基本概念和CURD
开发流程
1由Domain object -> mapping->db。(官方推荐)
2由DB开始,用工具生成mapping和Domain object。(使用较多)
3由映射文件开始。
Domain Object限制
1.默认的构造方法(必须的)。
2有无意义的标示符id(主键)(可选)
3非final的,对懒加载有影响(可选)
Domain Java Object(User)
public class User { private int id; private String name; private Date birthDay; //getter setter… }
Java代码
1.初始化代码(只做一次)
Configuration cfg = new Configuration(); cfg.configure(“config.cfg.xml”); // 也可以通过cfg.setProperty设置属性。 SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
所以将以上代码封装成工具类:
HibernateUtils.java
package com.dzq.utils; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; public class HibernateUntils { private static SessionFactory sessionFactory; private HibernateUntils() { } static { Configuration cfg = new Configuration(); cfg.configure();//如果不是hibernate.cfg.xml这个文件名,需要加上文件名 sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); } public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory(){ return sessionFactory; } public static Session getSession(){ return sessionFactory.openSession(); } }
工具类的使用:
public static void addUser(User user){ Session s=null; Transaction tx=null; try { s=HibernateUntils.getSession(); tx=s.beginTransaction(); s.save(user); tx.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { if(tx!=null) tx.rollback(); throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally{ if(s!=null){ s.close(); } } }
Session的几个主要方法
1.save,persist保存数据,persist在事务外不会产生insert语句。
2.delete,删除对象
3.update,更新对象,如果数据库中没有记录,会出现异常。
4.get,根据ID查,会立刻访问数据库。
5.Load,根据ID查,(返回的是代理,不会立即访问数据库)。
6.saveOrUpdate,merge(根据ID和version的值来确定是save或update),调用merge你的对象还是托管的。
7.lock(把对象变成持久对象,但不会同步对象的状态)。
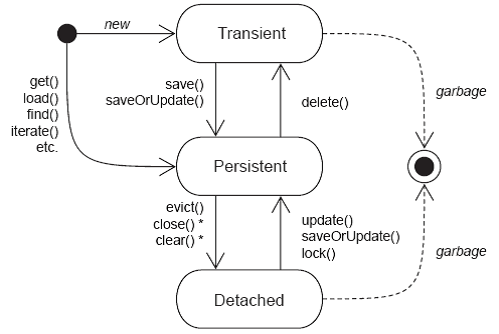
对象状态
瞬时(transient):数据库中没有数据与之对应,超过作用域会被JVM垃圾回收器回收,一般是new出来且与session没有关联的对象。
持久(persistent):数据库中有数据与之对应,当前与session有关联,并且相关联的session没有关闭,事务没有提交;持久对象状态发生改变,在事务提交时会影响到数据库(hibernate能检测到)。
脱管(detached):数据库中有数据与之对应,但当前没有session与之关联;托管对象状态发生改变,hibernate不能检测到。
工具类完善:
HibernateUtils.java
package com.dzq.utils; import java.io.Serializable; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; public class HibernateUntils { private static SessionFactory sessionFactory; private HibernateUntils() { } static { Configuration cfg = new Configuration(); cfg.configure();//如果不是hibernate.cfg.xml这个文件名,需要加上文件名 sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); } public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory(){ return sessionFactory; } public static Session getSession(){ return sessionFactory.openSession(); } /** * 添加 * @param entity */ public static void add(Object entity) { Session s = null; Transaction tx = null; try { s = HibernateUntils.getSession(); tx = s.beginTransaction(); s.save(entity); tx.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { if (tx != null) tx.rollback(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { if (s != null) { s.close(); } } } /** * 修改 * @param entity */ public static void update(Object entity) { Session s = null; Transaction tx = null; try { s = HibernateUntils.getSession(); tx = s.beginTransaction(); s.update(entity); tx.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { if (tx != null) tx.rollback(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { if (s != null) { s.close(); } } } /** * 删除 * @param entity */ public static void delete(Object entity) { Session s = null; Transaction tx = null; try { s = HibernateUntils.getSession(); tx = s.beginTransaction(); s.delete(entity); tx.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { if (tx != null) tx.rollback(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { if (s != null) { s.close(); } } } /** * 根据主键id查询 * @param clazz * @param id * @return */ public static Object get(Class clazz,Serializable id) { Session s = null; try { s = HibernateUntils.getSession(); Object obj=s.get(clazz, id); return obj; } finally { if (s != null) { s.close(); } } } }