1.栈的基本概念
栈是一种抽象型数据结构,主要要两个特点:1.只能从栈顶端访问数据(获取和添加数据),2.数据的访问规则遵循 “先进后出” 的原则。如下图所示:
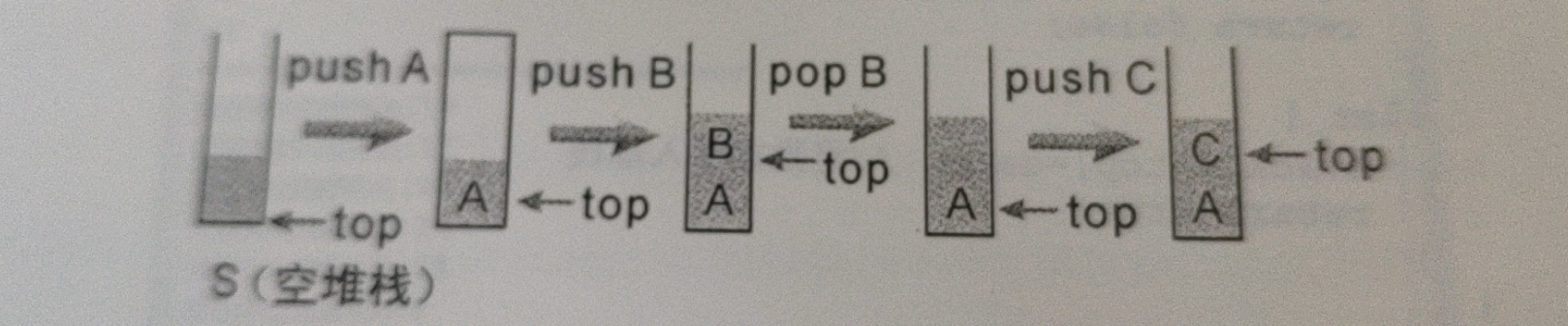
2.栈的实现
2.1.数组实现
package stack;
/**
* 数组实现栈的操作
*/
public class StackDemo {
private int maxSize; //栈的最大容量
private int top; //标记栈顶
private int stack[] ; //存储元素的数组
public StackDemo(int maxSize){
this.maxSize=maxSize;
stack=new int[maxSize];
top=-1;
}
/**
* 判断栈是否满
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull(){
return top==maxSize-1;
}
/**
* 判断栈是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return top==-1;
}
/**
* 向栈中添加元素
*/
public void push(int value){
if (!isFull()){
top++;
stack[top]=value;
}
}
/**
* 取出栈顶元素
* @return
*/
public int pop(){
if (!isEmpty()){
int value=stack[top];
top--;
return value ;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 遍历栈中的元素
*/
public void list(){
if (!isEmpty()){
for (int i = top; i >=0 ; i--) {
System.out.println(stack[i]);
}
}
}
}
2.2.链表实现
2.2.1.节点代码
class StackNode{
public Object object;
public StackNode next;
public StackNode(){
}
public StackNode(Object object,StackNode next){
this.object=object;
this.next=next;
}
}
2.2.2.入栈出栈代码实现
/**
* 利用链表实现栈
*/
public class LinkedStackDemo {
private StackNode first; //栈底端的指针
private StackNode last; //栈顶端的指针
private int size; //栈的大小
/**
* 栈是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return first==null;
}
/**
* 向栈中添加数据
* @param data
*/
public void push (Object data){
StackNode newNode=new StackNode(data,null);
if (isEmpty()){
first=newNode;
}else {
last.next=newNode;
}
last=newNode;
size++;
}
/**
* 打印栈中元素
*/
public void list() {
StackNode current = first;
StackNode before = null;
while (current != null) {
last = before;
before = current;
current = current.next;
before.next = last;
}
current = before;
while (current != null) {
System.out.println(current.object);
current = current.next;
}
}
/**
* 取出栈顶中的元素(其实就是删除链表尾部的数据)
* @return
*/
public Object pop(){
if (!isEmpty()){
StackNode current=first;
while (current.next!=last){ //这样判断可以取出最后一个元素的之前的元素
current=current.next;
}
StackNode lastNode =current.next; //最后一个节点
current.next=null;
last=current;
return lastNode.object;
}
return null;
}
}
每天进步一丢丢
完成。