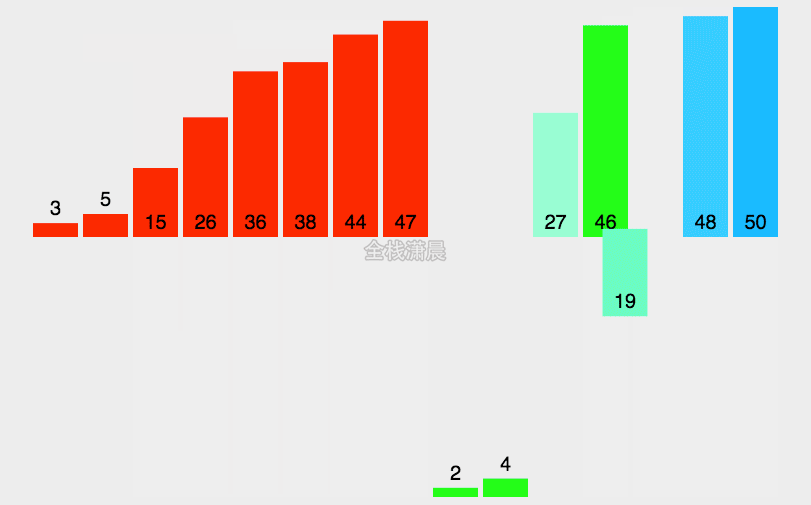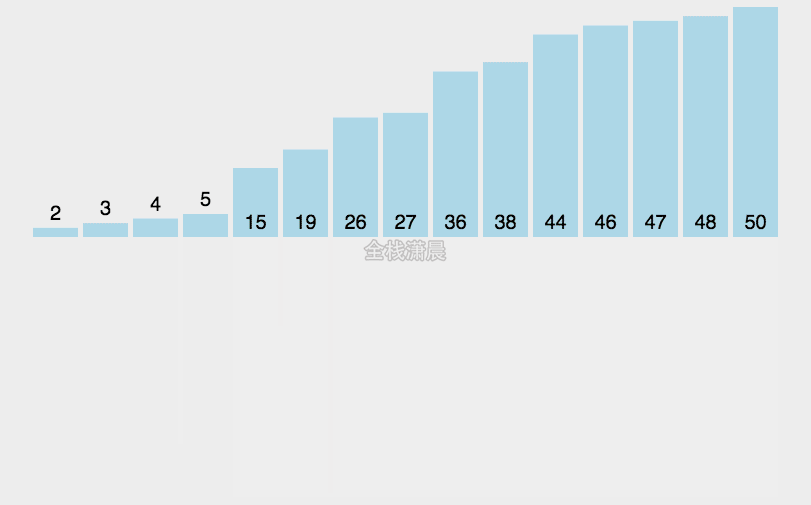
归并排序:时间复杂度O(nlogn),分的时间复杂度O(logn),合并的过程的复杂度是O(n)
-
分:把数组分成两半,递归子数组,进行分割操作,直到分成一个数
-
合:把两个字数组合并成一个有序数组,直到全部子数组合并完毕,合并前先准备一个空数组,存放合并之后的结果,然后不断取出两个子数组的第一个元素,比较他们的大小,小的先进入之前准备的空数组中,然后继续遍历其他元素,直到子数组中的元素都完成遍历
function mergeSort(arr) { //采用自上而下的递归方法
var len = arr.length;
if(len < 2) {
return arr;
}
var middle = Math.floor(len / 2),
left = arr.slice(0, middle),
right = arr.slice(middle);
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right));
}
function merge(left, right)
{
var result = [];
while (left.length && right.length) {
if (left[0] <= right[0]) {
result.push(left.shift());
} else {
result.push(right.shift());
}
}
while (left.length)
result.push(left.shift());
while (right.length)
result.push(right.shift());
return result;
}
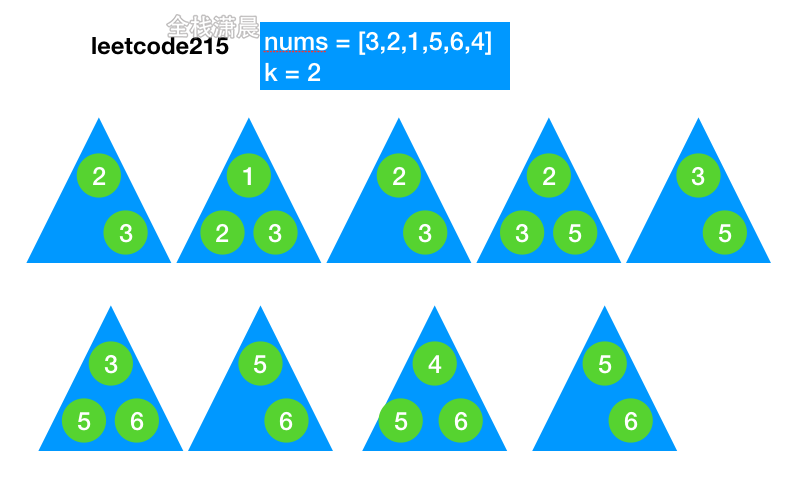
快速排序:时间复杂度O(nlogn),递归复杂度是O(logn),分区复杂度O(n)
- 分区:从数组中选一个基准值,比基准值小的放在它的前面,比基准值大的放在它的后面
- 递归:递归对基准值前后的子数组进行第一步的操作
function quickSort(arr, left, right) {
var len = arr.length,
partitionIndex,
left = typeof left != 'number' ? 0 : left,
right = typeof right != 'number' ? len - 1 : right;
if (left < right) {
partitionIndex = partition(arr, left, right);
quickSort(arr, left, partitionIndex-1);
quickSort(arr, partitionIndex+1, right);
}
return arr;
}
function partition(arr, left ,right) { //分区操作
//设定基准值位置(pivot)当然也可以选择最右边的元素为基准 也可以随机选择然后和最左或最右元素交换
var pivot = left,
index = pivot + 1;
for (var i = index; i <= right; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[pivot]) {
swap(arr, i, index);
index++;
}
}
swap(arr, pivot, index - 1);
return index-1;
}
function swap(arr, i, j) {
var temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 (medium)
方法1.维护大小为k的小顶堆,当堆的元素个数小于等于k时,遍历数组,让数组的元素不断加入堆,当堆的大小大于k时,让堆顶元素出列,遍历完数组之后,小顶堆堆顶的元素就是第k大元素。
复杂度:时间复杂度O(nlogk),循环n次,每次堆的操作是O(logk)。空间复杂度O(k),
js:
class Heap {
constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a - b, data = []) {
this.data = data;
this.comparator = comparator;//比较器
this.heapify();//堆化
}
heapify() {
if (this.size() < 2) return;
for (let i = Math.floor(this.size() / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.bubbleDown(i);//bubbleDown操作
}
}
peek() {
if (this.size() === 0) return null;
return this.data[0];//查看堆顶
}
offer(value) {
this.data.push(value);//加入数组
this.bubbleUp(this.size() - 1);//调整加入的元素在小顶堆中的位置
}
poll() {
if (this.size() === 0) {
return null;
}
const result = this.data[0];
const last = this.data.pop();
if (this.size() !== 0) {
this.data[0] = last;//交换第一个元素和最后一个元素
this.bubbleDown(0);//bubbleDown操作
}
return result;
}
bubbleUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1;//父节点的位置
//如果当前元素比父节点的元素小,就交换当前节点和父节点的位置
if (this.comparator(this.data[index], this.data[parentIndex]) < 0) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex);//交换自己和父节点的位置
index = parentIndex;//不断向上取父节点进行比较
} else {
break;//如果当前元素比父节点的元素大,不需要处理
}
}
}
bubbleDown(index) {
const lastIndex = this.size() - 1;//最后一个节点的位置
while (true) {
const leftIndex = index * 2 + 1;//左节点的位置
const rightIndex = index * 2 + 2;//右节点的位置
let findIndex = index;//bubbleDown节点的位置
//找出左右节点中value小的节点
if (
leftIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[leftIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = leftIndex;
}
if (
rightIndex <= lastIndex &&
this.comparator(this.data[rightIndex], this.data[findIndex]) < 0
) {
findIndex = rightIndex;
}
if (index !== findIndex) {
this.swap(index, findIndex);//交换当前元素和左右节点中value小的
index = findIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
swap(index1, index2) {//交换堆中两个元素的位置
[this.data[index1], this.data[index2]] = [this.data[index2], this.data[index1]];
}
size() {
return this.data.length;
}
}
var findKthLargest = function (nums, k) {
const h = new Heap((a, b) => a - b);
for (const num of nums) {
h.offer(num);//加入堆
if (h.size() > k) {//堆的size超过k时,出堆
h.poll();
}
}
return h.peek();
};
方法2:堆排序
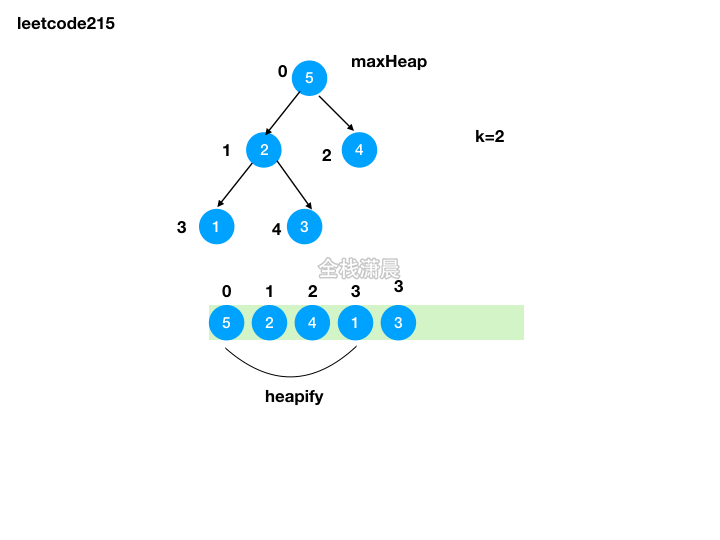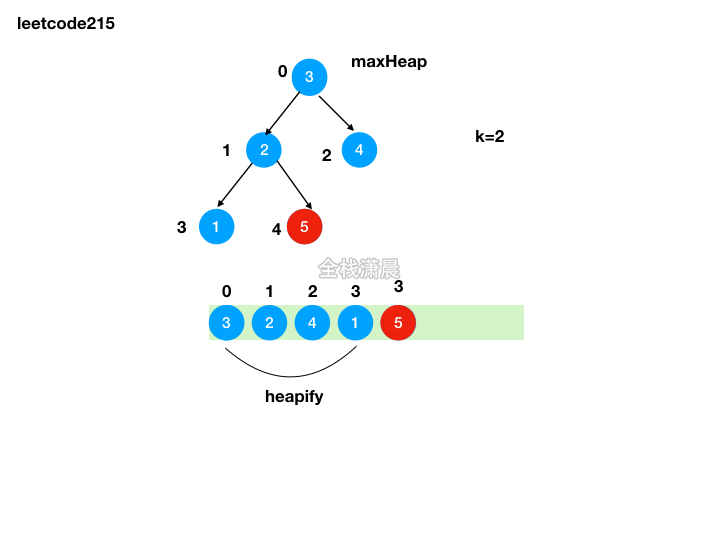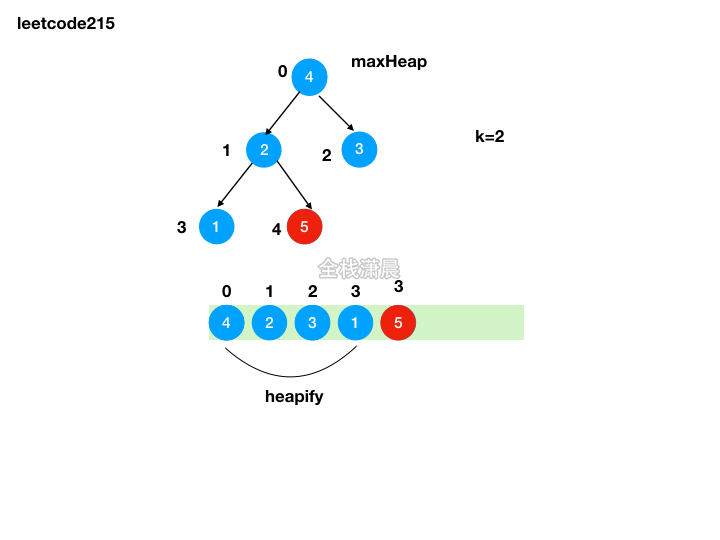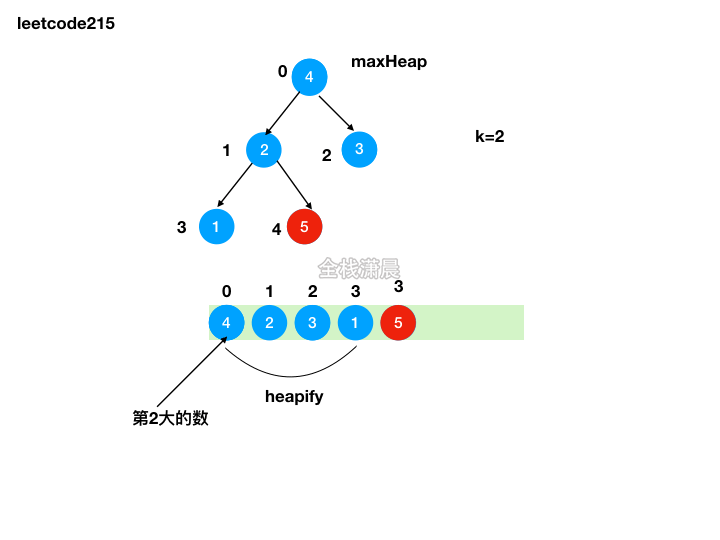
- 思路:利用原地堆排序的思想,将前k-1大的元素加入队尾,最后队顶的元素就是第k大的元素
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(nlogn),堆的创建复杂度是O(n),移动前k-1大的元素然后堆化复杂度是O(klogn),k<=n,最差的情况下是O(nlogn),空间复杂度O(logn),递归的栈空间
js:
var findKthLargest = function (nums, k) {
let heapSize = nums.length;
buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize); //构建大顶堆 大小为heapSize
//大顶堆 前k-1个堆顶元素不断和数组的末尾元素交换 然后重新heapify堆顶元素
//这个操作就是之前小顶堆出堆顶的操作,只不过现在是原地排序
for (let i = nums.length - 1; i >= nums.length - k + 1; i--) {
swap(nums, 0, i);//交换堆顶和数组末尾元素
--heapSize; //堆大小减1
maxHeapify(nums, 0, heapSize);//重新heapify
}
return nums[0];//返回堆顶元素,就是第k大的元素
function buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize) {
for (let i = Math.floor(heapSize / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {//从第一个非叶子节点开始构建
maxHeapify(nums, i, heapSize);
}
}
// 从左向右,自上而下的调整节点
function maxHeapify(nums, i, heapSize) {
let l = i * 2 + 1;//左节点
let r = i * 2 + 2;//右节点
let largest = i;
if (l < heapSize && nums[l] > nums[largest]) {
largest = l;
}
if (r < heapSize && nums[r] > nums[largest]) {
largest = r;
}
if (largest !== i) {
swap(nums, i, largest); //找到左右节点中大的元素交换
//递归交换后面的节点
maxHeapify(nums, largest, heapSize);
}
}
function swap(a, i, j) {//交换函数
let temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
};
java:
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int heapSize = nums.length;
buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize);
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= nums.length - k + 1; --i) {
swap(nums, 0, i);
--heapSize;
maxHeapify(nums, 0, heapSize);
}
return nums[0];
}
public void buildMaxHeap(int[] a, int heapSize) {
for (int i = heapSize / 2; i >= 0; --i) {
maxHeapify(a, i, heapSize);
}
}
public void maxHeapify(int[] a, int i, int heapSize) {
int l = i * 2 + 1, r = i * 2 + 2, largest = i;
if (l < heapSize && a[l] > a[largest]) {
largest = l;
}
if (r < heapSize && a[r] > a[largest]) {
largest = r;
}
if (largest != i) {
swap(a, i, largest);
maxHeapify(a, largest, heapSize);
}
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
方法3:快速排序的分区方法
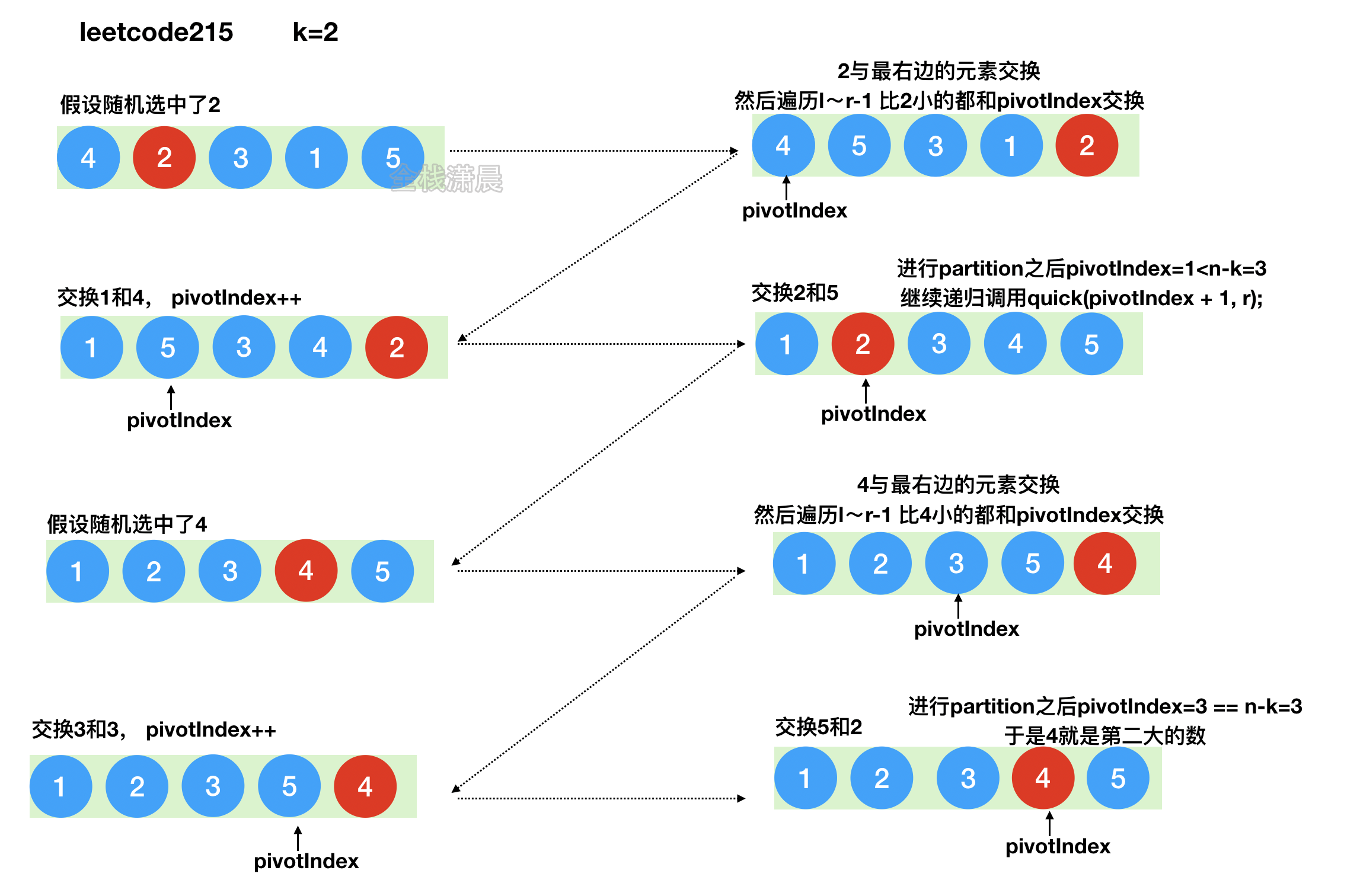
-
思路:借鉴快排的思路,不断随机选择基准元素,看进行partition之后,该元素是不是在
n-k的位置。 -
复杂度:
-
时间复杂度
O(nlogn) -
空间复杂度
O(logn),递归的深度
-
js:
const findKthLargest = (nums, k) => {
const n = nums.length;
const quick = (l, r) => {
if (l > r) return;//递归终止条件
let random = Math.floor(Math.random() * (r - l + 1)) + l; //随机选取一个索引
swap(nums, random, r); //将它和位置r的元素交换,让nums[r]作为基准元素
//对基准元素进行partition
let pivotIndex = partition(nums, l, r);
//进行partition之后,基准元素左边的元素都小于它 右边的元素都大于它
//如果partition之后,这个基准元素的位置pivotIndex正好是n-k 则找大了第k大的数
//如果n-k<pivotIndex,则在pivotIndex的左边递归查找
//如果n-k>pivotIndex,则在pivotIndex的右边递归查找
if (n - k < pivotIndex) {
quick(l, pivotIndex - 1);
} else {
quick(pivotIndex + 1, r);
}
};
quick(0, n - 1);//函数开始传入的left=0,right= n - 1
return nums[n - k]; //最后找到了正确的位置 也就是n-k等于pivotIndex 这个位置的元素就是第k大的数
};
function partition(nums, left, right) {
let pivot = nums[right]; //最右边的元素为基准
let pivotIndex = left; //pivotIndex初始化为left
for (let i = left; i < right; i++) { //遍历left到right-1的元素
if (nums[i] < pivot) { //如果当前元素比基准元素小
swap(nums, i, pivotIndex); //把它交换到pivotIndex的位置
pivotIndex++; //pivotIndex往前移动一步
}
}
swap(nums, right, pivotIndex); //最后交换pivotIndex和right
return pivotIndex; //返回pivotIndex
}
function swap(nums, p, q) {//交换数组中的两个元素
const temp = nums[p];
nums[p] = nums[q];
nums[q] = temp;
}
java:
class Solution {
Random random = new Random();
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
return quickSelect(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, nums.length - k);
}
public int quickSelect(int[] a, int l, int r, int index) {
int q = randomPartition(a, l, r);
if (q == index) {
return a[q];
} else {
return q < index ? quickSelect(a, q + 1, r, index) : quickSelect(a, l, q - 1, index);
}
}
public int randomPartition(int[] a, int l, int r) {
int i = random.nextInt(r - l + 1) + l;
swap(a, i, r);
return partition(a, l, r);
}
public int partition(int[] a, int l, int r) {
int x = a[r], i = l - 1;
for (int j = l; j < r; ++j) {
if (a[j] <= x) {
swap(a, ++i, j);
}
}
swap(a, i + 1, r);
return i + 1;
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
148. 排序链表(medium)
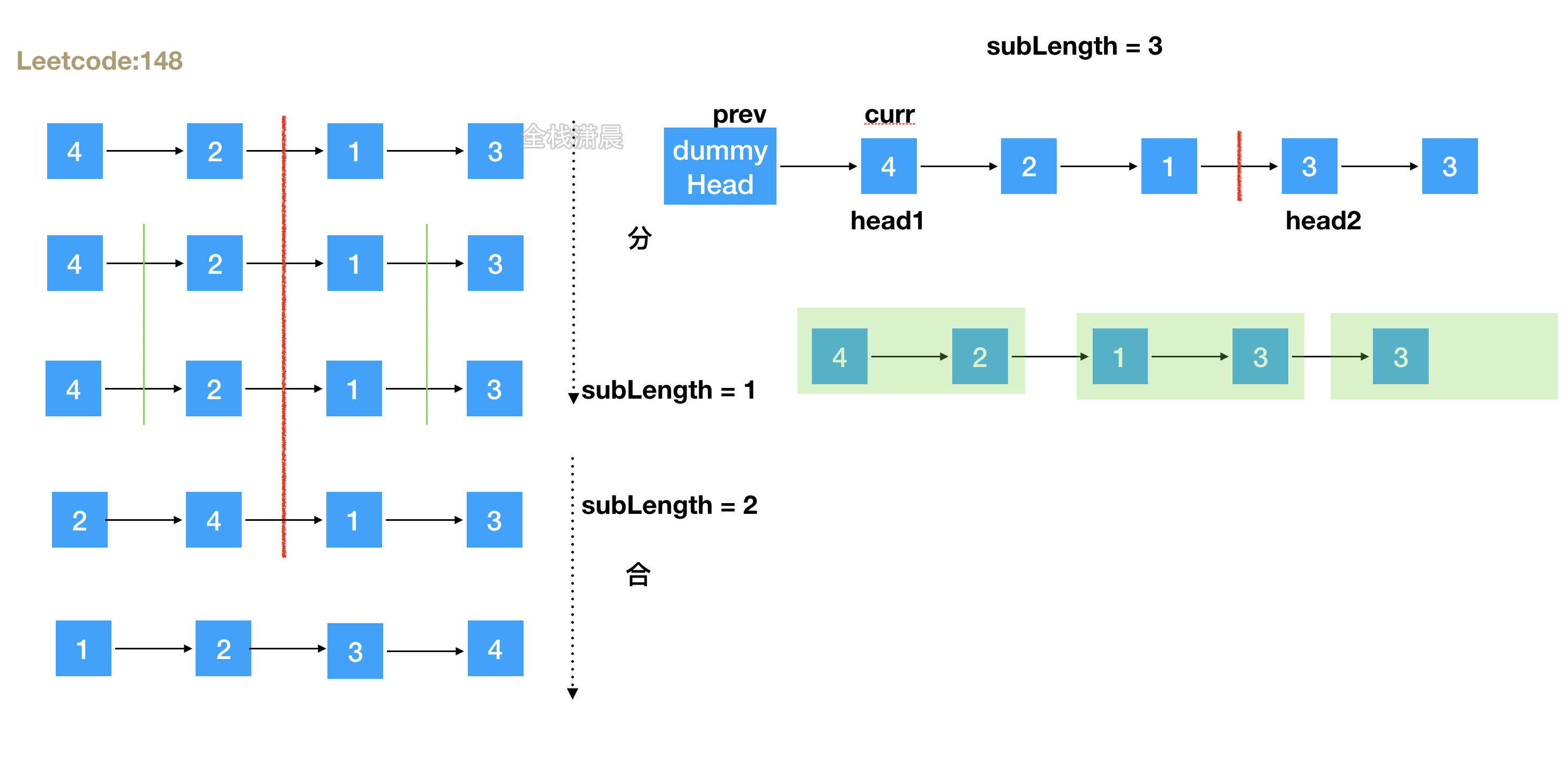
方法1:自顶向下
- 思路:用归并排序的思路,先不断分割,知道每个子区间只有一个节点位置,然后开始合并。
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(nlogn),和归并排序的复杂度一样。空间复杂度O(logn),递归的栈空间
js:
const merge = (head1, head2) => {
const dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
let temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 !== null && temp2 !== null) {//合并子区间 小的节点先连
if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) {
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
} else {
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 !== null) {//两条链表还有节点没合并完,直接合并过来
temp.next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 !== null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
const toSortList = (head, tail) => {
if (head === null) {//极端情况
return head;
}
if (head.next === tail) {//分割到只剩一个节点
head.next = null;
return head;
}
let slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast !== tail) {//的到中间节点
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast !== tail) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
const mid = slow;
return merge(toSortList(head, mid), toSortList(mid, tail));//分割区间 递归合并
}
var sortList = function(head) {
return toSortList(head, null);
};
java:
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return toSortList(head, null);
}
public ListNode toSortList(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.next == tail) {
head.next = null;
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != tail) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast != tail) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
ListNode mid = slow;
ListNode list1 = toSortList(head, mid);
ListNode list2 = toSortList(mid, tail);
ListNode sorted = merge(list1, list2);
return sorted;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) {
if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) {
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
} else {
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 != null) {
temp.next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 != null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
方法2:自底向上
- 思路:直接进行循环合并操作。
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(nlogn),空间复杂度O(1)
js:
const merge = (head1, head2) => {
const dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
let temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 !== null && temp2 !== null) {
if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) {
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
} else {
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 !== null) {
temp.next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 !== null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
var sortList = function(head) {
if (head === null) {
return head;
}
let length = 0;
let node = head;
while (node !== null) {
length++;
node = node.next;
}
const dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
for (let subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1) {
let prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next;
while (curr !== null) {
let head1 = curr;
for (let i = 1; i < subLength && curr.next !== null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
let head2 = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
curr = head2;
for (let i = 1; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next !== null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
let next = null;
if (curr !== null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
}
const merged = merge(head1, head2);
prev.next = merged;
while (prev.next !== null) {
prev = prev.next;
}
curr = next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
};
java:
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
int length = 0;
ListNode node = head;
while (node != null) {
length++;
node = node.next;
}
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head);
for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1) {
ListNode prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode head1 = curr;
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr.next != null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode head2 = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
curr = head2;
for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next != null; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode next = null;
if (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
}
ListNode merged = merge(head1, head2);
prev.next = merged;
while (prev.next != null) {
prev = prev.next;
}
curr = next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) {
if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) {
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
} else {
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 != null) {
temp.next = temp1;
} else if (temp2 != null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}